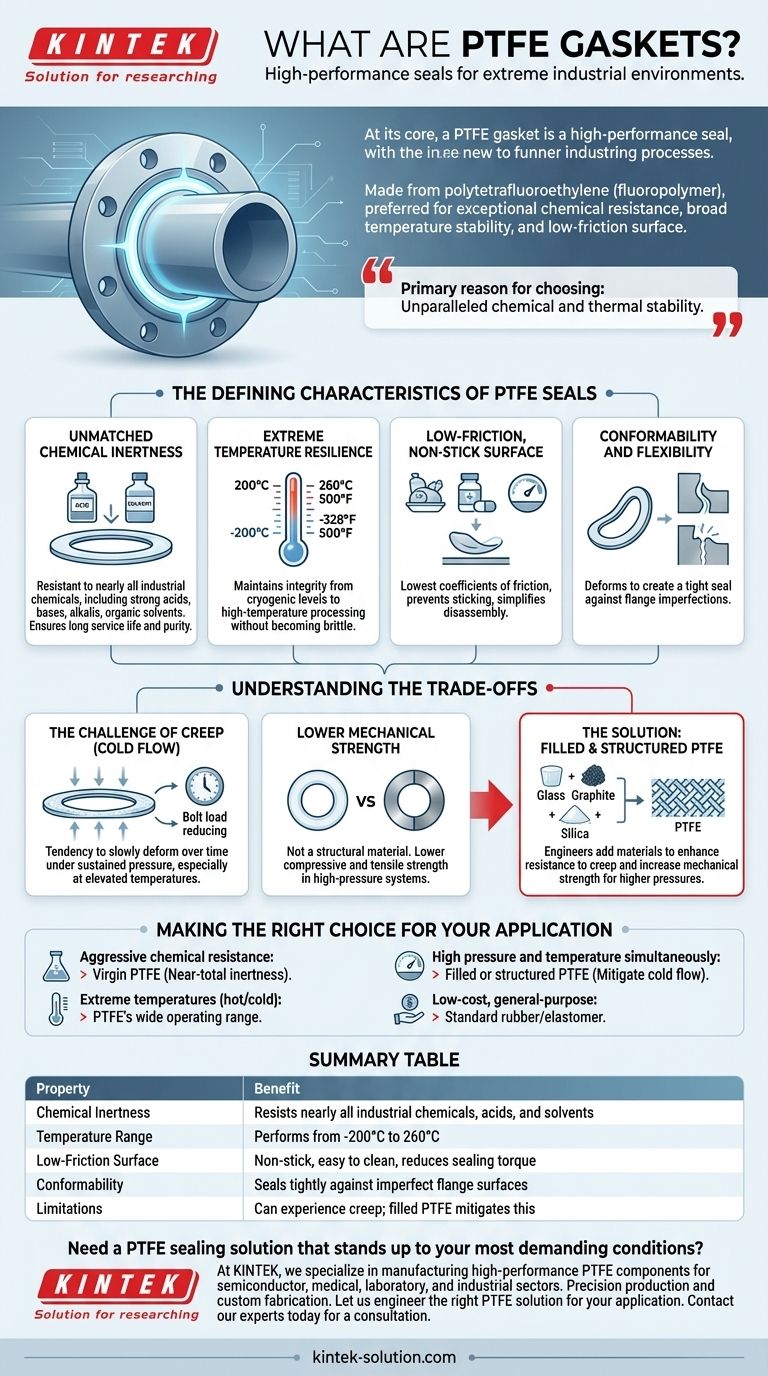
At its core, a PTFE gasket is a high-performance seal designed for extreme industrial environments. Made from a fluoropolymer called polytetrafluoroethylene, these gaskets are preferred in critical applications due to their exceptional chemical resistance, broad temperature stability, and low-friction surface, ensuring a reliable seal where other materials would quickly fail.
The primary reason for choosing a PTFE gasket is its unparalleled chemical and thermal stability. It provides a reliable, long-lasting seal in environments with aggressive chemicals or extreme temperatures that would compromise or destroy conventional sealing materials.

The Defining Characteristics of PTFE Seals
To understand why PTFE is a superior sealing material, we must look at its unique combination of properties. No single characteristic makes it effective; rather, it is the synergy of all of them.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
The standout feature of PTFE is its resistance to nearly all industrial chemicals, including strong acids, bases, alkalis, and organic solvents.
This chemical stability means the gasket will not degrade, swell, or leach contaminants when exposed to aggressive media, ensuring both a long service life and the purity of the process fluid.
Extreme Temperature Resilience
PTFE maintains its integrity and flexibility across an exceptionally wide temperature range, typically from cryogenic levels of -200°C up to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F).
This allows it to be used reliably in applications ranging from liquid nitrogen handling to high-temperature chemical processing without becoming brittle or losing its sealing capability.
Low-Friction, Non-Stick Surface
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, creating a non-adhesive surface.
This property prevents materials from sticking to the gasket, which is critical in food and pharmaceutical applications. It also reduces the torque needed to seal a flanged joint and simplifies disassembly for maintenance.
Conformability and Flexibility
Despite its resilience, PTFE is a relatively soft and flexible material.
This softness allows the gasket to deform and flow into minor imperfections on flange surfaces, creating an exceptionally tight and comprehensive seal against leaks.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE's properties are impressive, no material is perfect for every situation. Its primary strengths are also linked to its limitations, which must be considered for a successful application.
The Challenge of Creep (Cold Flow)
The very softness that allows PTFE to conform so well can also be a liability under certain conditions. Creep, or "cold flow," is the tendency of the material to slowly deform over time when subjected to sustained pressure, especially at elevated temperatures.
This can cause the gasket to thin out, reducing the bolt load on the flange and potentially leading to a leak.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Compared to metallic or harder composite gaskets, pure PTFE has lower compressive and tensile strength. It is not a structural material.
In high-pressure systems, this lower mechanical strength can make it more susceptible to being forced out of place or damaged.
The Solution: Filled and Structured PTFE
Engineers have overcome these mechanical limitations by creating filled PTFE gaskets. By adding materials like glass, graphite, or silica to the raw PTFE, manufacturers enhance its resistance to creep and increase its mechanical strength.
This creates a composite material that retains PTFE's chemical and thermal benefits while performing reliably under higher pressures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct gasket requires matching the material's properties to the demands of the operating environment.
- If your primary focus is aggressive chemical resistance: Virgin PTFE is almost always the superior choice due to its near-total chemical inertness.
- If your application involves extreme temperatures (hot or cold): PTFE's exceptionally wide operating range makes it a highly reliable sealing material.
- If you are dealing with high pressure and temperature simultaneously: A filled or structured PTFE gasket is the recommended solution to mitigate the risk of cold flow and ensure seal integrity.
- If your priority is a low-cost, general-purpose seal for non-critical media: A standard rubber or elastomer gasket may be a more cost-effective solution.
Understanding these core principles allows you to select a sealing solution based on proven performance, not just material type.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists nearly all industrial chemicals, acids, and solvents |
| Temperature Range | Performs from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F) |
| Low-Friction Surface | Non-stick, easy to clean, reduces sealing torque |
| Conformability | Seals tightly against imperfect flange surfaces |
| Limitations | Can experience creep under sustained pressure; filled PTFE mitigates this |
Need a PTFE sealing solution that stands up to your most demanding conditions?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—including seals, gaskets, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision production and custom fabrication capabilities ensure you get a perfect seal, whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders.
Let us engineer the right PTFE solution for your application. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F



















