The primary advantages of PTFE/PFA lined ball valves are their exceptional corrosion resistance, reliable sealing performance, and operational efficiency when handling aggressive or high-purity media. By encapsulating all internal metal components with an inert fluoropolymer liner, these valves provide a cost-effective and durable solution for controlling highly corrosive fluids like acids, alkalis, and salts that would quickly destroy standard metal valves.
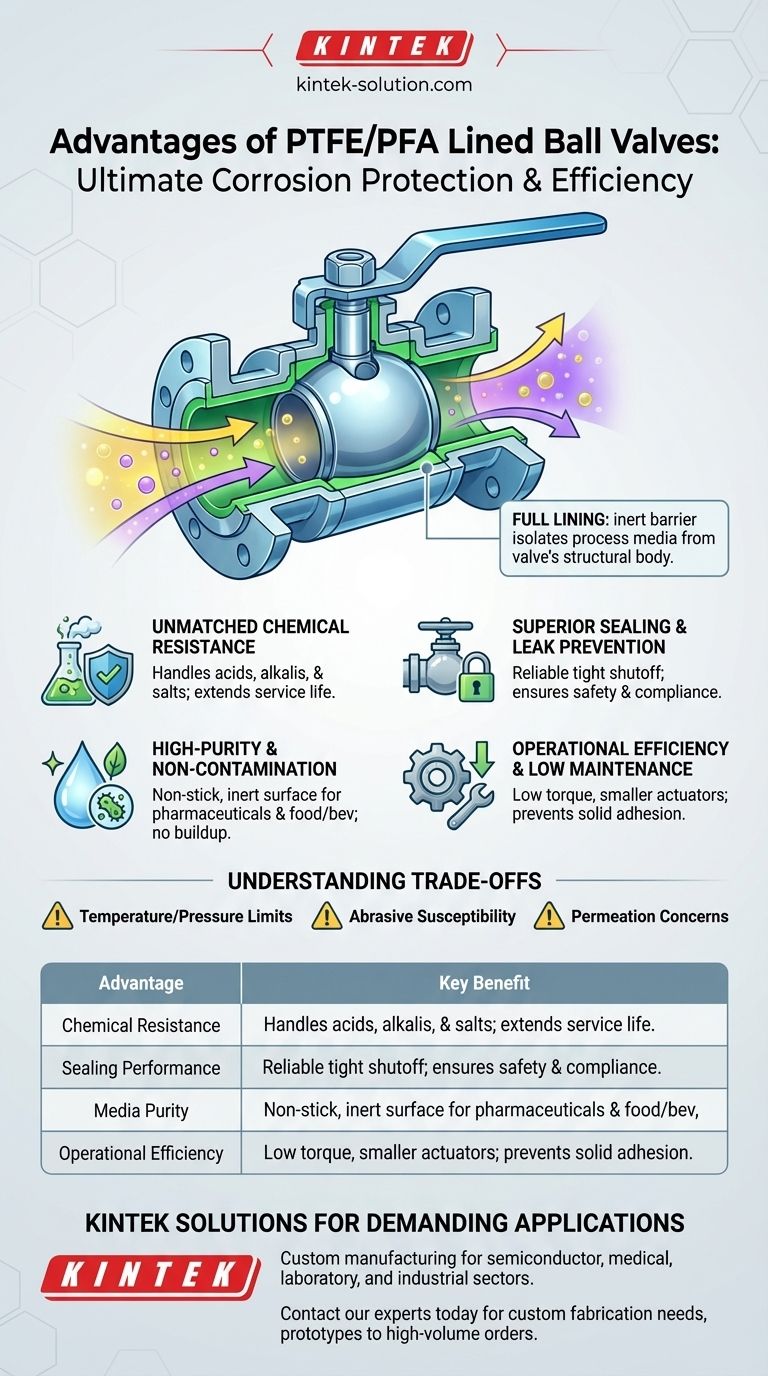
The core value of a lined ball valve is not just one feature, but the creation of a complete, chemically inert barrier. This design isolates the process media from the valve's structural body, combining the strength of metal with the near-universal chemical resistance of PTFE/PFA.

How a Lined Valve Achieves Total Protection
To understand the advantages, you must first understand the design principle. A lined valve isn't merely coated; it's a system designed for total media isolation.
The Concept of Full Lining
The defining feature is that all wetted parts—the valve body, ball, and stem—are completely encapsulated with a thick, uniform layer of PTFE or PFA.
This ensures that the corrosive or pure process fluid never comes into contact with the metallic structural components of the valve.
The Role of PTFE and PFA
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) and PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy alkane) are fluoropolymers known for their remarkable properties.
They are chemically inert to nearly all industrial chemicals, possess a very low coefficient of friction (making them non-stick), and can handle high temperatures.
Construction and Integrity
These valves typically feature a two-piece bolted body. This construction securely locks the liner in place, preventing it from collapsing under vacuum or blowing out under high pressure, which is a critical reliability feature.
Core Advantages in Demanding Applications
The unique construction of lined ball valves delivers several key operational benefits that make them ideal for harsh chemical services.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
This is the principal advantage. The inert liner allows the valve to manage a vast range of aggressive media without risk of corrosion, extending the valve's service life dramatically.
Superior Sealing and Leak Prevention
The design provides reliable sealing, which is critical for safety and environmental compliance when handling hazardous fluids. The liners and seats create a tight shutoff, preventing dangerous leaks.
High-Purity and Non-Contamination
Because the PTFE/PFA surface is non-stick and does not leach, these valves are excellent for applications where media purity is essential, such as in the pharmaceutical or food and beverage industries. The smooth surface prevents media buildup and bacterial growth.
Operational Efficiency and Low Maintenance
The low-friction properties of the liner mean the valve requires low torque to operate, allowing for smaller, less expensive actuators. Its non-stick nature also reduces maintenance needs by preventing solids from adhering to and clogging the valve internals.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, lined valves are not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires understanding their operational boundaries.
Temperature and Pressure Boundaries
PTFE and PFA have strict temperature and pressure limits that are lower than those of solid metal or exotic alloy valves. Exceeding these specifications can lead to liner failure.
Susceptibility to Abrasives
Lined valves are best suited for clean liquids. Abrasive slurries or solids in the media can physically damage or erode the liner over time, compromising its protective barrier.
Permeation Concerns
While rare, highly diffusive gases or specific chemicals at high temperatures can sometimes permeate the liner. This is a specialized consideration but is important for certain critical applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct valve depends entirely on your specific process conditions and priorities.
- If your primary focus is handling highly corrosive chemicals: A fully lined valve offers one of the most reliable and cost-effective solutions for ensuring long-term asset integrity.
- If your primary focus is maintaining media purity: The inert, non-stick surface of a PTFE/PFA lined valve is ideal for preventing contamination and ensuring a clean process.
- If your application involves high temperatures, high pressures, or abrasive solids: You must carefully verify the valve's specifications and consider a metal-seated or alloy valve as a more suitable alternative.
Ultimately, choosing a PTFE/PFA lined ball valve is a strategic decision to ensure safety, reliability, and purity in your most demanding chemical applications.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Handles highly corrosive acids, alkalis, and salts. |
| Sealing Performance | Provides reliable shutoff, preventing hazardous leaks. |
| Media Purity | Non-stick, inert surface prevents contamination. |
| Operational Efficiency | Low operating torque and reduced maintenance needs. |
Need a reliable PTFE/PFA lined ball valve for your demanding application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE components, including custom-lined ball valves for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We ensure your valves provide the ultimate protection against corrosion and contamination.
Let us help you enhance the safety and efficiency of your process. Contact our experts today to discuss your custom fabrication needs, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What makes PTFE balls ideal for chemical applications? Unmatched Inertness for Demanding Environments
- What are the tolerances for PTFE balls based on size? Precision vs. Standard Grade Explained
- What are the common applications of PTFE balls? Leverage Unmatched Chemical Resistance & Low Friction
- What are PTFE balls made of and what are their key properties? Unlock Superior Chemical & Thermal Performance
- What temperature range can PTFE balls withstand? Unlock Extreme Thermal Stability from -200°C to 260°C



















