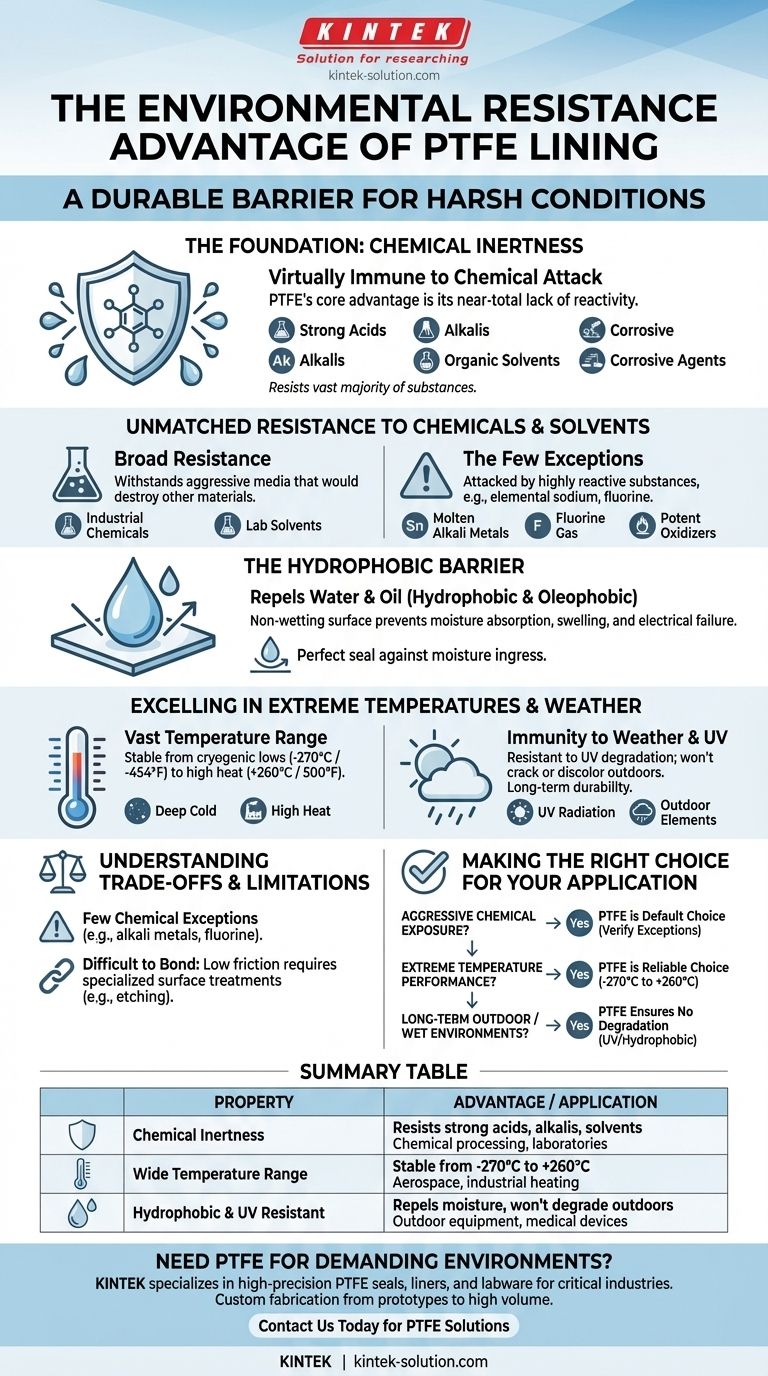
In short, a PTFE lining provides exceptional environmental resistance by being virtually immune to chemical attack, stable across extreme temperatures, and impervious to moisture and UV radiation. This unique combination of properties makes it one of the most durable and reliable barrier materials for harsh service conditions.
The true advantage of PTFE is not just a list of resistances, but its fundamental chemical inertness. This property is the source of its ability to withstand corrosive chemicals, extreme weather, and moisture, making it a reliable barrier where most other materials would degrade and fail.

The Foundation of PTFE's Resilience: Chemical Inertness
The core of PTFE's environmental resistance is its near-total lack of chemical reactivity. This inert nature is the primary reason it is specified for the most demanding applications.
Unmatched Resistance to Chemicals and Solvents
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is chemically inert, meaning it does not react with the vast majority of substances it contacts.
This makes it highly resistant to aggressive media that would destroy other materials, including strong acids, alkalis, corrosive agents, and organic solvents like acetone and chloroform.
The Hydrophobic Barrier
PTFE's surface is both hydrophobic (repels water) and oleophobic (repels oil). This is the same property that gives it its famous non-stick characteristic.
This non-wetting surface prevents moisture absorption, a common cause of material degradation, swelling, or electrical failure in other polymers. It acts as a perfect seal against moisture ingress.
Excelling in Extreme Temperature and Weather Conditions
Beyond chemical exposure, PTFE withstands extreme physical environments, from the deep cold of space to the high heat of industrial processes.
A Vast Operational Temperature Range
PTFE maintains its structural integrity and protective properties across an exceptionally wide temperature spectrum.
It remains stable and functional from cryogenic lows around -270°C (-454°F) up to continuous high-heat conditions of +260°C (500°F).
Immunity to Weather and UV Degradation
Unlike many plastics that become brittle and fail when exposed to sunlight, PTFE is highly resistant to degradation from ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
This immunity, combined with its inherent moisture resistance, gives it outstanding durability for long-term outdoor applications where it will not crack, discolor, or lose its properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. While PTFE's environmental resistance is elite, its unique properties come with specific constraints that are critical to understand.
The Few Chemical Exceptions
While its chemical resistance is remarkably broad, PTFE is not completely invincible.
It can be attacked by a small group of highly reactive substances, most notably liquid or dissolved alkali metals (e.g., elemental sodium), fluorine gas, and a few other extremely potent oxidizers.
Physical and Mechanical Constraints
PTFE's extremely low friction and non-stick surface, while advantages in many contexts, make it very difficult to bond to other materials using conventional adhesives.
Achieving a strong bond often requires specialized and costly surface treatments like chemical etching, which must be factored into the design and manufacturing process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use this guidance to determine if PTFE's environmental resistance profile meets the specific needs of your project.
- If your primary focus is aggressive chemical exposure: PTFE is the default choice for containing nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents, but always verify your specific medium against its few known exceptions.
- If your primary focus is performance across extreme temperatures: PTFE's stability from cryogenic cold to high heat makes it an exceptionally reliable choice for aerospace, industrial, and scientific equipment.
- If your primary focus is long-term outdoor or wet environments: The combination of hydrophobicity and UV resistance ensures the lining will not degrade, absorb water, or become brittle over time.
By understanding both its profound strengths and specific limitations, you can confidently leverage PTFE to protect critical components in the most demanding environments.
Summary Table:
| Property | Advantage | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists strong acids, alkalis, and solvents | Chemical processing, laboratories |
| Wide Temperature Range | Stable from -270°C to +260°C | Aerospace, industrial heating |
| Hydrophobic & UV Resistant | Repels moisture, won't degrade outdoors | Outdoor equipment, medical devices |
Need a PTFE component that can withstand your most demanding environment?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We combine precision production with custom fabrication, from prototypes to high-volume orders, to deliver the environmental resistance your application requires.
Contact us today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can protect your critical systems.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Magnetic Stirring Bar
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range that PTFE can withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Demanding Applications
- What is the hardness range of PTFE on the Shore D scale? Leveraging Its Softness for Superior Performance
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation
- What are some applications of CNC machined PTFE parts? Critical Components for Medical, Electrical & Food Industries
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications



















