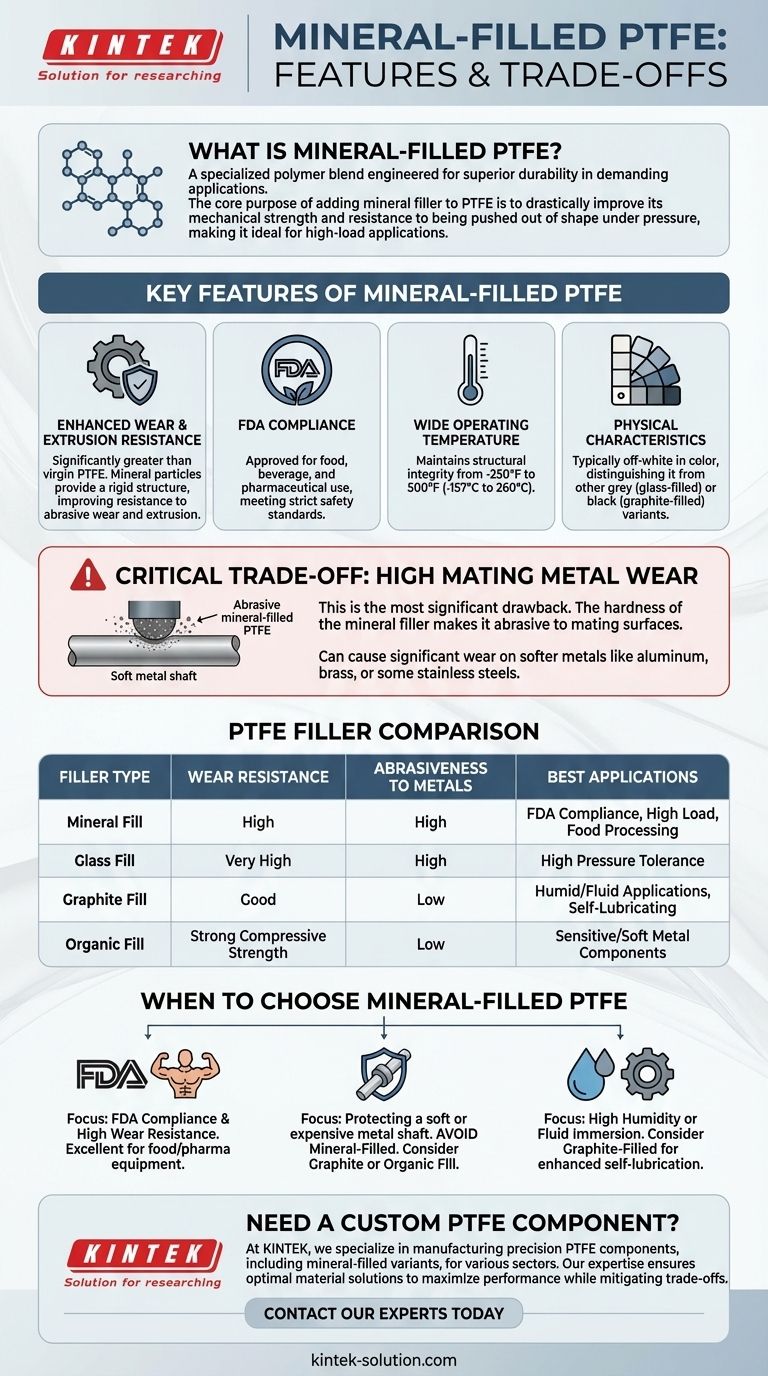
Mineral-filled Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a specialized polymer blend engineered for superior durability in demanding applications. Its key features include significantly greater wear and extrusion resistance compared to virgin PTFE, a wide operating temperature range of -250°F to 500°F, and FDA approval for food-grade use. However, its most critical characteristic is its high abrasiveness, which can cause significant wear on mating metal surfaces.
The core purpose of adding a mineral filler to PTFE is to drastically improve its mechanical strength and resistance to being pushed out of shape under pressure. This makes it ideal for high-load applications, but this hardness comes at the cost of being abrasive to softer metals.

The Role of Fillers in PTFE
PTFE, commonly known by the brand name Teflon, is a high-performance fluoropolymer composed of carbon and fluorine. Its base properties make it extremely useful across many industries.
The Properties of Virgin PTFE
Virgin, or unfilled, PTFE is renowned for its exceptional characteristics. It possesses extremely high chemical resistance, a very low coefficient of friction (making it self-lubricating), and high thermal stability with a melting point around 620°F. It is also a fantastic electrical insulator and is biocompatible.
Why Add a Filler?
While virgin PTFE has excellent properties, it is mechanically soft. Under high pressure or load, it can deform or "creep." Adding fillers, such as minerals, glass, or graphite, fundamentally changes its mechanical behavior, creating a composite material tailored for specific performance needs.
Key Features of Mineral-Filled PTFE
Adding a mineral filler creates a composite with a distinct set of performance attributes.
Enhanced Wear and Extrusion Resistance
The primary benefit of this formulation is its improved mechanical strength. The mineral particles embedded within the PTFE matrix provide a rigid structure, making the material much more resistant to abrasive wear and less likely to be extruded from a seal or bearing under high pressure.
FDA Compliance
Mineral-filled PTFE is FDA approved. This certification is critical for applications where the material may come into contact with food, beverages, or pharmaceuticals, ensuring it meets strict safety standards.
Wide Operating Temperature Range
This material maintains its structural integrity and performance across a broad thermal spectrum, reliably operating in environments from -250°F to 500°F (-157°C to 260°C).
Physical Characteristics
Mineral-filled PTFE is typically off-white in color. This can be a useful identifier when distinguishing it from other filled PTFE variants, which are often grey (glass-filled) or black (graphite-filled).
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material choice is without compromise. Understanding the specific downsides of mineral-filled PTFE is essential for successful application design.
High Mating Metal Wear
This is the most significant drawback. The hardness of the mineral filler that provides excellent wear resistance for the PTFE part also makes it abrasive to the surfaces it contacts. When used against softer metals like aluminum or brass, or even some stainless steels, it can accelerate wear on the shaft or bore.
Comparison to Other Common Fillers
Choosing the right filler depends entirely on the application's demands.
- Glass Fill: Offers very high wear and pressure tolerance but, similar to mineral fill, can be abrasive to mating surfaces.
- Graphite Fill: Provides good wear resistance and is an excellent choice for humid or fluid applications due to its lubricity. Crucially, it causes low mating metal wear.
- Organic Fill: Delivers strong compressive strength and also features low mating metal wear, making it suitable for applications with sensitive or soft metal components.
When to Choose Mineral-Filled PTFE
Your final decision should be guided by the primary requirements of your specific engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is FDA compliance and high wear resistance: Mineral-filled PTFE is an excellent choice, especially in food processing or pharmaceutical equipment where durability and safety are paramount.
- If your primary focus is protecting a soft or expensive metal shaft: You should avoid mineral-filled PTFE and instead consider a graphite-filled or organic-filled variant.
- If your application involves high humidity or fluid immersion: A graphite-filled PTFE is likely a superior choice due to its enhanced self-lubricating properties in wet conditions.
Ultimately, selecting the right material requires a clear understanding of both its strengths and its critical trade-offs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Wear & Extrusion Resistance | Significantly greater than virgin PTFE, ideal for high-load applications. |
| Operating Temperature | Wide range from -250°F to 500°F (-157°C to 260°C). |
| FDA Compliance | Approved for food-grade use in food, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries. |
| Abrasiveness | High; can cause significant wear on softer mating metal surfaces. |
| Color | Typically off-white, distinguishing it from other filled PTFE types. |
Need a custom PTFE component that balances durability with application-specific requirements?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including mineral-filled variants, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise in custom fabrication ensures you get the optimal material solution for your specific needs—maximizing performance while mitigating trade-offs like mating surface wear.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and discover how our tailored PTFE solutions can enhance your product's reliability and longevity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















