At its core, the choice between PTFE and Nylon comes down to a fundamental trade-off. PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is the material of choice for its extreme chemical resistance, high-temperature stability, and exceptionally low friction, whereas Nylon (Polyamide) is selected for its superior mechanical strength, elasticity, and cost-effectiveness in less demanding environments.
Your decision is not about which plastic is universally "better," but which one possesses the specific properties required by your application's environment and mechanical demands. One excels in harsh conditions with low friction, while the other provides structural integrity at a lower cost.
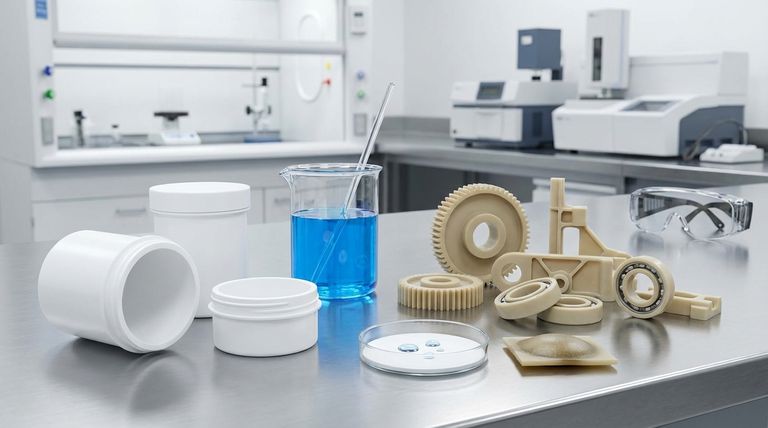

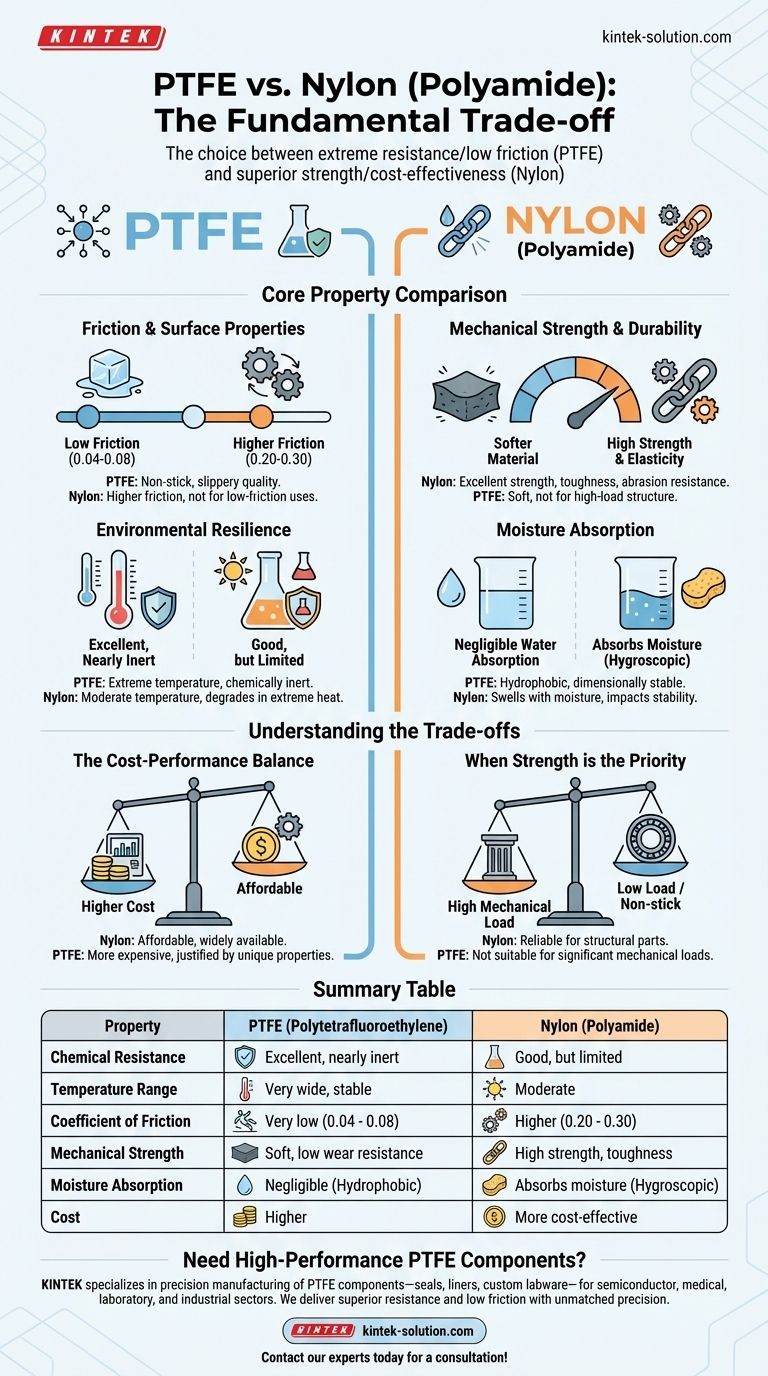
Core Property Comparison
Understanding the fundamental differences in material properties is the first step in making an informed decision. Each plastic has a distinct profile tailored to specific uses.
Friction and Surface Properties
PTFE is famous for having one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, typically between 0.04 and 0.08. This gives it its characteristic non-stick, or "slippery," quality.
Nylon has a significantly higher coefficient of friction, generally in the range of 0.20 to 0.30. While still a useful engineering plastic, it does not compare to PTFE for low-friction applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Nylon is the clear winner for mechanical performance. It offers high tensile strength, elasticity, and excellent abrasion resistance, making it suitable for gears, structural parts, and high-impact components.
PTFE is a much softer material. While durable in its own right, it lacks the strength and wear resistance of Nylon and is not typically used for high-load structural applications.
Environmental Resilience
PTFE provides exceptional performance in extreme environments. It can withstand a very wide temperature range and is nearly inert, resisting almost all industrial chemicals and solvents.
Nylon is suitable for moderate temperature environments but will degrade when exposed to extreme heat. Its chemical resistance is good but far more limited compared to PTFE.
Moisture Absorption
This is a critical differentiator. PTFE is hydrophobic and has negligible water absorption, ensuring its properties and dimensions remain stable even when submerged.
Nylon, by contrast, is hygroscopic and tends to absorb moisture from the air. This absorption can cause the material to swell and can negatively impact its dimensional stability and stiffness.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a material involves balancing its advantages against its limitations. The ideal choice for one project may be entirely wrong for another.
The Cost-Performance Balance
Nylon is a widely available and affordable material, making it the default choice for many cost-sensitive projects that require good mechanical properties.
PTFE is significantly more expensive due to its complex manufacturing process and superior performance characteristics. Its use is justified when its unique properties are a strict requirement.
The Impact of Water Absorption in Nylon
For applications requiring high precision, Nylon's tendency to absorb moisture can be a disqualifying factor. The resulting dimensional changes can compromise tight tolerances.
Engineers must account for this behavior in the design phase, which may add complexity. In humid or wet environments, PTFE's stability is a major advantage.
When Strength is the Priority
While PTFE's low friction is excellent for bearings or non-stick coatings, its softness makes it unsuitable for parts that must bear significant mechanical loads.
In these scenarios, Nylon's combination of strength, toughness, and wear resistance makes it the far more reliable and durable option.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct material, prioritize your application's single most important requirement.
- If your primary focus is low-friction performance or chemical resistance: Choose PTFE for its unmatched non-stick properties and ability to withstand aggressive environments.
- If your primary focus is structural strength and cost-effectiveness: Choose Nylon for its durability, toughness, and affordability in mechanically demanding roles.
- If your primary focus is dimensional stability in a humid environment: Choose PTFE, as Nylon's tendency to absorb moisture makes it unsuitable for high-precision applications.
By aligning your material choice with your primary operational demand, you ensure optimal performance and efficiency for your project.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) | Nylon (Polyamide) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, nearly inert | Good, but limited |
| Temperature Range | Very wide, high-temperature stable | Moderate |
| Coefficient of Friction | Very low (0.04 - 0.08) | Higher (0.20 - 0.30) |
| Mechanical Strength | Soft, low wear resistance | High strength, toughness, and abrasion resistance |
| Moisture Absorption | Negligible (hydrophobic) | Absorbs moisture (hygroscopic) |
| Cost | Higher | More cost-effective |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components?
Selecting the right material is critical for your project's success. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We deliver the superior chemical resistance, low friction, and thermal stability of PTFE with unmatched precision, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let's discuss your specific requirements and ensure optimal performance. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications



















