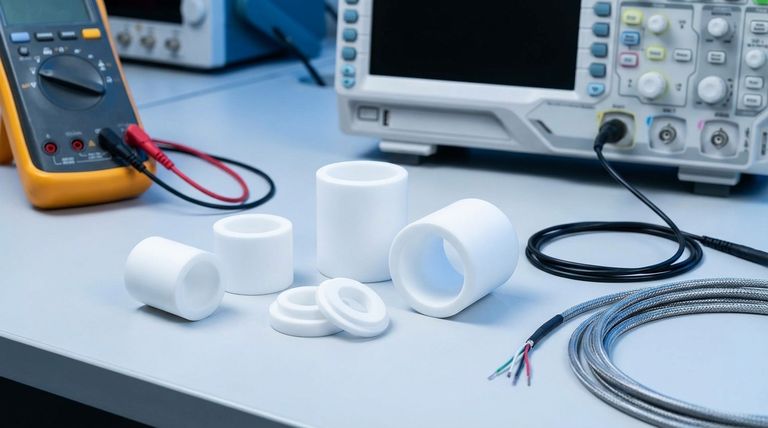
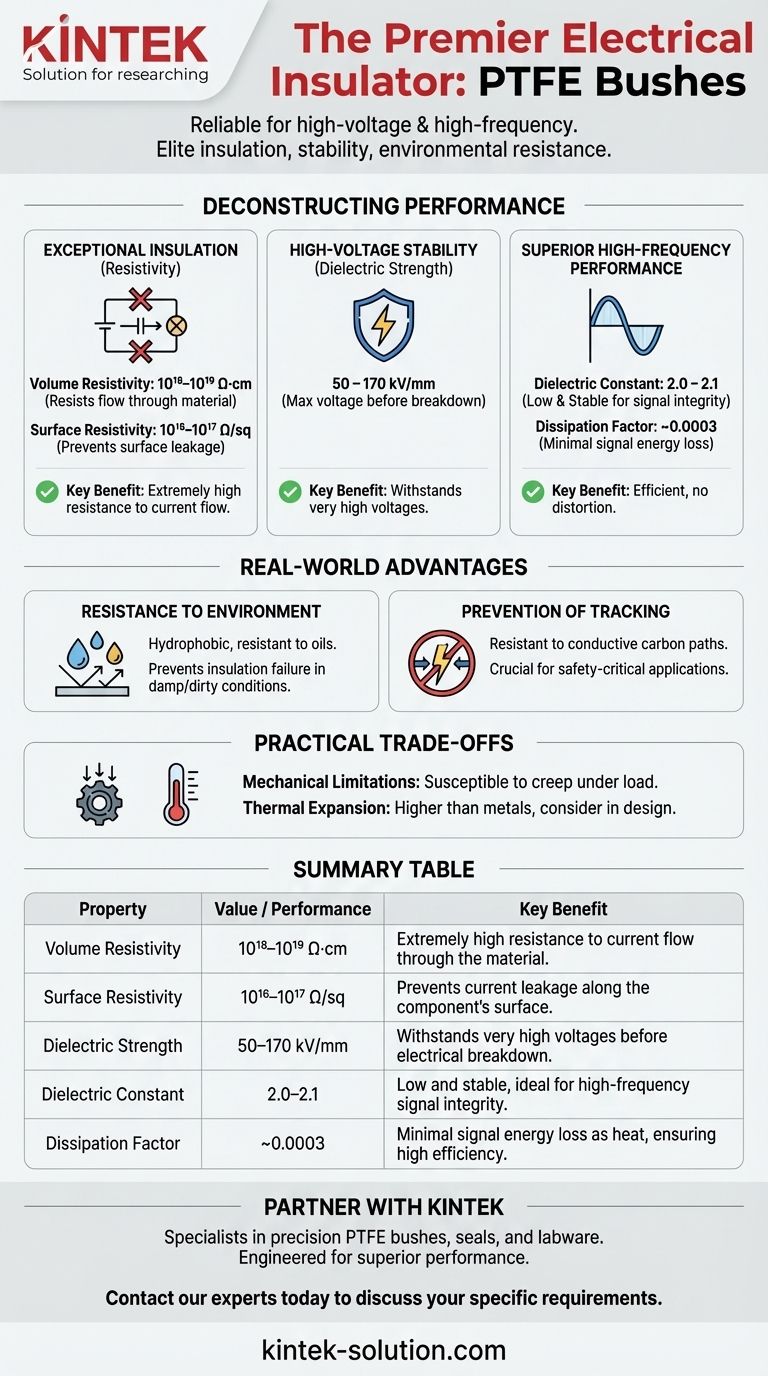
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a premier electrical insulator. Its properties make it one of the most reliable materials for applications requiring exceptional electrical isolation, especially under high-voltage or high-frequency conditions. PTFE bushes exhibit extremely high volume and surface resistivity, a very high dielectric strength, and a remarkably low and stable dielectric constant.
The core reason PTFE is so valued in electrical applications is not just one superior property, but its unique combination of elite insulation, stability across a vast range of frequencies, and inherent resistance to environmental factors like moisture.

Deconstructing PTFE's Electrical Performance
To understand why PTFE is a superior choice for electrical bushes, we must look beyond the general label of "insulator" and examine the specific metrics that define its performance. These properties are a direct result of its highly symmetric molecular structure.
Exceptional Insulation (Resistivity)
Volume resistivity measures the resistance to electrical current flowing through the bulk of the material. PTFE's is exceptionally high, typically 10¹⁸ to 10¹⁹ Ω·cm.
Surface resistivity measures the resistance to current flowing across the surface. PTFE also excels here, with a value around 10¹⁶ to 10¹⁷ Ω/sq. This prevents current leakage along the surface, a common failure point in lesser insulators.
High-Voltage Stability (Dielectric Strength)
Dielectric strength is the maximum voltage a material can withstand before it breaks down and an arc passes through it.
PTFE has a very high dielectric strength, ranging from 50 to 170 kV/mm. This makes it an extremely reliable choice for preventing electrical arcing in high-voltage equipment, enhancing both safety and component longevity.
Superior High-Frequency Performance
For applications involving alternating currents, especially at high frequencies (like radio or microwave signals), two properties are paramount.
Dielectric Constant reflects a material's ability to store electrical energy. PTFE has a very low and stable dielectric constant of 2.0-2.1 across a wide frequency spectrum. This ensures that the signal passing through is not distorted or delayed.
Dissipation Factor (or loss tangent) measures how much electrical energy is lost as heat within the material. PTFE's dissipation factor is incredibly low at ~0.0003. This means it is highly efficient, wasting almost no signal energy.
Why These Properties Matter in Practice
These technical specifications translate directly into tangible real-world advantages, particularly for components like bushes that serve both a mechanical and electrical function.
Resistance to Environmental Contamination
PTFE has an extremely low surface tension, making it highly hydrophobic (water-repellent) and resistant to oils.
Since moisture and surface contamination are primary causes of insulation failure, PTFE's ability to shed these contaminants ensures its electrical properties remain stable over time, even in damp or dirty environments.
Prevention of Tracking
Tracking is the formation of a conductive carbon path along the surface of an insulator due to repeated electrical arcing.
PTFE is highly resistant to tracking currents. This reliability is crucial in safety-critical applications where a component failure could lead to catastrophic equipment damage.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every application. While PTFE's electrical properties are outstanding, its mechanical characteristics must be considered.
Mechanical Limitations
PTFE is a relatively soft material. Under a constant compressive load, it can be susceptible to creep, or slow deformation over time. For a bush in a high-load mechanical application, this must be carefully evaluated.
Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion compared to metals. This difference must be accounted for in designs that experience wide temperature fluctuations to avoid issues with fit and tolerance.
Cost and Manufacturing
PTFE is often more expensive than other commodity plastics. Machining it requires specific tooling and expertise to maintain tight tolerances and a good surface finish.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, selecting PTFE for a bushing depends on whether its elite electrical properties are the driving requirement for your design.
- If your primary focus is high-voltage insulation: PTFE's exceptional dielectric strength and high resistivity make it an ideal choice for preventing arcing and ensuring safety.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency signals (RF/Microwave): Its low dielectric constant and minimal dissipation factor are critical for maintaining signal integrity and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is reliability in harsh environments: PTFE's resistance to moisture and chemicals ensures its insulating properties will not degrade over time.
- If your primary focus is a high-load mechanical joint: You must weigh PTFE's superior electrical properties against its potential for mechanical creep and choose a filled grade or alternative material if necessary.
By understanding this balance of properties, you can confidently determine if PTFE is the optimal material for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value / Performance | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Volume Resistivity | 10¹⁸ – 10¹⁹ Ω·cm | Extremely high resistance to current flow through the material. |
| Surface Resistivity | 10¹⁶ – 10¹⁷ Ω/sq | Prevents current leakage along the component's surface. |
| Dielectric Strength | 50 – 170 kV/mm | Withstands very high voltages before electrical breakdown. |
| Dielectric Constant | 2.0 – 2.1 | Low and stable, ideal for high-frequency signal integrity. |
| Dissipation Factor | ~0.0003 | Minimal signal energy loss as heat, ensuring high efficiency. |
Need high-performance PTFE components that guarantee electrical reliability?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE bushes, seals, liners, and custom labware. Our components are engineered to deliver the superior insulation, high-frequency stability, and environmental resistance detailed in this article. We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and specialized industrial sectors, offering custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Ensure your application's success with components built for elite performance. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F



















