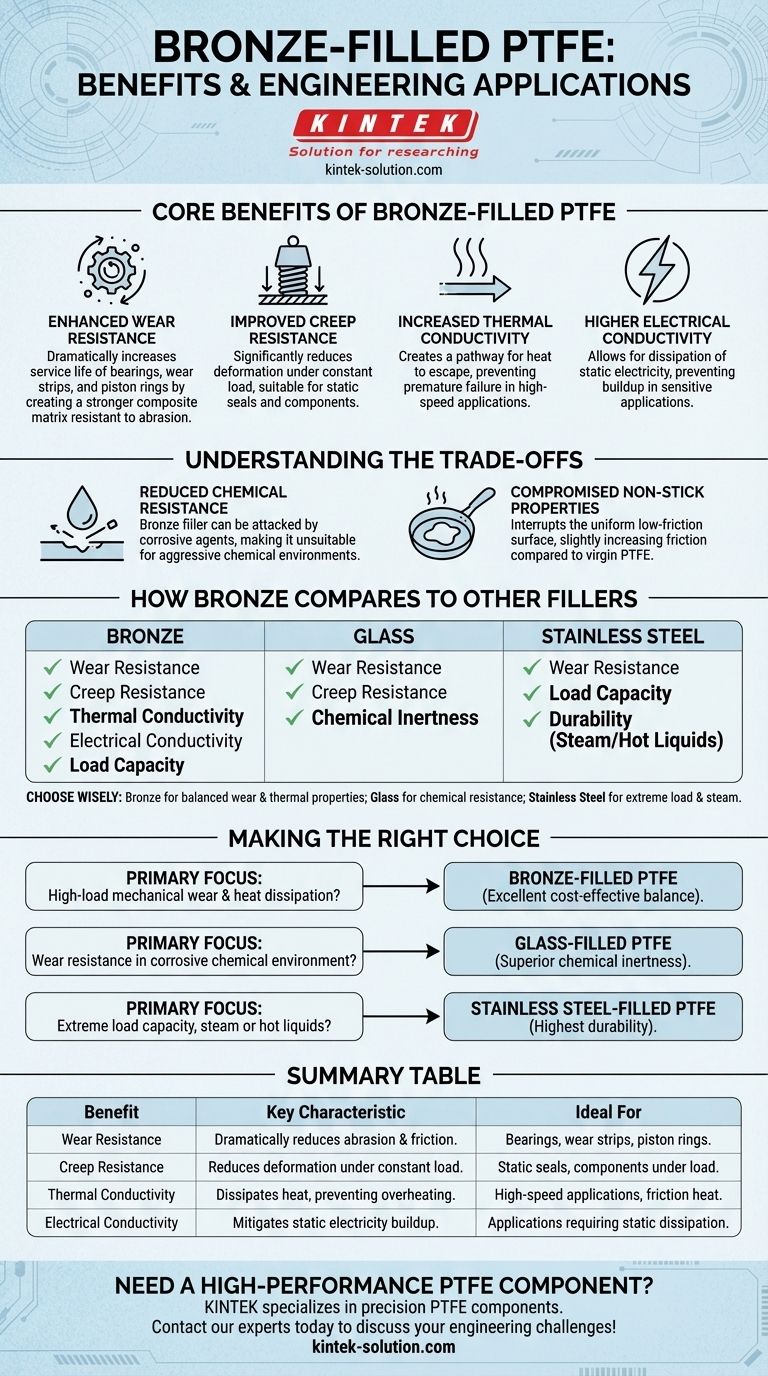
Adding bronze to Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) significantly enhances its resistance to mechanical wear and deformation under load (creep). It also fundamentally changes PTFE from a thermal and electrical insulator into a more conductive material, allowing for the dissipation of heat and static electricity.
The core benefit of bronze filler is the transformation of PTFE into a high-strength engineering material suited for mechanical applications. However, this improvement comes at the direct cost of reduced chemical resistance and non-stick properties.
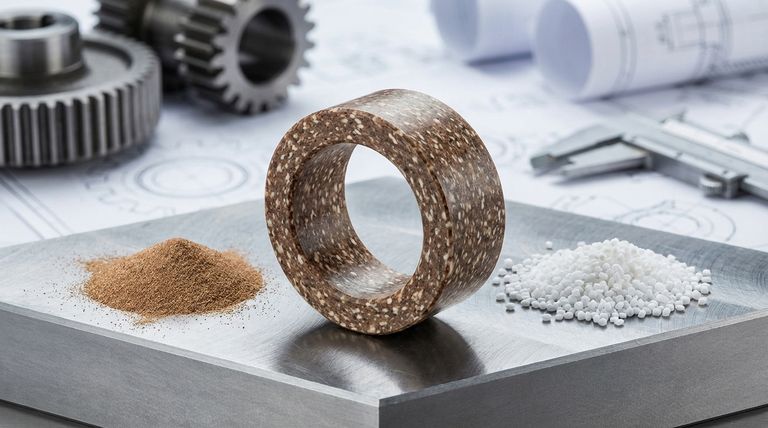

Core Benefits of Bronze-Filled PTFE
Virgin PTFE is known for its extreme chemical inertness and low friction, but it is mechanically soft. Adding a filler like bronze creates a composite material with vastly different performance characteristics.
Enhanced Wear Resistance
Bronze particles dispersed within the PTFE create a stronger composite matrix. This matrix is much more resistant to abrasion and friction, dramatically increasing the service life of components like bearings, wear strips, and piston rings.
Improved Creep Resistance
Creep is the tendency of a solid material to deform permanently under the influence of persistent mechanical stress. The rigid bronze particles reinforce the soft PTFE, significantly reducing its tendency to creep, making it suitable for static seals and components under constant load.
Increased Thermal Conductivity
Pure PTFE is an excellent thermal insulator, which can be a problem in high-speed applications where friction generates heat. Bronze is thermally conductive, creating a pathway for heat to escape and preventing premature failure due to overheating.
Higher Electrical Conductivity
While not a true conductor, bronze-filled PTFE is significantly less insulating than virgin PTFE. This property is useful in applications where the buildup and discharge of static electricity must be prevented.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a filled PTFE is always an exercise in balancing competing requirements. The advantages gained by adding bronze come with clear compromises.
Reduced Chemical Resistance
The primary trade-off is a loss of chemical inertness. While PTFE itself is resistant to nearly all chemicals, the bronze filler can be attacked by corrosive agents. This makes bronze-filled grades unsuitable for many chemically aggressive environments.
Compromised Non-Stick Properties
The addition of bronze particles interrupts the uniform, low-friction surface of pure PTFE. This slightly increases the coefficient of friction and reduces the material's non-stick quality compared to its unfilled state.
How Bronze Compares to Other Common Fillers
Understanding your application's specific demands is key to choosing the right filler. Bronze is a popular general-purpose choice, but other fillers excel in specific conditions.
Bronze vs. Glass
Glass filler also provides excellent wear and creep resistance. Its key advantage is that it maintains PTFE's chemical inertness, making it a better choice for corrosive environments. Bronze, however, offers superior thermal conductivity.
Bronze vs. Stainless Steel
Stainless steel filler provides the highest increase in wear and load resistance. It is particularly effective in applications involving steam or hot liquids, where it offers superior durability compared to bronze.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The ideal material is determined entirely by the operational environment and performance goals.
- If your primary focus is high-load mechanical wear and heat dissipation: Bronze-filled PTFE is an excellent, cost-effective choice due to its balance of wear resistance and thermal conductivity.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance in a corrosive chemical environment: Glass-filled PTFE is the superior option as it provides mechanical strength without compromising chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is extreme load capacity, especially with steam or hot liquids: Stainless steel-filled PTFE offers the highest level of durability for these specific, demanding conditions.
Ultimately, selecting the correct filled PTFE requires a clear understanding of the specific mechanical, thermal, and chemical stresses your component will face.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Characteristic | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Wear Resistance | Dramatically reduces abrasion and friction. | Bearings, wear strips, piston rings. |
| Creep Resistance | Reduces deformation under constant load. | Static seals, components under load. |
| Thermal Conductivity | Dissipates heat, preventing overheating. | High-speed applications generating friction heat. |
| Electrical Conductivity | Mitigates static electricity buildup. | Applications requiring static dissipation. |
Need a high-performance PTFE component?
Choosing the right filled PTFE is critical for your application's success. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components (seals, liners, labware, and more) for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We offer expert guidance on material selection and provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders to ensure optimal performance and durability.
Contact our experts today to discuss how bronze-filled or other specialized PTFE grades can solve your engineering challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















