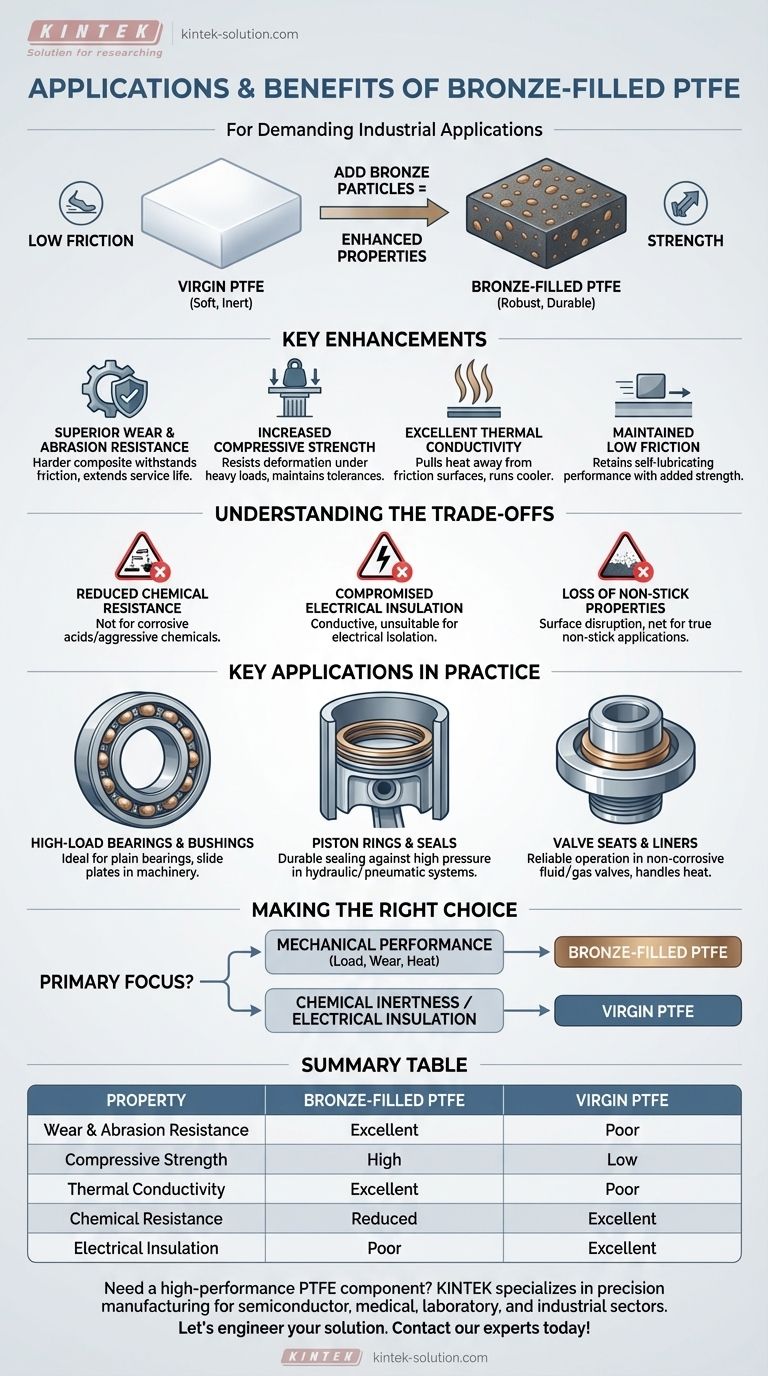
For demanding industrial applications, bronze-filled PTFE is the material of choice where high mechanical strength, wear resistance, and thermal conductivity are required. It excels in components like high-load bearings, piston rings, and seals, particularly in machinery and automotive systems where pure PTFE would fail under pressure and heat.
The core principle is simple: adding bronze to PTFE transforms a soft, chemically inert polymer into a robust, durable engineering material. This enhancement comes at the specific cost of chemical resistance and electrical insulation, a trade-off that defines its ideal applications.
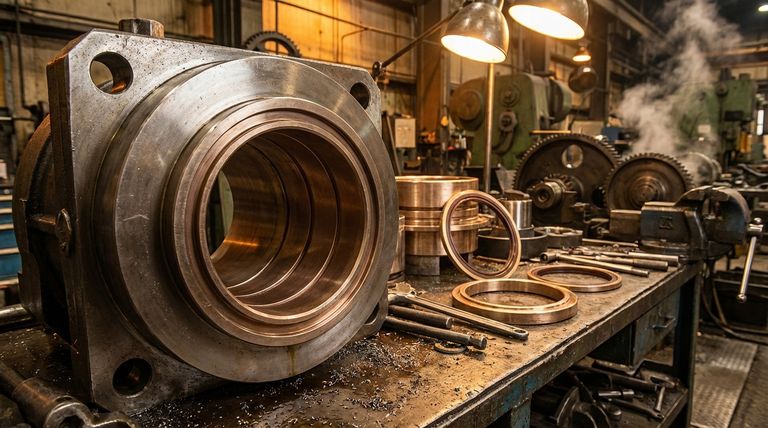

Why Add Bronze to PTFE? The Core Enhancements
Virgin PTFE is known for its low friction and chemical inertness, but it suffers from low mechanical strength and "cold flow," where it deforms under sustained pressure. Adding bronze particles directly addresses these weaknesses.
Superior Wear and Abrasion Resistance
Bronze particles act as a reinforcing agent within the PTFE matrix.
This creates a much harder composite material that can withstand significant friction and abrasion, dramatically extending the service life of moving parts.
Increased Compressive Strength and Hardness
The inclusion of bronze gives the material the rigidity it needs to resist deformation under heavy loads.
This high compressive strength is critical for components like bearings and bushings that must maintain their shape and tolerances to function correctly.
Excellent Thermal Conductivity
Pure PTFE is a thermal insulator, meaning it traps heat. In high-friction applications, this can lead to overheating and premature failure.
Bronze is an excellent thermal conductor. It pulls heat away from friction surfaces, allowing components to run cooler and at higher speeds and loads.
Maintained Low Friction
Despite the addition of a filler, bronze-filled PTFE retains a very low coefficient of friction.
This allows it to deliver the smooth, self-lubricating performance PTFE is known for while providing the mechanical strength it naturally lacks.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The benefits of bronze filler are significant, but they come with compromises. Understanding these limitations is crucial for proper material selection.
Reduced Chemical Resistance
The primary drawback is a loss of chemical inertness. Bronze is a metal alloy that will react with corrosive acids and other aggressive chemicals that pure PTFE would easily resist.
Therefore, bronze-filled PTFE is unsuitable for applications involving highly corrosive media.
Compromised Electrical Insulation
While pure PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator, bronze is a conductor.
This makes bronze-filled PTFE unsuitable for any application that requires electrical isolation.
Loss of Non-Stick Properties
The bronze particles disrupt the famously smooth, non-stick surface of virgin PTFE.
While still very low-friction, it is not the right choice for applications where a true non-stick or release surface is the primary requirement, such as in cookware or certain food processing equipment.
Key Applications in Practice
The unique property profile of bronze-filled PTFE makes it a premier choice for specific, demanding mechanical roles.
High-Load Bearings and Bushings
This is a primary application. The material's ability to handle heavy loads, dissipate heat, and operate with low friction makes it ideal for plain bearings, slide plates, and bushings in industrial machinery.
Piston Rings and Seals
In hydraulic and pneumatic systems, as well as compressors and engines, its superior wear resistance allows for a durable, long-lasting seal against high pressures.
Valve Seats and Liners
For industrial valves handling non-corrosive fluids or gases, bronze-filled PTFE provides the durability and sealing capability needed for reliable, long-term operation, especially where heat is a factor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires aligning its properties with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is mechanical performance under load: Bronze-filled PTFE is an excellent choice for its combination of high compressive strength, wear resistance, and thermal conductivity.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical inertness: You must use virgin PTFE or a PTFE filled with a more inert material like glass or carbon.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation: Avoid bronze-filled PTFE entirely and specify virgin PTFE for its exceptional dielectric properties.
By understanding these core trade-offs, you can confidently specify bronze-filled PTFE for your most demanding mechanical challenges.
Summary Table:
| Property | Bronze-Filled PTFE | Virgin PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Wear & Abrasion Resistance | Excellent | Poor |
| Compressive Strength | High | Low |
| Thermal Conductivity | Excellent (Heat Dissipation) | Poor (Thermal Insulator) |
| Chemical Resistance | Reduced (Unsuitable for corrosives) | Excellent |
| Electrical Insulation | Poor (Conductive) | Excellent |
| Primary Application | High-load mechanical parts (bearings, seals) | Chemical, electrical, non-stick applications |
Need a high-performance PTFE component that can handle extreme pressure and wear?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision manufacturing of bronze-filled PTFE components like seals, liners, and bearings for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our custom fabrication services, from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensure you get a part that perfectly meets your application's demands for strength, durability, and thermal management.
Let's engineer your solution. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















