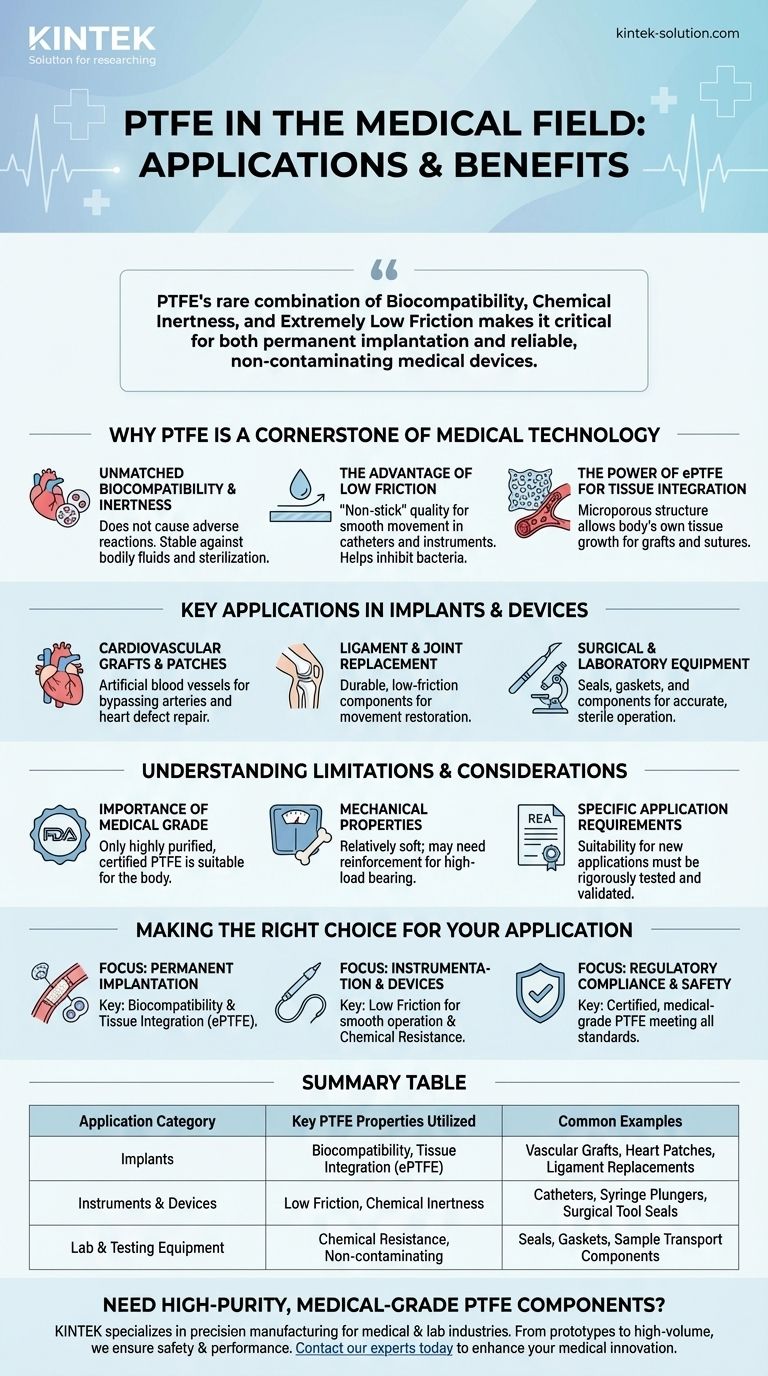
In the medical field, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a critical material used for a range of life-saving and high-performance applications. Its most prominent uses are in cardiovascular grafts, heart patches, and ligament replacements, as well as essential components in surgical instruments, catheters, and medical testing equipment.
The core reason for PTFE's widespread medical use is not just one property, but its rare combination of biocompatibility, chemical inertness, and extremely low friction. This makes it one of the few materials trusted for both permanent implantation within the human body and for creating reliable, non-contaminating medical devices.

Why PTFE is a Cornerstone of Medical Technology
The value of PTFE in medicine extends far beyond a single application. Its fundamental material characteristics solve several core challenges faced by medical engineers and surgeons.
Unmatched Biocompatibility and Inertness
PTFE is highly biocompatible, meaning it does not cause an adverse reaction when introduced to the human body.
Because it is chemically inert, it does not degrade when exposed to bodily fluids or aggressive sterilization chemicals. This stability is paramount for any long-term implant.
The Advantage of Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid, giving it a "non-stick" quality. This is vital for medical devices.
Coatings on catheters reduce friction during insertion and can help inhibit the buildup of bacteria. In instruments like syringe plungers and pump seals, this property ensures smooth, precise, and hygienic movement.
The Power of ePTFE for Tissue Integration
A specialized form called expanded PTFE (ePTFE) is a game-changer for implants.
ePTFE features a microporous structure with billions of tiny pores. This allows the body's own tissue to grow into the material, creating a strong, natural integration for things like vascular grafts and surgical sutures.
Key Applications in Implants and Devices
PTFE's properties translate directly into specific, critical medical uses where performance and safety are non-negotiable.
Cardiovascular Grafts and Patches
Perhaps its most well-known application, PTFE is used to create artificial blood vessels to bypass blocked arteries. It is also shaped into patches to repair defects in the heart, relying on its inertness and strength.
Ligament and Joint Replacement
Due to its durability and low friction, PTFE can be used as a material in ligament replacements and certain components of artificial joints, helping to restore movement and function.
Surgical and Laboratory Equipment
PTFE is a workhorse material inside medical equipment. It is used for seals, gaskets, sample transport mechanisms, and other components where chemical resistance and frictionless movement are essential for accurate and sterile operation.
Understanding the Limitations and Considerations
While incredibly useful, PTFE is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to its proper application.
The Importance of Medical Grade
Only highly purified, medical-grade PTFE that complies with FDA regulations is suitable for use in the body. Industrial grades may contain impurities and are not safe for medical applications.
Mechanical Properties
Standard PTFE is relatively soft and may not be suitable for high-load-bearing applications, such as a complete artificial hip joint, without reinforcement. Its performance depends entirely on the specific mechanical demands of the device.
Specific Application Requirements
The design and use of any medical device are subject to strict regulations. While PTFE is a compliant material, its suitability for a new application must always be rigorously tested and validated.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material is a critical decision in medical device engineering. The optimal choice depends entirely on the primary goal of the device.
- If your primary focus is permanent implantation (like a graft): The key is PTFE's biocompatibility, and for ePTFE, its unique ability to promote natural tissue integration.
- If your primary focus is instrumentation or devices (like a catheter): The crucial properties are low friction for smooth operation and chemical resistance for reliable sterilization.
- If your primary focus is regulatory compliance and safety: You must source certified, medical-grade PTFE that meets all relevant FDA and international standards.
Ultimately, PTFE's distinct combination of properties solves fundamental challenges in patient safety, device reliability, and surgical success.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key PTFE Properties Utilized | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Implants | Biocompatibility, Tissue Integration (ePTFE) | Vascular Grafts, Heart Patches, Ligament Replacements |
| Instruments & Devices | Low Friction, Chemical Inertness | Catheters, Syringe Plungers, Surgical Tool Seals |
| Lab & Testing Equipment | Chemical Resistance, Non-contaminating | Seals, Gaskets, Sample Transport Components |
Need High-Purity, Medical-Grade PTFE Components?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, and custom components for the medical, laboratory, and other specialized industries. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume production of biocompatible parts, our expertise ensures your devices meet the strictest safety and performance standards.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our custom PTFE fabrication can enhance your next medical innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















