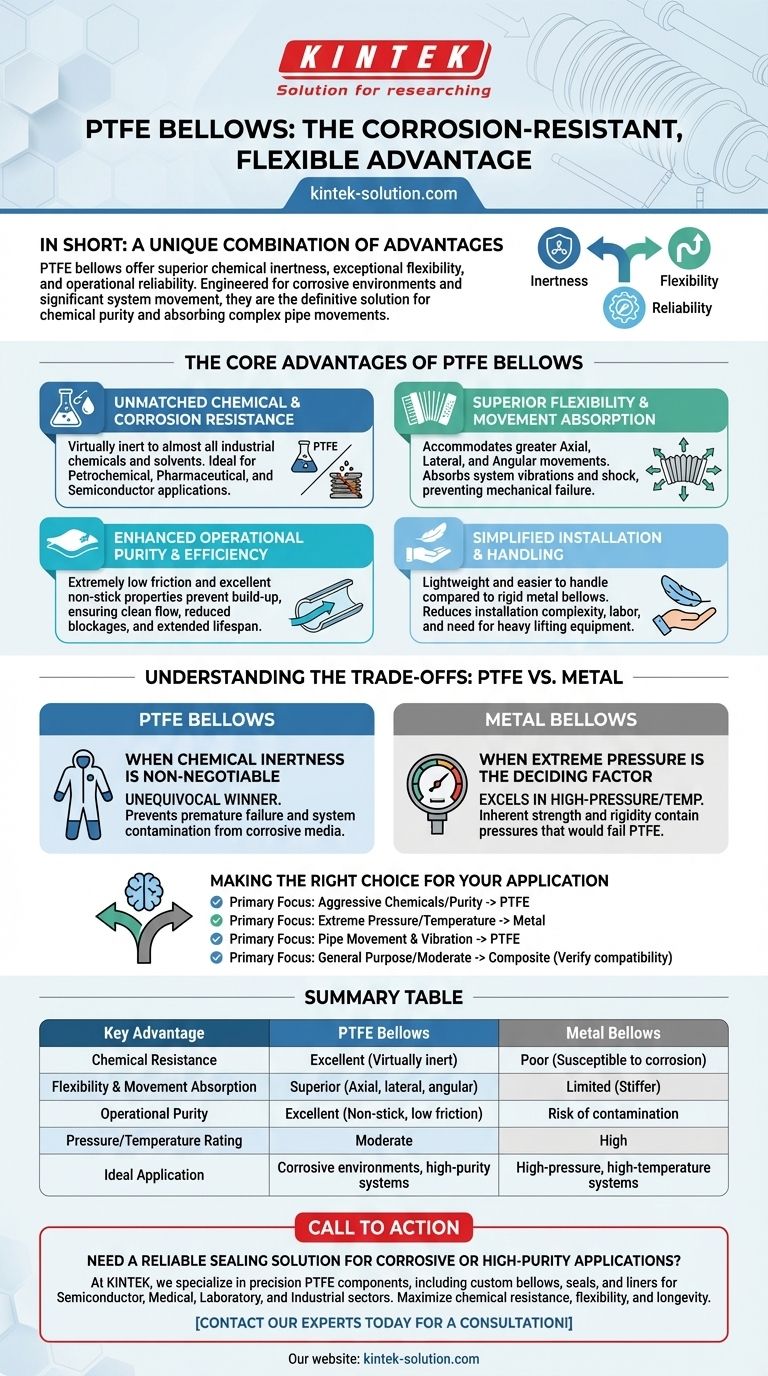
In short, PTFE bellows offer a unique combination of advantages centered on superior chemical inertness, exceptional flexibility, and operational reliability. Unlike metal or composite alternatives, they are specifically engineered to perform in corrosive environments while accommodating significant system movement, making them a first-choice material for specialized applications.
The decision between bellow types is a trade-off between chemical compatibility and mechanical strength. While metal bellows are chosen for extreme pressure and temperature, PTFE is the definitive solution for systems that demand chemical purity, corrosion resistance, and the ability to absorb complex pipe movements.
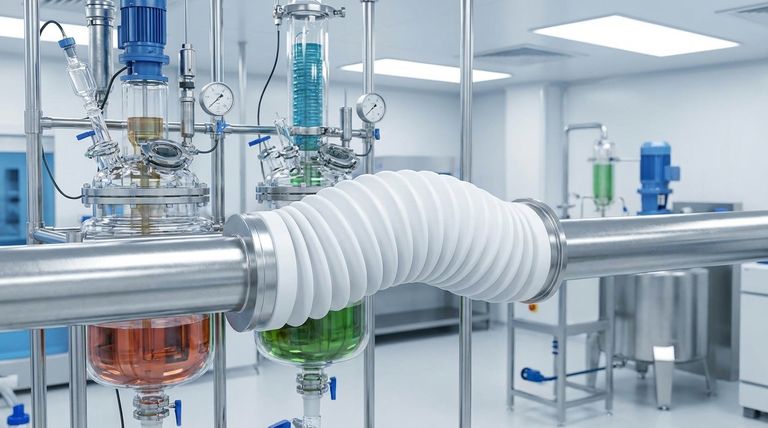

The Core Advantages of PTFE Bellows
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) possesses inherent material properties that translate directly into significant operational advantages over other materials. These benefits address common failure points in demanding industrial systems.
Unmatched Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals and solvents. This makes it an essential choice for aggressive applications in petrochemical pipelines, pharmaceutical processing, and semiconductor manufacturing.
Where metal bellows would corrode and fail, PTFE provides a long, reliable service life, protecting both the system and the product from contamination.
Superior Flexibility and Movement Absorption
PTFE expansion bellows are significantly more flexible than their metal counterparts. They are designed to accommodate greater axial (compression/extension), lateral (offset), and angular (bending) movements.
This superior flexibility allows them to absorb system vibrations and shock, preventing stress from being transferred to pipes, pumps, or vessels and reducing the risk of mechanical failure.
Enhanced Operational Purity and Efficiency
The material has an extremely low coefficient of friction and excellent non-stick properties. This prevents deposits, sludge, or other media from building up on the internal surfaces.
This ensures a clean, efficient flow, reduces the risk of blockages, and minimizes wear, which extends the product's lifespan and lowers maintenance costs.
Simplified Installation and Handling
Compared to heavy and rigid metal bellows, PTFE bellows are lightweight and easier to handle.
This characteristic simplifies the installation process, often reducing the need for specialized lifting equipment and decreasing labor costs.
Understanding the Trade-offs: PTFE vs. Metal
Choosing the correct bellow material requires a clear understanding of the primary operational challenge you are trying to solve. The comparison between PTFE and metal highlights this clearly.
When Chemical Inertness is Non-Negotiable
If the primary challenge is handling corrosive media, PTFE is the unequivocal winner. Metal bellows are susceptible to corrosion from a wide range of chemicals, leading to premature failure and potential system contamination.
When Extreme Pressure is the Deciding Factor
Metal bellows excel in high-pressure and high-temperature environments where PTFE may not be suitable. The inherent strength and rigidity of metal allow it to contain pressures that would cause a PTFE bellow to fail.
The Flexibility and Vibration Dilemma
For systems with significant thermal expansion, pipe misalignment, or dynamic vibration, PTFE's flexibility is a critical advantage. Stiffer metal bellows are less tolerant of these movements and can transfer damaging stress to the surrounding system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the most critical demand of your specific system.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals or preventing contamination: Choose PTFE for its unmatched chemical inertness and non-stick surfaces.
- If your primary focus is containing extreme pressure or temperature: Metal bellows provide the necessary mechanical strength and rigidity.
- If your primary focus is accommodating significant pipe movement and vibration: PTFE's superior flexibility offers a more reliable and durable solution.
- If your primary focus is a general-purpose application with moderate demands: Composite bellows can offer a balance, but always verify their chemical compatibility against PTFE's near-universal resistance.
By prioritizing your system's most critical need, you can confidently select the material that ensures long-term safety, reliability, and efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | PTFE Bellows | Metal Bellows |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (Virtually inert) | Poor (Susceptible to corrosion) |
| Flexibility & Movement Absorption | Superior (Axial, lateral, angular) | Limited (Stiffer) |
| Operational Purity | Excellent (Non-stick, low friction) | Risk of contamination |
| Pressure/Temperature Rating | Moderate | High |
| Ideal Application | Corrosive environments, high-purity systems | High-pressure, high-temperature systems |
Need a reliable sealing solution for corrosive or high-purity applications?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom bellows, seals, and liners, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your systems achieve maximum chemical resistance, flexibility, and longevity.
Let us help you select or fabricate the perfect PTFE bellow for your specific needs—from prototype to high-volume production. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining



















