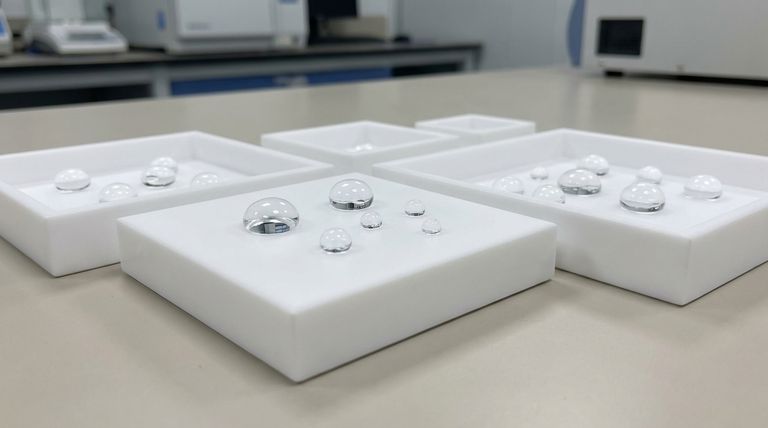
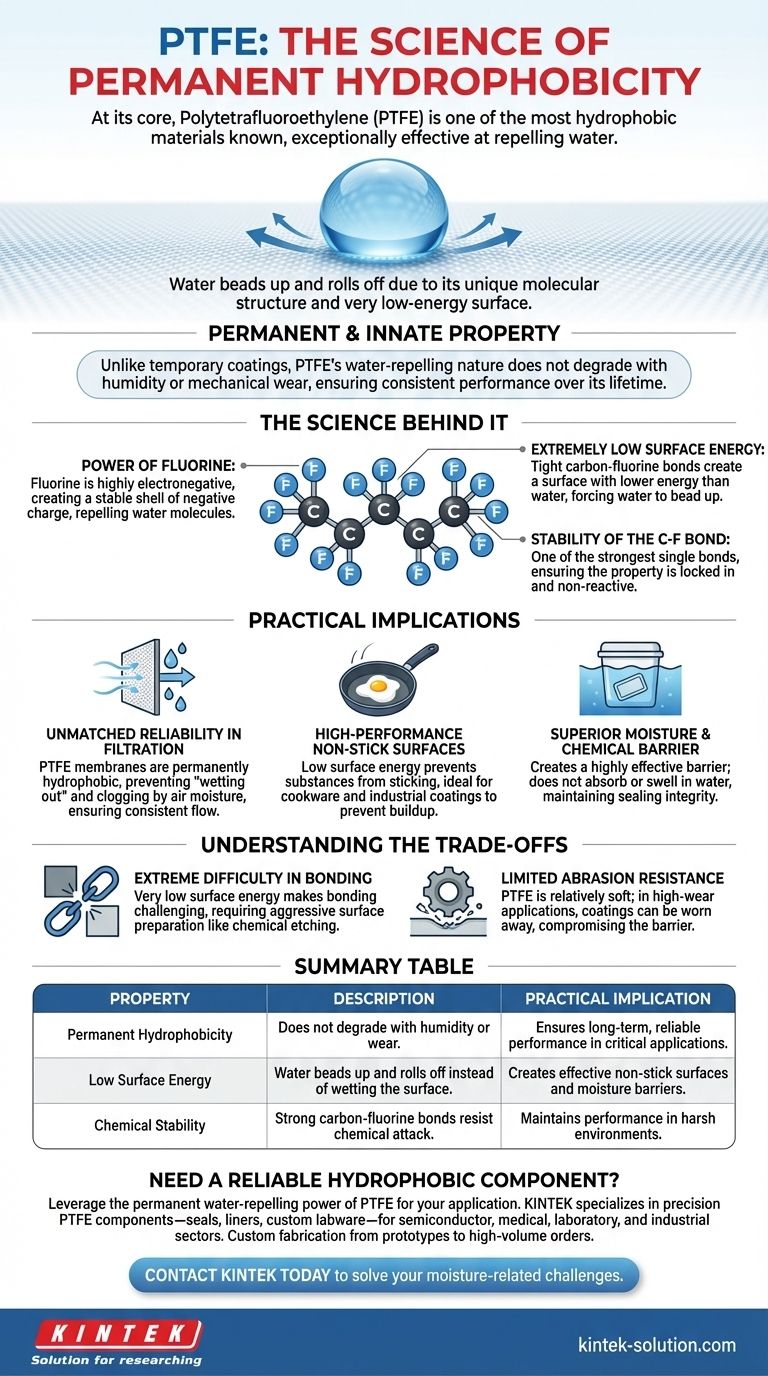
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is one of the most hydrophobic materials known. This means it is exceptionally effective at repelling water. The unique molecular structure of PTFE creates a very low-energy surface that water cannot easily wet, causing it to bead up and roll off.
The critical takeaway is not just that PTFE is hydrophobic, but that this property is permanent and innate. Unlike temporary coatings, PTFE’s water-repelling nature does not degrade with humidity or mechanical wear, ensuring consistent and reliable performance over its lifetime.

The Science Behind PTFE's Hydrophobicity
To understand why PTFE is so effective, we must look at its chemical structure. The material's properties are a direct result of its unique atomic composition.
The Power of Fluorine
PTFE consists of a long chain of carbon atoms completely surrounded by fluorine atoms. Fluorine is the most electronegative element, meaning it has a powerful attraction for electrons.
This creates a dense, stable shell of negative charge around the carbon backbone, leaving no room for water molecules to form attractive bonds.
An Extremely Low Surface Energy
The tight bond between carbon and fluorine results in an exceptionally low surface energy. For a liquid like water, which has a high surface tension, this low-energy surface is difficult to spread across.
Instead of wetting the surface, the water molecules are more attracted to each other. This forces them to minimize their contact with the PTFE, forming distinct beads.
The Stability of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
The carbon-fluorine bond is one of the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry. This makes the entire PTFE molecule incredibly stable and non-reactive.
This stability ensures that the hydrophobic properties are locked in and are not compromised by chemical exposure or environmental factors like humidity.
Practical Implications of This Property
The permanent hydrophobicity of PTFE is not just a scientific curiosity; it is the foundation for its use in countless critical applications where moisture control is essential.
Unmatched Reliability in Filtration
In applications like venting or gas filtration, PTFE membranes are invaluable. Because they are permanently hydrophobic, they will not become saturated or blocked by moisture from the air.
This prevents "wetting out," a common failure mode in hydrophilic filters where moisture clogs the pores. PTFE ensures a consistent and reliable flow of air or gas, regardless of ambient humidity.
High-Performance Non-Stick Surfaces
The same low surface energy that repels water also prevents other substances from sticking to it. This is the principle behind non-stick cookware and is also used for industrial coatings on pipes, tanks, and rollers to prevent buildup and simplify cleaning.
Superior Moisture and Chemical Barrier
When used as a coating, sealant, or gasket, PTFE creates a highly effective barrier against moisture. It does not absorb or swell when exposed to water, maintaining its dimensional stability and sealing integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its hydrophobicity is a major advantage, it also creates certain engineering challenges that are important to recognize.
Extreme Difficulty in Bonding
The very low surface energy that makes PTFE non-stick also makes it extremely difficult to bond to other materials using conventional adhesives.
Successfully gluing PTFE requires aggressive surface preparation, such as chemical etching, which alters the surface chemistry to allow an adhesive to grip it.
Limited Abrasion Resistance
While chemically durable, PTFE is a relatively soft material. In applications with high mechanical wear or abrasion, a PTFE coating can be worn away, compromising its hydrophobic barrier.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding how to leverage PTFE's hydrophobicity depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is reliable gas exchange or venting: PTFE's permanent hydrophobicity makes it the ideal material for membranes that must perform flawlessly in humid or wet conditions.
- If your primary focus is creating a non-stick or self-cleaning surface: PTFE's low surface energy is a top-tier solution, but you must factor in the complexity and cost of bonding it to a substrate.
- If your primary focus is sealing against moisture: PTFE's inability to absorb water makes it a superior choice for gaskets and seals that must remain stable and effective over long periods.
Ultimately, harnessing the power of PTFE begins with recognizing that its hydrophobicity is a direct, reliable consequence of its fundamental chemistry.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description | Practical Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Permanent Hydrophobicity | Does not degrade with humidity or wear. | Ensures long-term, reliable performance in critical applications. |
| Low Surface Energy | Water beads up and rolls off instead of wetting the surface. | Creates effective non-stick surfaces and moisture barriers. |
| Chemical Stability | Strong carbon-fluorine bonds resist chemical attack. | Maintains performance in harsh environments. |
Need a Reliable Hydrophobic Component?
Leverage the permanent water-repelling power of PTFE for your application. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring you get a solution perfectly tailored to your needs.
Contact KINTEB today to discuss how our PTFE expertise can solve your moisture-related challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- How was PTFE discovered and developed? From Lab Accident to Essential High-Performance Polymer
- What is Teflon and what are its alternative names? Understanding PTFE, the Material Behind the Brand
- How does PTFE react to common solvents? Discover Its Near-Total Chemical Immunity
- What is Teflon and what is its chemical name? Unpacking the Science of PTFE
- What are the additional properties of PTFE? Beyond Non-Stick: Extreme Chemical, Thermal & Electrical Performance



















