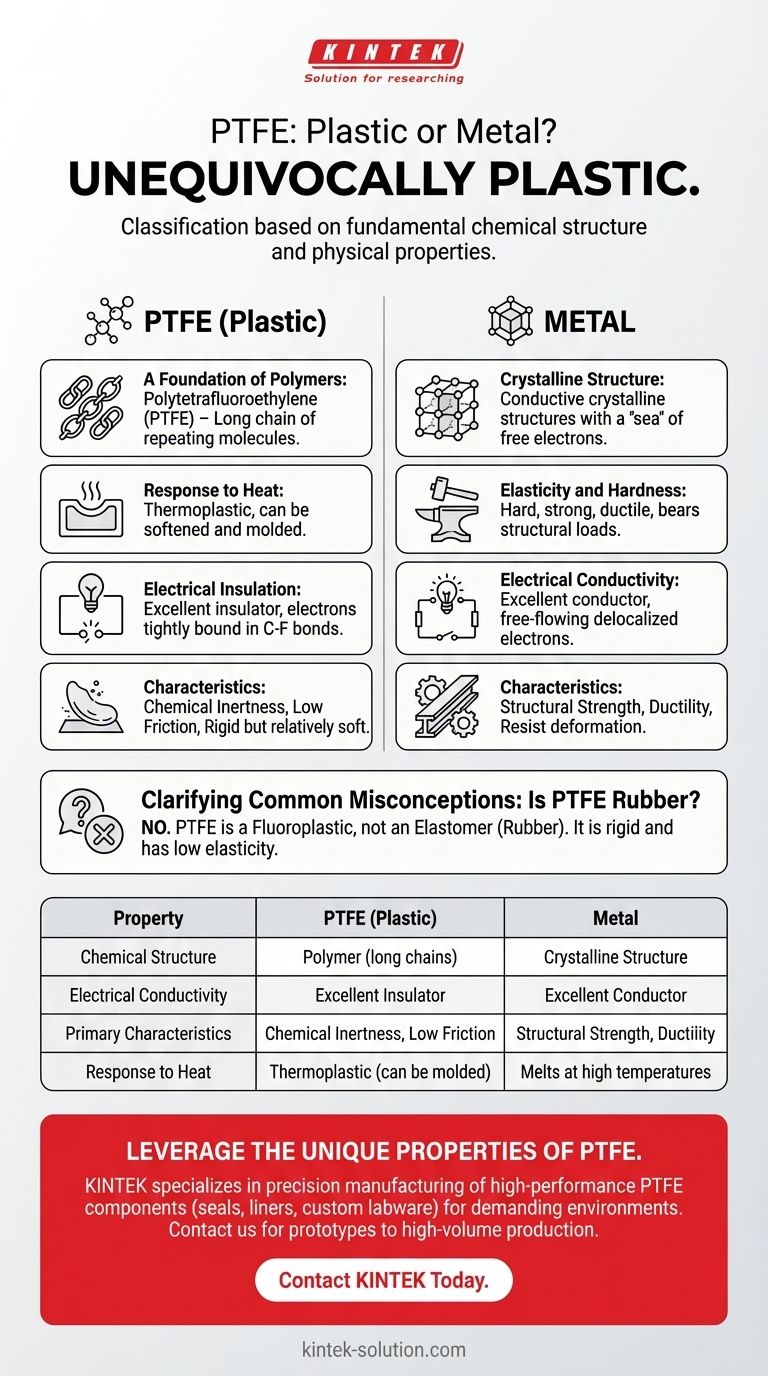
To be clear, PTFE is unequivocally a plastic. Its classification is not a matter of debate but is based on its fundamental chemical structure and physical properties. While it offers high performance often associated with specialized materials, its characteristics firmly place it within the polymer family, entirely distinct from metals.
The core distinction lies in its molecular makeup and behavior. PTFE is a polymer—a long chain of repeating molecules—which gives it the properties of a plastic: it is an electrical insulator and can be molded, unlike metals, which are conductive crystalline structures.

The Defining Characteristics of a Plastic
To understand why PTFE is a plastic, we must first define what a plastic is. The classification comes down to a material's chemical foundation and its response to energy.
A Foundation of Polymers
At its core, a plastic is a polymer. This means it's made of very large molecules (macromolecules) composed of repeating subunits, known as monomers.
The very name PTFE stands for Polytetrafluoroethylene, with the "Poly" prefix explicitly identifying it as a polymer and, therefore, a type of plastic.
Response to Heat and Force
A defining feature of plastics is their ability to be molded or shaped, a property known as plasticity. PTFE, like other thermoplastics, can be softened with heat and formed into desired shapes.
Metals can also be shaped, but the underlying mechanism is different, involving the deformation of a crystalline lattice rather than the movement of tangled polymer chains.
Electrical and Thermal Insulation
Plastics are generally excellent electrical and thermal insulators. They do not have the free-flowing electrons that allow electricity to pass through them easily.
PTFE is prized for its exceptional insulating properties, making it a stark contrast to metals, which are defined by their high conductivity.
Why PTFE is Fundamentally Different from Metal
The properties that make metals useful are almost the exact opposite of the properties that make PTFE valuable. Their atomic and molecular structures dictate these different behaviors.
Electrical Conductivity
Metals possess a "sea" of delocalized electrons that move freely, making them excellent conductors of electricity.
PTFE's electrons are tightly bound within its strong carbon-fluorine bonds, making it one of the best electrical insulators known.
Elasticity and Hardness
Metals are typically hard, strong, and ductile. They resist deformation and can bear significant structural loads.
While PTFE is a rigid plastic, it is relatively soft compared to metals and is not used for primary load-bearing applications. Its value comes from other properties, like its low friction.
Clarifying Common Misconceptions
PTFE's high performance can sometimes lead to confusion, placing it mentally alongside other robust industrial materials. It is crucial to distinguish it from other categories as well.
Is PTFE a Type of Rubber?
No, PTFE is not rubber. Rubber is a class of polymers known as elastomers, which are defined by their high elasticity—the ability to be stretched and return to their original shape.
PTFE is a fluoroplastic. It is rigid and has very low elasticity, meaning it will deform permanently if stretched beyond a minimal point.
The Source of the Confusion
Confusion often arises because PTFE is a high-performance material used in demanding applications (aerospace, chemical processing) where specialty metal alloys are also common.
However, its role in these applications is based on its plastic properties: chemical inertness, high-temperature resistance, and an extremely low coefficient of friction (slipperiness).
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding this classification is essential for proper material selection. Using PTFE where a metal is needed (or vice versa) will lead to immediate failure.
- If your primary focus is electrical conductivity or structural strength: You must choose a metal, as PTFE is an insulator with limited load-bearing capacity.
- If your primary focus is low friction, chemical resistance, or electrical insulation: PTFE is a superior choice, far outperforming metals in these specific domains.
- If your primary focus is elasticity and resilience: You need to look at elastomers (rubbers), as neither PTFE nor metals fulfill this role.
Ultimately, classifying a material correctly is the first step in leveraging its unique strengths for your specific goal.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE (Plastic) | Metal |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Polymer (long chains) | Crystalline Structure |
| Electrical Conductivity | Excellent Insulator | Excellent Conductor |
| Primary Characteristics | Chemical Inertness, Low Friction | Structural Strength, Ductility |
| Response to Heat | Thermoplastic (can be molded) | Melts at high temperatures |
Leverage the unique properties of PTFE for your application.
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume production, our expertise ensures you get the right plastic solution for demanding environments.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our custom PTFE fabrication can benefit your project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments



















