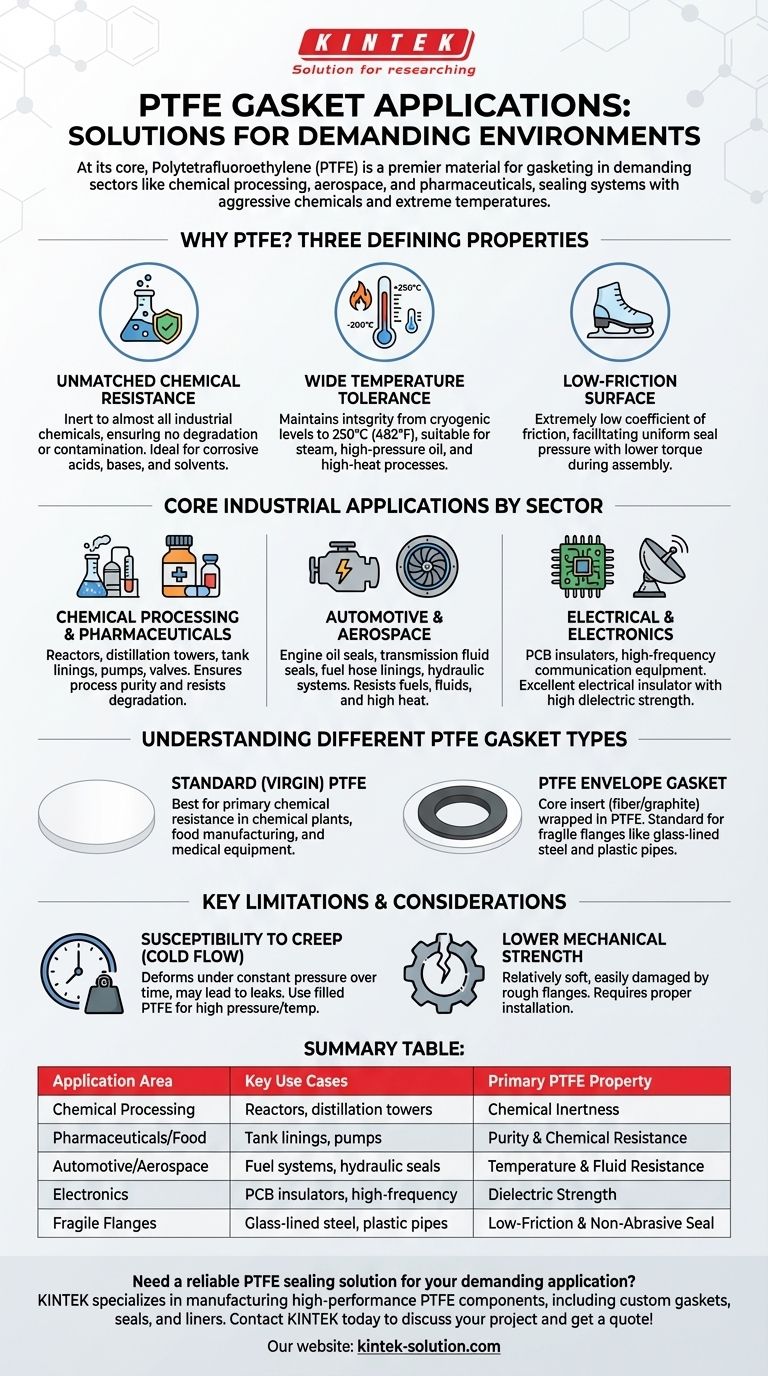
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a go-to material for gasketing in demanding environments. Its applications span nearly every major industry, from chemical processing and aerospace to pharmaceuticals and electronics. PTFE gaskets are commonly found sealing pipes, valves, heat exchangers, and high-pressure vessels, especially where aggressive chemicals or extreme temperatures are present.
The widespread use of PTFE gaskets is not accidental. It stems directly from the material's three defining properties: near-universal chemical inertness, a wide operational temperature range, and an extremely low coefficient of friction.

Why PTFE is a Premier Gasketing Material
Before listing applications, it's critical to understand why PTFE is so frequently specified. Its molecular structure gives it a unique combination of characteristics that other materials cannot match.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals and solvents. This makes it an essential choice for systems handling corrosive acids, bases, or other aggressive media.
This property ensures the gasket will not degrade, swell, or contaminate the process fluid, which is critical in pharmaceutical and food-grade applications.
Wide Temperature Tolerance
PTFE gaskets maintain their integrity and sealing capability across a broad temperature spectrum, typically from cryogenic levels up to 250°C (482°F).
This allows them to be used reliably in applications involving steam, high-pressure oil, or high-heat manufacturing processes.
Low-Friction Surface
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, often compared to wet ice on wet ice.
While less critical for static seals, this property is beneficial during assembly, as it allows for a uniform seal pressure with lower torque.
Core Industrial Applications by Sector
Different industries leverage PTFE's properties to solve specific challenges. The applications are diverse but always trace back to the material's core strengths.
Chemical Processing & Pharmaceuticals
This is PTFE's primary domain. Its inertness is non-negotiable for maintaining process purity and resisting degradation.
Common uses include gaskets for distillation towers, chemical reactors, tank linings, pumps, and valves. They are also essential for sealing pipes conveying aggressive chemicals, steam, or exhaust.
Automotive & Aerospace
In these sectors, resistance to fuels, hydraulic fluids, and heat is paramount.
PTFE is used for engine oil seals, transmission fluid seals, fuel hose linings, and aircraft hydraulic systems. Its temperature resistance also makes it a superior alternative to polyethylene in high-heat aerospace and computer components.
Electrical & Electronics
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator with a high dielectric strength, making it ideal for protecting sensitive components.
It serves as an insulator on printed circuit boards (PCBs) and is used in high-frequency communication and radar equipment where signal integrity is critical.
Understanding Different PTFE Gasket Types
Not all PTFE gaskets are the same. The specific construction is often tailored to the application for optimal performance.
Standard (Virgin) PTFE Gaskets
These are cut from a solid sheet of PTFE. They are best suited for applications where chemical resistance is the primary concern, such as in chemical plants, food manufacturing, and medical equipment.
PTFE Envelope Gaskets
These gaskets feature a core insert material (like compressed fiber or graphite) wrapped in a thin layer of PTFE. This design combines the strength and resilience of the core with the chemical resistance of the PTFE "envelope."
They are the standard choice for sealing fragile flange connections, such as glass-lined steel, plastic pipes, and enamel flanges, where high compression force could cause damage.
Key Limitations and Considerations
While highly capable, PTFE is not a universal solution. Understanding its trade-offs is crucial for proper application.
Susceptibility to Creep (Cold Flow)
PTFE has a tendency to deform or "creep" over time under constant pressure, especially at elevated temperatures. This can lead to a loss of bolt torque and potential leaks.
This is why filled PTFE (which includes materials like glass or carbon) or envelope gaskets are often used in high-pressure or high-temperature applications to improve creep resistance.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Compared to metallic or some fiber gaskets, PTFE is a relatively soft material. It can be easily damaged by scratched or uneven flange surfaces.
Proper installation and flange surface preparation are critical to achieving a reliable seal with PTFE.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct PTFE gasket depends entirely on the demands of your specific application.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals or ensuring process purity: A standard, virgin PTFE gasket is the most reliable and cost-effective choice for low to moderate pressures.
- If your primary focus is sealing fragile or potentially uneven flanges (glass, enamel, plastic): A PTFE envelope gasket provides the necessary chemical resistance while using a resilient core to create a tight seal without damaging the flange.
- If your primary focus is a high-pressure or high-temperature chemical environment: Consider a modified or filled PTFE gasket designed specifically to resist creep and maintain its mechanical integrity under stress.
Ultimately, choosing the right PTFE gasket is about matching the material's unparalleled chemical and thermal properties to the specific mechanical demands of your system.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Use Cases | Primary PTFE Property Utilized |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Processing | Reactors, distillation towers, pipe seals | Chemical Inertness |
| Pharmaceuticals/Food | Tank linings, pumps, valves | Purity & Chemical Resistance |
| Automotive/Aerospace | Fuel systems, hydraulic seals, engine components | Temperature & Fluid Resistance |
| Electronics | PCB insulators, high-frequency equipment | Dielectric Strength & Insulation |
| Fragile Flanges | Glass-lined steel, plastic pipes (via envelope gaskets) | Low-Friction & Non-Abrasive Seal |
Need a reliable PTFE sealing solution for your demanding application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom gaskets, seals, and liners. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, we provide precision-engineered parts that offer unmatched chemical resistance and thermal stability.
We work with you from prototype to high-volume production to ensure a perfect fit and optimal performance for your specific environment.
Contact KINTEB today to discuss your project requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance



















