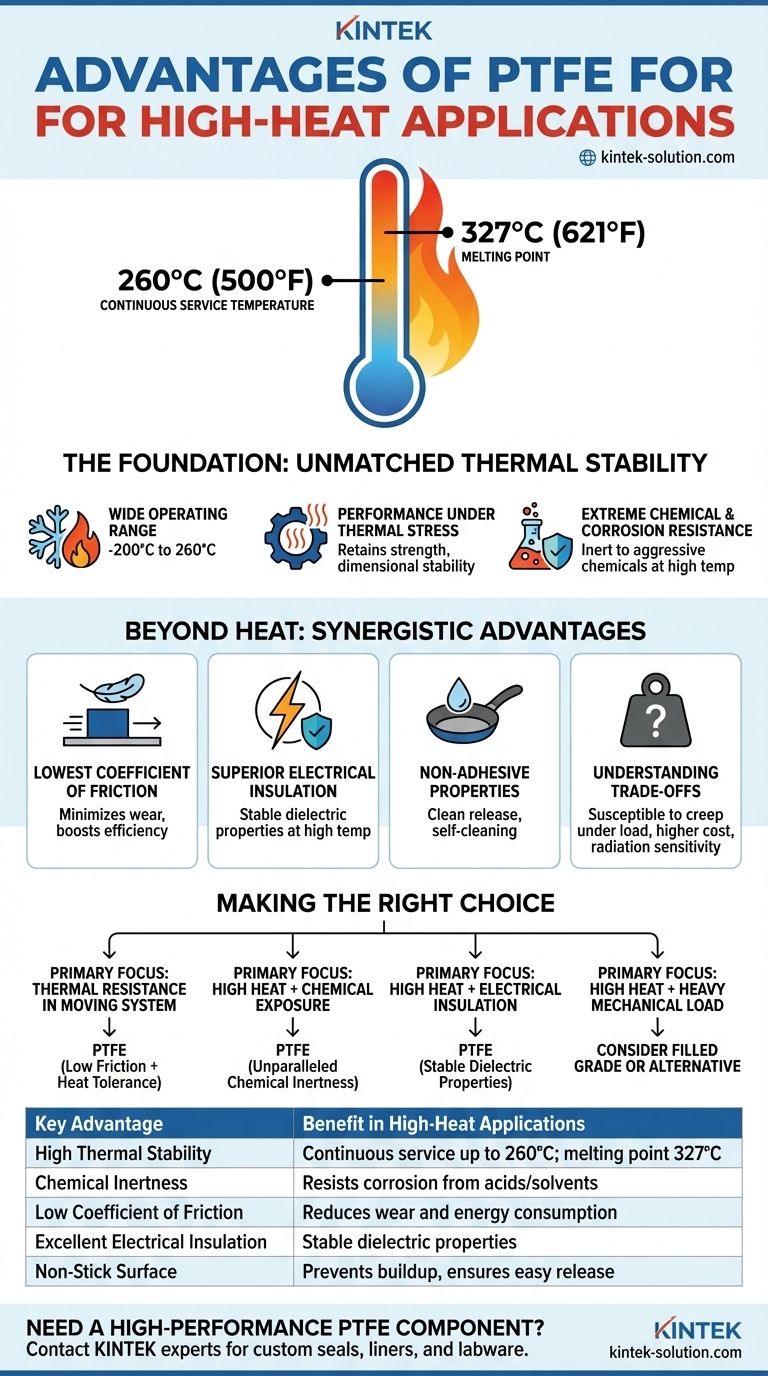
The primary advantage of PTFE for high-heat applications is its exceptionally high melting point compared to other plastics, allowing it to maintain its critical properties and structural integrity at continuous service temperatures up to 260°C (500°F). This thermal stability is rooted in the powerful carbon-fluorine bonds that make up its molecular structure.
While its ability to withstand high temperatures is its most famous trait, the true value of PTFE in demanding environments comes from the powerful combination of this heat resistance with its other unique properties, such as near-total chemical inertness and an extremely low coefficient of friction.

The Foundation: Unmatched Thermal Stability
The core of PTFE's utility in hot environments is its ability to perform reliably where other polymers would degrade or fail completely.
High Melting Point
PTFE has a melting point of around 327°C (621°F). This allows it to have a continuous working temperature of 260°C (500°F), far exceeding that of most conventional plastics.
Wide Operating Temperature Range
Beyond just its high-temperature tolerance, PTFE is versatile. It maintains its properties across a vast temperature spectrum, from cryogenic lows around -200°C (-328°F) up to its maximum service temperature.
Performance Under Thermal Stress
PTFE doesn't just resist melting; it retains its high flexural strength and dimensional stability at elevated temperatures. This ensures components made from PTFE do not deform or fail when subjected to thermal cycling and operational heat.
Beyond Heat: Synergistic Advantages in Demanding Applications
In most high-heat applications, temperature is only one of several challenges. PTFE's other elite characteristics work in tandem with its thermal stability to solve complex engineering problems.
Extreme Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
High-temperature processes often involve aggressive chemicals, acids, or solvents. PTFE is virtually inert and will not corrode or react, making it essential for sealing and fluid handling in hostile environments like oil and gas or chemical processing.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
High-heat applications frequently involve moving parts, such as bearings, seals, and gaskets in engines. PTFE’s incredibly low friction coefficient minimizes wear and reduces the energy needed to overcome resistance, boosting efficiency and extending component lifespan.
Superior Electrical Insulation
Temperature can degrade the performance of insulating materials. PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator with dielectric properties that remain stable even at high temperatures and across a wide range of frequencies.
Non-Adhesive Properties
In industries like food processing or manufacturing, preventing material from sticking to surfaces at high temperatures is critical. PTFE’s non-stick, non-wetting nature ensures a clean release, which improves operational efficiency and promotes self-cleaning.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every situation. Being an effective advisor means acknowledging where a material has limitations.
Mechanical Properties
While thermally robust, PTFE is a relatively soft material. It can be susceptible to "creep," or slow deformation, under a sustained heavy load, especially at higher temperatures. It also has lower tensile strength and wear resistance compared to some specialized engineering plastics.
Cost and Processing
PTFE is more expensive than commodity plastics like polyethylene or polypropylene. Its unique properties also mean it cannot be processed using conventional melt techniques, which can add complexity and cost to manufacturing custom components.
Radiation Sensitivity
PTFE has poor resistance to high-energy radiation, which can cause its molecular structure to break down. It is generally not a suitable choice for applications involving significant radiation exposure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if PTFE is the optimal material, consider the full range of environmental stressors, not just the heat.
- If your primary focus is thermal resistance in a moving system: PTFE is an elite choice, as its low friction works with its heat tolerance to ensure longevity and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is high heat combined with chemical exposure: PTFE is almost certainly the best option due to its unparalleled chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is high heat and electrical insulation: PTFE's stable dielectric properties make it a top-tier candidate for high-performance wiring and electronic components.
- If your primary focus is high heat under a heavy mechanical load: You may need to consider a filled grade of PTFE or an alternative high-performance polymer to prevent creep.
Ultimately, choosing the right material requires evaluating the complete performance profile against the specific demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Benefit in High-Heat Applications |
|---|---|
| High Thermal Stability | Continuous service up to 260°C (500°F); melting point of 327°C (621°F). |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists corrosion from aggressive acids and solvents, even at high temperatures. |
| Low Coefficient of Friction | Reduces wear and energy consumption in moving parts like seals and bearings. |
| Excellent Electrical Insulation | Maintains stable dielectric properties across a wide temperature and frequency range. |
| Non-Stick Surface | Prevents material buildup, promotes self-cleaning, and ensures easy release. |
Need a high-performance PTFE component that can withstand extreme heat and harsh chemicals?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in custom fabrication ensures you get a solution tailored to your specific thermal and mechanical requirements, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance the durability and efficiency of your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Magnetic Stirring Bar
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability



















