The primary advantage of PTFE shovels is their exceptional chemical resistance. This stems from the fact that Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is one of the most chemically inert materials known. It can handle a vast range of aggressive and corrosive substances—including strong acids, alkalis, and solvents—without degrading, corroding, or reacting with the material it contacts.
The core reason to use a PTFE shovel is its near-total chemical inertness. This quality ensures that the shovel will not be damaged by corrosive materials and, just as importantly, that it will not contaminate the substance being handled.

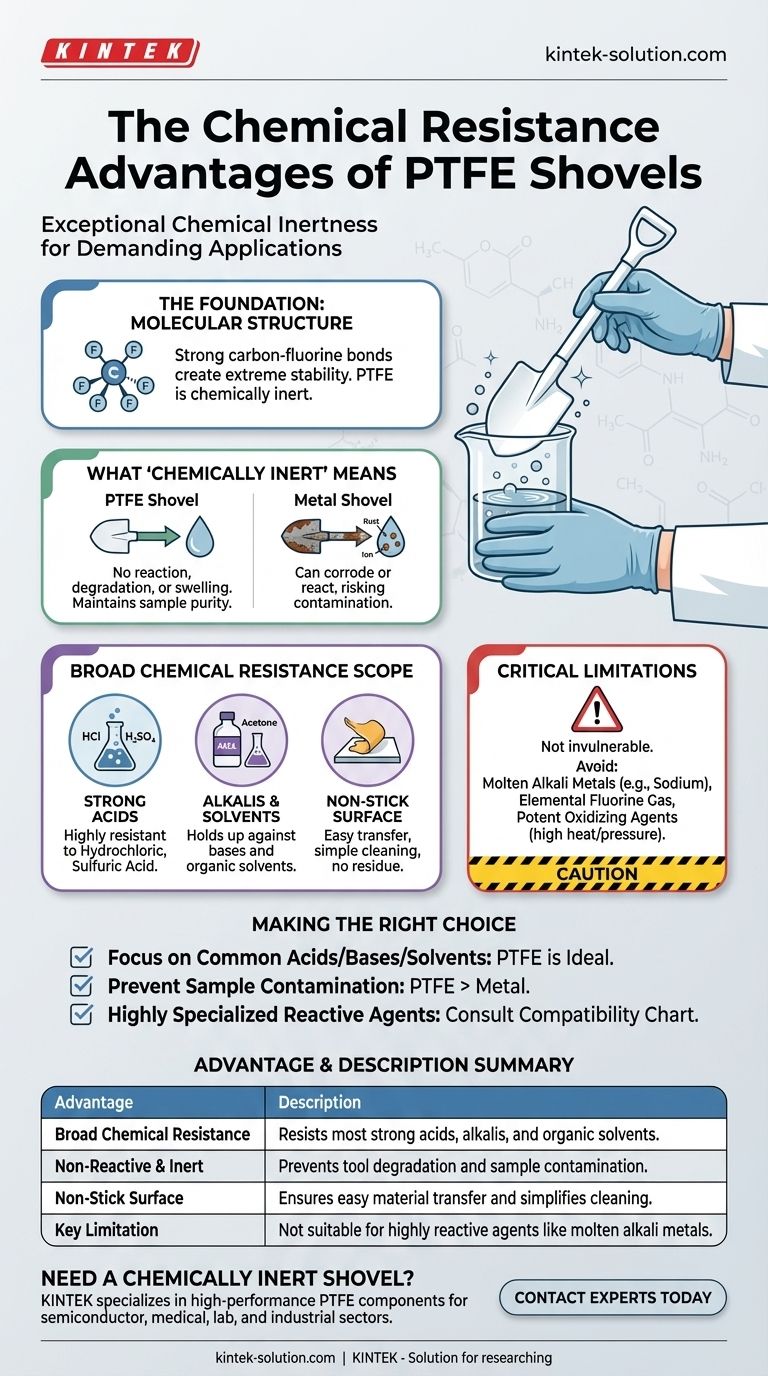
The Foundation of PTFE's Chemical Resistance
The unique molecular structure of PTFE is what grants it these remarkable properties. The strong carbon-fluorine bonds are extremely stable and non-reactive, creating a material that is ideal for demanding chemical handling applications.
What "Chemically Inert" Means in Practice
Being chemically inert means the shovel will not participate in a chemical reaction with the substances it touches.
This prevents the tool from dissolving, swelling, or becoming brittle. It ensures the integrity of the shovel and the purity of the sample are maintained.
A Superior Alternative to Metal
Unlike metal shovels, which can corrode or react when exposed to acids and other harsh chemicals, PTFE remains stable.
This eliminates the risk of metallic ions leaching into and contaminating a sensitive sample, which is critical in laboratory and industrial settings.
The Scope of PTFE's Resistance
PTFE's resilience is not limited to a few specific chemicals; its resistance is famously broad, making it a reliable choice for environments where a variety of substances are used.
Resistance to Common Corrosive Agents
PTFE is highly resistant to most strong acids like hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid.
It also holds up exceptionally well against powerful alkalis (bases) and a wide range of organic solvents, such as acetone and chloroform.
Non-Stick Properties Add Value
A secondary benefit of PTFE is its well-known non-stick surface. When handling sticky or viscous chemical compounds, this property ensures a more complete transfer of material and makes the shovel much easier to clean and decontaminate.
Understanding the Critical Limitations
While its resistance is extensive, no material is completely invulnerable under all possible conditions. Understanding the specific, albeit rare, exceptions is crucial for safe and effective use.
What PTFE Cannot Handle
PTFE is known to react with a very small and specific group of highly reactive substances.
These include liquid or dissolved alkali metals (like sodium), elemental fluorine gas, and a few other extremely potent oxidizing agents, particularly under high heat and pressure.
The Importance of Context
For the vast majority of applications in a lab or industrial plant, you will not encounter these specific chemicals.
However, if your work involves these highly specialized reactive agents, a PTFE shovel is not a suitable tool, and you must consult a material compatibility chart for an appropriate alternative.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct tool is a matter of safety and operational integrity. PTFE's properties make it an excellent default choice for chemical handling, but context is always key.
- If your primary focus is handling common acids, bases, and solvents: A PTFE shovel is an ideal and highly reliable choice that ensures both tool longevity and sample purity.
- If your primary focus is preventing sample contamination: PTFE's inert nature is superior to metal, which can corrode and leach into the substance being handled.
- If you are working with highly specialized reactive agents: You must verify compatibility, as PTFE is vulnerable to a short list of extreme chemicals like molten alkali metals and fluorine gas.
Ultimately, understanding the properties of your tools is the first step toward safe and effective work.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Broad Chemical Resistance | Resists most strong acids (e.g., hydrochloric, sulfuric), alkalis, and organic solvents (e.g., acetone, chloroform). |
| Non-Reactive & Inert | Prevents tool degradation and sample contamination, unlike metal shovels that can corrode and leach ions. |
| Non-Stick Surface | Ensures easy, complete material transfer and simplifies cleaning of sticky or viscous substances. |
| Key Limitation | Not suitable for a small group of highly reactive agents like molten alkali metals or fluorine gas. |
Need a chemically inert shovel for your specific application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE components, including shovels, seals, liners, and custom labware. Our PTFE shovels are engineered for superior chemical resistance, ensuring the integrity of your materials in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, tailoring solutions to your exact needs. Ensure purity and durability in your processes—contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
People Also Ask
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers



















