At its core, Teflon (PTFE) is one of the most effective electrical insulators known. Its exceptional performance stems from a combination of extremely high electrical resistivity, high dielectric strength, and a low dielectric constant. This makes it a benchmark material for preventing the flow of electricity, especially in demanding high-voltage and high-frequency applications.
The true value of Teflon as an insulator isn't just one single property, but how its entire molecular structure, defined by strong carbon-fluorine bonds, creates a suite of elite electrical characteristics that remain stable across a wide range of temperatures and chemical environments.

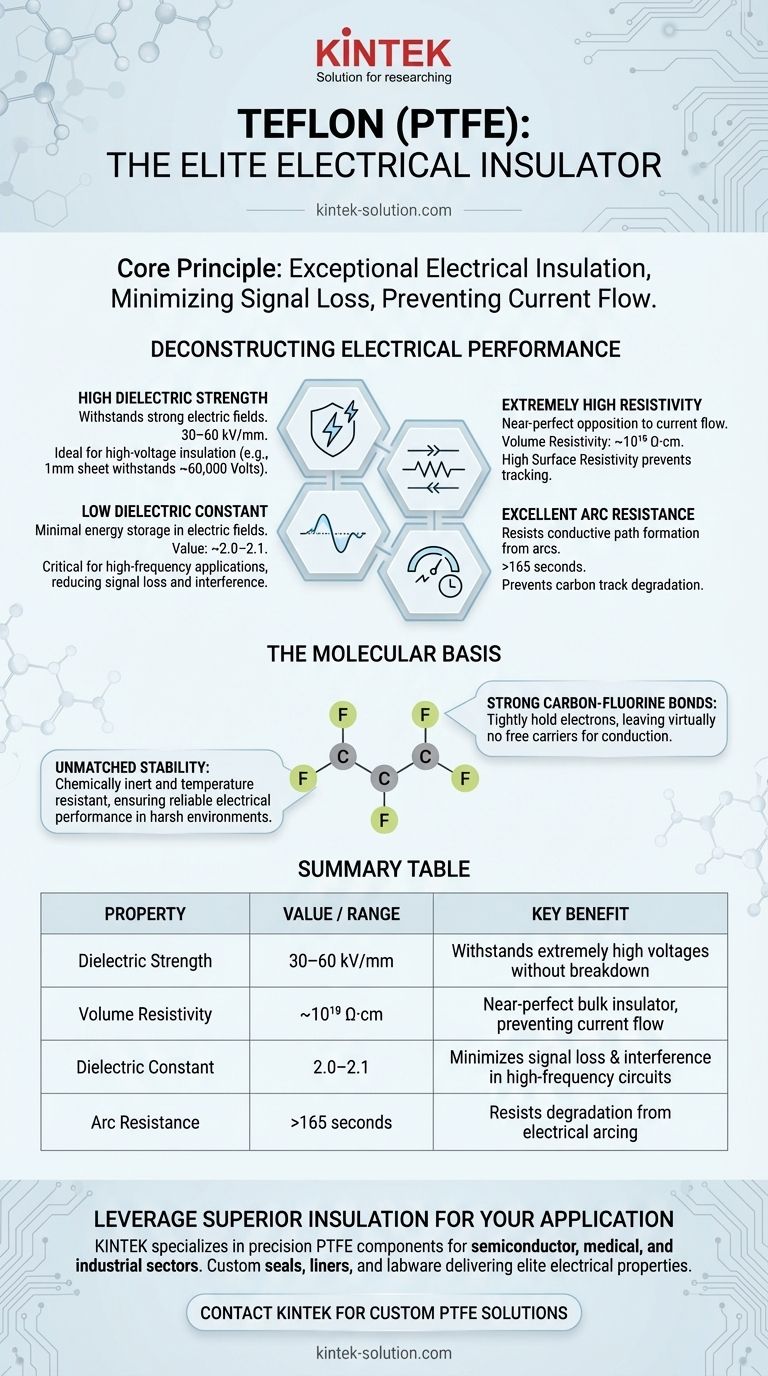
Deconstructing Teflon's Electrical Performance
To understand why Teflon is a go-to insulator, we must look at its specific metrics. Each property serves a distinct purpose in managing electrical stress and ensuring signal integrity.
High Dielectric Strength
Dielectric strength measures a material's ability to withstand a strong electric field without breaking down and conducting electricity.
Teflon excels here, with a dielectric strength typically in the range of 30–60 kV/mm. This means a 1 mm thick sheet of Teflon can theoretically withstand up to 60,000 volts before failing, making it ideal for high-voltage insulation.
Extremely High Resistivity
Resistivity is the fundamental measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. Teflon's resistivity is exceptionally high.
Its volume resistivity is in the order of 10¹⁸ Ω·cm, signifying it is a near-perfect insulator through its bulk. Similarly, its high surface resistivity prevents current from easily tracking across its surface.
Low Dielectric Constant
The dielectric constant indicates a material's ability to store electrical energy when placed in an electric field. For insulation in many electronic applications, a lower value is better.
Teflon has a very low dielectric constant, around 2.0–2.1. This property is critical in high-frequency applications, as it minimizes signal loss and prevents interference between adjacent conductors.
Excellent Arc Resistance
Arc resistance is the time in seconds that a material can resist the formation of a conductive path when exposed to a high-voltage arc.
With an arc resistance often exceeding 165 seconds, Teflon demonstrates a robust ability to endure electrical arcing without degrading into a conductive carbon track, which is a common failure mode for many other polymers.
The Molecular Basis for Superior Insulation
Teflon's electrical properties are not accidental; they are a direct result of its unique molecular structure.
The Power of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
The entire Teflon polymer is constructed from repeating chains of carbon atoms completely sheathed by fluorine atoms.
The carbon-fluorine (C-F) bond is incredibly strong. Fluorine is the most electronegative element, meaning it holds onto its electrons very tightly, leaving virtually no free electrons available to move and conduct electricity.
Unmatched Stability
This same chemical structure that provides its famous non-stick and chemical-resistant properties also ensures its electrical performance is reliable.
Teflon is inert to most chemicals and stable across a wide temperature range. This means its insulating properties will not degrade when exposed to harsh industrial environments, moisture, or thermal cycling.
Understanding the Practical Context
While its electrical properties are elite, selecting any material requires a holistic view of its characteristics in the context of an application.
An Insulator, Not a Conductor
It is crucial to state the obvious: Teflon's properties make it fundamentally unsuitable for any part of a design that requires electrical conductivity. Its entire purpose is to prevent current flow.
Mechanical Considerations
Teflon is a relatively soft material and can be susceptible to "cold flow" or creep under sustained mechanical load. This must be accounted for in designs where the component is both an insulator and a structural element.
Manufacturing Consistency
The exact electrical values cited can vary slightly based on the specific grade of PTFE, processing methods, and manufacturing quality. Always refer to the specific datasheet from your material supplier for design-critical values.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting Teflon is about matching its specific strengths to the primary challenge of your application.
- If your primary focus is high-voltage insulation: Its exceptional dielectric strength and high resistivity make it one of the most reliable choices for insulating cables, transformers, and electronic components.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency performance: Its low dielectric constant is the critical factor, ensuring minimal signal loss and interference in RF, microwave, and high-speed digital circuits.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability in harsh environments: Its chemical and thermal stability guarantees that its world-class electrical properties will not degrade over time.
By understanding these distinct properties, you can confidently leverage Teflon as a powerful solution for your most demanding electrical insulation challenges.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value/Range | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Strength | 30–60 kV/mm | Withstands extremely high voltages without breakdown |
| Volume Resistivity | ~10¹⁸ Ω·cm | Near-perfect bulk insulator, preventing current flow |
| Dielectric Constant | 2.0–2.1 | Minimizes signal loss & interference in high-frequency circuits |
| Arc Resistance | >165 seconds | Resists degradation from electrical arcing |
Leverage Teflon's Superior Insulation for Your Application
For engineers and designers in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, the right insulator is critical for performance and safety. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including custom seals, liners, and labware—that deliver on Teflon's promise of elite electrical properties.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your components meet exact specifications for dielectric strength, resistivity, and stability. Let's discuss how our expertise can solve your high-voltage or high-frequency insulation challenges.
Contact our team today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials



















