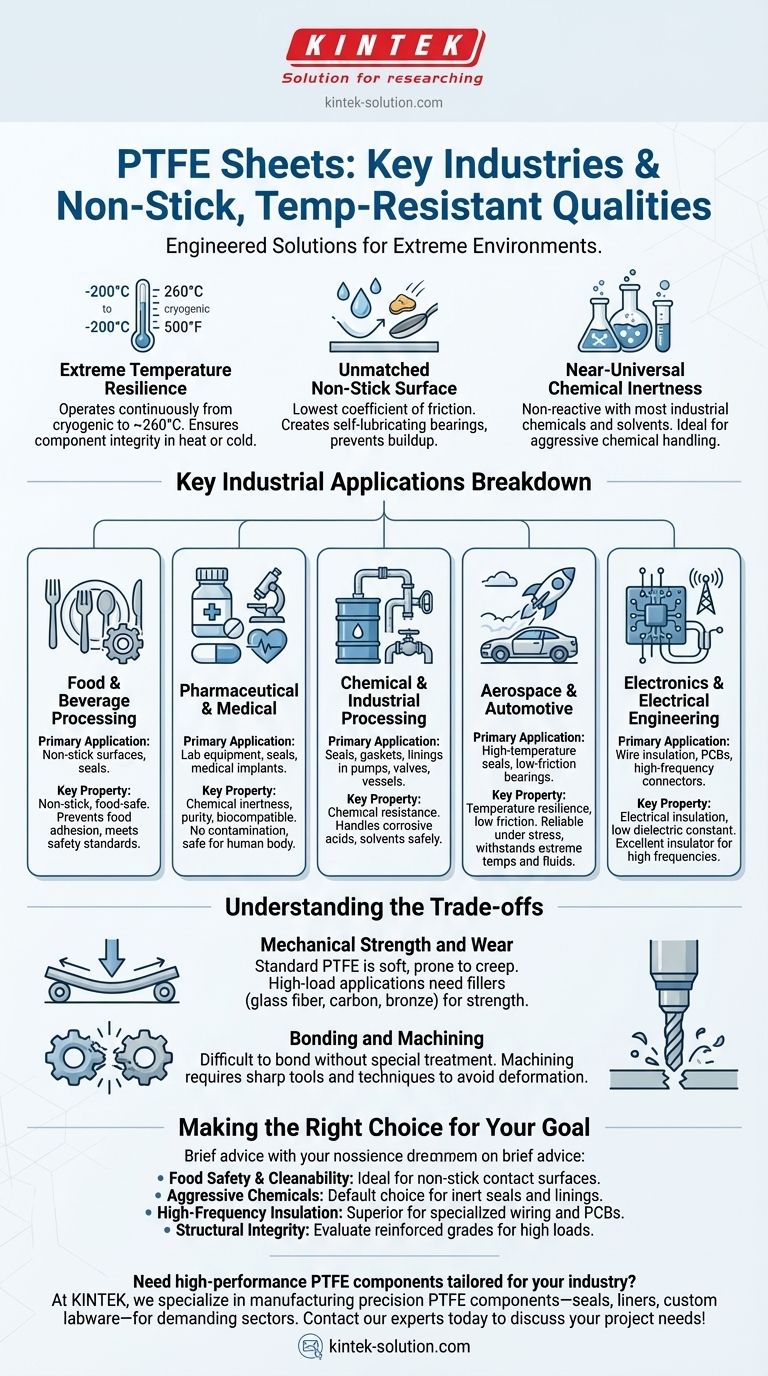
To be direct, PTFE sheets are most commonly used in the food and beverage, pharmaceutical, chemical processing, aerospace, and electronics industries. Their unique combination of non-stick, high-temperature resistance, and chemical inertness makes them indispensable for applications where other materials would fail.
PTFE is not just another plastic; it is an engineered solution for extreme environments. Its value comes from a rare trifecta of properties—thermal stability, chemical immunity, and an exceptionally low-friction surface—that solves critical challenges across multiple high-stakes industries.

The Core Properties Driving Adoption
Before diving into specific industries, it's essential to understand the fundamental properties that make PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) so valuable. These characteristics are the root cause of its widespread adoption.
Extreme Temperature Resilience
PTFE maintains its integrity and performance across a remarkably wide temperature range. It can operate continuously in environments from cryogenic lows up to approximately 260°C (500°F).
This thermal stability ensures that components like seals and bearings do not degrade or become brittle when exposed to processing heat or extreme cold.
Unmatched Non-Stick Surface
Famously known for its use in non-stick cookware, PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material.
This "slipperiness" is critical in industrial settings for creating self-lubricating slide bearings, preventing material buildup on conveyor guides, and ensuring clean, efficient operation in food or pharmaceutical processing.
Near-Universal Chemical Inertness
PTFE is chemically inert, meaning it does not react with the vast majority of industrial chemicals and solvents, even at high temperatures.
Its strong internal polymer bonds make it the default choice for seals, gaskets, and linings in equipment that handles highly corrosive or aggressive chemicals. The only common exceptions are molten alkali metals and some fluorine compounds.
Key Industrial Applications Breakdown
The core properties of PTFE translate directly into specific, problem-solving applications within various sectors.
Food & Beverage Processing
In this industry, hygiene and efficiency are paramount. PTFE's non-stick surface prevents food products from adhering to machinery like rollers, scrapers, and guides, reducing waste and cleaning time.
Because it is physiologically inert and meets stringent food safety standards, it is trusted for components that come into direct contact with consumable products.
Pharmaceutical & Medical
Purity is the primary concern here. PTFE's chemical inertness ensures that it will not react with or contaminate sensitive pharmaceutical compounds during manufacturing.
It is also biocompatible, meaning it is non-toxic and can be used within the human body, making it suitable for certain medical implants, equipment, and laboratory instruments.
Chemical & Industrial Processing
This is where PTFE's chemical resistance shines. It is used extensively for seals, gaskets, and linings in pumps, valves, and vessels that contain highly aggressive acids, solvents, and other corrosive substances.
Without PTFE, manufacturing and transporting these chemicals safely and reliably would be significantly more difficult and expensive.
Aerospace & Automotive
In these high-performance fields, reliability under stress is key. PTFE is used for high-temperature seals, low-friction washers, and slide bearings that must operate without conventional lubrication.
Its ability to withstand temperature extremes and resist degradation from fuels and hydraulic fluids makes it a critical material for ensuring safety and performance.
Electronics & Electrical Engineering
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator with a very low dielectric constant. This means it does not store electrical energy well, making it ideal for high-frequency applications.
It is used as insulation for high-performance wiring and cables and as a substrate for printed circuit boards (PCBs) used in microwave and radio-frequency technologies.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, PTFE is not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires understanding its limitations.
Mechanical Strength and Wear
Standard PTFE is a relatively soft material. It can be prone to "creep," or deforming slowly over time when placed under a constant mechanical load.
For high-load structural applications, it is often unsuitable unless reinforced with fillers like glass fiber, carbon, or bronze to improve its compressive strength and wear resistance.
Bonding and Machining
The same non-stick property that makes PTFE so valuable also makes it extremely difficult to bond to other materials using conventional adhesives. Special surface treatments are required.
While it can be machined, its softness requires sharp tools and specific techniques to achieve clean cuts and tight tolerances without causing the material to deform.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge effectively, align the material's strengths with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is food safety and cleanability: PTFE is an ideal choice for non-stick contact surfaces and chemically inert seals that will not contaminate your product.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals: Its near-universal chemical inertness makes it the default choice for seals, gaskets, and linings in extreme environments.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical insulation: PTFE's exceptional dielectric properties make it a superior material for specialized wiring, connectors, and circuit boards.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity under high load: You should carefully evaluate if standard PTFE is sufficient or if a filled, reinforced grade is necessary to prevent deformation.
Ultimately, PTFE is a specialized material designed to solve engineering problems that commodity plastics simply cannot handle.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Application | Key PTFE Property Utilized |
|---|---|---|
| Food & Beverage | Non-stick surfaces, seals | Non-stick, food-safe |
| Pharmaceutical | Lab equipment, seals | Chemical inertness, purity |
| Chemical Processing | Seals, gaskets, linings | Chemical resistance |
| Aerospace | High-temperature seals, bearings | Temperature resilience |
| Electronics | Wire insulation, PCBs | Electrical insulation |
Need high-performance PTFE components tailored for your industry?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for demanding sectors like semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, our custom fabrication ensures your PTFE parts meet exact specifications for non-stick performance, chemical resistance, and thermal stability.
Let us help you solve your most challenging material requirements: Contact our experts today to discuss your project needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application



















