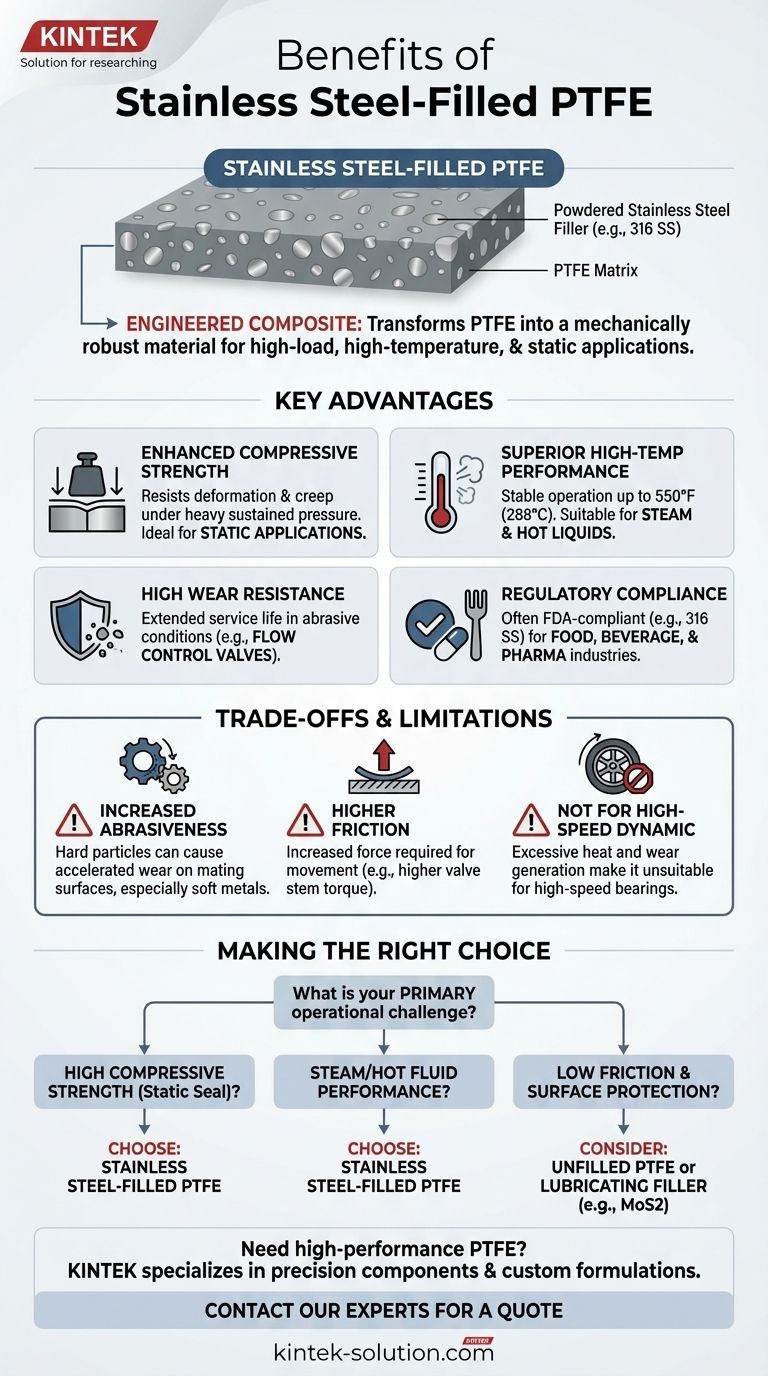
At its core, stainless steel-filled PTFE is a composite material engineered to overcome the inherent softness and thermal limitations of virgin PTFE. By embedding powdered stainless steel within the PTFE matrix, it gains significant compressive strength, improved high-temperature performance, and greater rigidity, making it ideal for high-load applications.
The central takeaway is that stainless steel filler transforms PTFE into a mechanically robust material for high-load, high-temperature, and static applications. This enhancement, however, comes at the cost of increased friction and abrasiveness against mating surfaces.

Key Advantages of Stainless Steel Filler
The addition of stainless steel particles fundamentally changes the properties of PTFE, targeting specific mechanical and thermal weaknesses.
Enhanced Compressive Strength and Load Capacity
Virgin PTFE is prone to deformation, or "creep," under sustained pressure.
The stainless steel particles act as a reinforcing skeleton within the polymer, dramatically increasing the material's ability to resist heavy loads without deforming. This makes it exceptionally well-suited for static applications where high pressure is a primary concern.
Superior Performance in High Temperatures
Unfilled PTFE has a limited operating temperature range.
Stainless steel improves the material's thermal conductivity and stability, allowing it to perform reliably in applications involving steam and hot liquids. Some formulations can operate effectively at temperatures up to 550°F (288°C).
High Wear Resistance
In environments with abrasive media, standard PTFE can wear down quickly.
The hardness of the steel filler provides excellent wear resistance for the component itself, extending its service life in demanding conditions, such as in flow control valves handling particulates.
Suitability for Regulated Industries
The use of specific grades, like 316 powdered stainless steel, ensures the material is safe for sensitive applications.
This composition is often FDA-compliant, making it a trusted choice for components used in the food, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries where both performance and safety are critical.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material choice is without compromise. The very properties that make stainless steel-filled PTFE strong also introduce critical limitations that must be understood.
Increased Abrasiveness and Mating Surface Wear
This is the most significant drawback. The hard steel particles can act like an abrasive, causing accelerated wear on adjacent surfaces, especially softer metals like aluminum or brass.
This makes it a poor choice for dynamic applications where it would rub against a valuable or sensitive mating part.
Higher Coefficient of Friction
While PTFE is famous for its low friction, adding steel particles increases it.
This results in a higher force required to initiate movement, such as increased stem torque in a valve. It is not the ideal choice when minimizing friction is the most important design goal.
Not Ideal for High-Speed Dynamic Applications
The combination of higher friction and abrasiveness makes this material unsuitable for high-speed bearings or seals.
The heat generated from friction can become excessive, and the wear on both the PTFE component and the mating surface would be unacceptably high.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct material requires a clear understanding of your primary operational challenge.
- If your primary focus is high compressive strength in a static seal: Stainless steel-filled PTFE is an excellent choice due to its superior load-bearing capabilities.
- If your primary focus is performance with steam or hot fluids: This material's enhanced thermal stability makes it a reliable option for valve seats and seals in these environments.
- If your primary focus is low friction and protecting a mating surface: You should consider unfilled PTFE or a version with a lubricating filler like MoS2.
Choosing the right material is about aligning its specific strengths with the unique demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Compressive Strength | Resists deformation under heavy loads | Static seals, high-pressure components |
| Superior High-Temp Performance | Stable operation up to 550°F (288°C) | Steam, hot liquid applications |
| High Wear Resistance | Extended service life in abrasive conditions | Valves handling particulates |
| Regulatory Compliance | Often FDA-compliant (with 316 SS) | Food, beverage, pharmaceutical industries |
Need a high-performance PTFE component for a demanding application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom stainless steel-filled formulations. We provide the material expertise and custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—to ensure your parts meet exact specifications for strength, temperature resistance, and compliance.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications



















