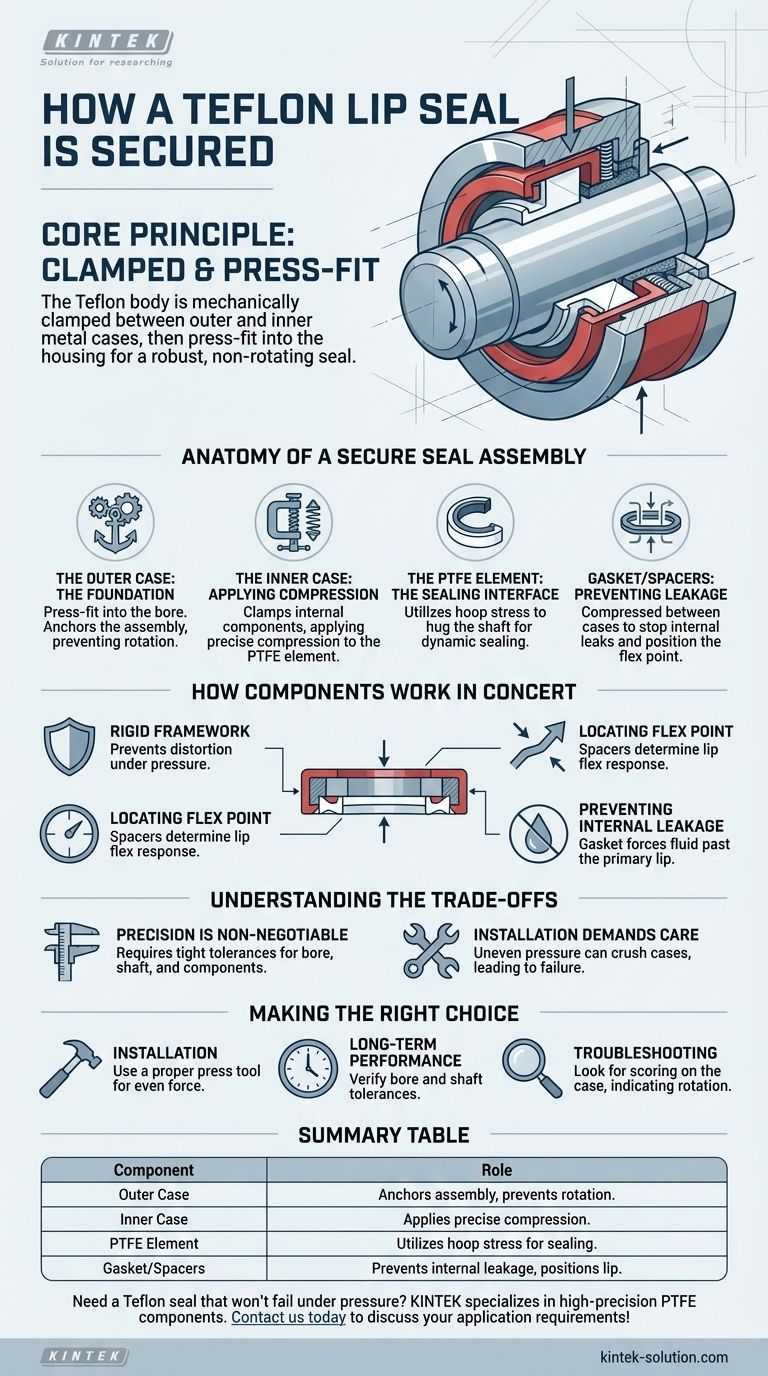
In most designs, the body of a Teflon (PTFE) lip seal is secured by being mechanically clamped between an outer and an inner metal case. This entire assembly is then press-fit into the equipment's housing or bore, creating a robust, non-rotating seal that maintains consistent pressure on the sealing element.
The core principle is not just to hold the seal in place, but to create a rigid housing that prevents rotation and precisely compresses the internal components, ensuring the PTFE lip maintains its critical sealing force against the shaft.

The Anatomy of a Secure Seal Assembly
Understanding how a Teflon lip seal is secured requires looking at the individual components that make up its housing. Each part has a distinct role in creating a stable and effective seal.
The Outer Case: The Foundation
The outer case is the seal's primary structural component. It is designed to be press-fit directly into the equipment's bore.
This press-fit serves two critical functions: it creates a static seal against the bore to prevent external leakage and, most importantly, it anchors the entire assembly, preventing it from rotating with the shaft.
The Inner Case: Applying Compression
The inner case works in tandem with the outer case. Its primary job is to clamp down on the internal components, most notably the PTFE sealing element itself.
This compression is vital for maintaining the seal's designed geometry and ensuring the forces are correctly transmitted to the lip.
The PTFE Element: The Sealing Interface
While the metal cases provide the structure, the PTFE element is the part that does the dynamic sealing. It is mechanically formed to be slightly smaller than the shaft.
The securement provided by the cases allows the element to utilize its natural hoop stress, hugging the shaft to create a tight, low-friction seal.
How These Components Work in Concert
The effectiveness of the seal comes from the precise interaction of these parts. The design is an engineered system meant to overcome the challenges of high-speed and high-pressure applications.
Establishing a Rigid Framework
By clamping the softer PTFE element between two rigid metal cases, the design ensures the seal does not distort under pressure or due to temperature changes. This stability is key to its long-term performance.
Locating the Flex Point
Components like internal spacers are also secured by this clamping force. These spacers are critical for positioning the "bend point" of the PTFE element, which dictates how the lip flexes and responds to shaft movement and pressure.
Preventing Internal Leakage
In many designs, a gasket is also compressed between the cases. This gasket prevents any fluid from leaking through the seal body itself, forcing it to follow the intended path past the primary sealing lip. It also helps accommodate for minor manufacturing tolerances.
Understanding the Trade-offs
This robust, multi-component design offers superior performance, but it also introduces specific considerations that are important to understand.
Precision is Non-Negotiable
The effectiveness of the press-fit and clamping mechanism depends entirely on holding tight tolerances for the bore, the shaft, and the seal components themselves. An out-of-spec bore can lead to a loose fit (causing rotation and leakage) or an overly tight fit (damaging the seal during installation).
Installation Demands Care
Unlike a simple elastomeric o-ring, a cased Teflon seal must be installed carefully with proper tools. Applying uneven pressure can crush the cases, altering the internal compression and leading to premature failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding the seal's construction directly informs its proper use and installation.
- If your primary focus is reliable installation: Always use a proper press tool that applies even force to the outer case of the seal to ensure it seats squarely in the bore without damage.
- If your primary focus is long-term performance: Verify that your bore and shaft dimensions are strictly within the tolerances specified by the seal manufacturer, as this is critical for proper securement.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting a failure: Look for scoring on the outside of the seal case, which indicates it was spinning in the bore—a clear sign of an improper press-fit.
Ultimately, the sophisticated method of clamping a Teflon element within metal cases is what allows it to perform reliably in demanding conditions where simpler seals would fail.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in Securing the Seal |
|---|---|
| Outer Case | Press-fit into the bore to anchor the assembly and prevent rotation. |
| Inner Case | Clamps down on internal components to apply precise compression. |
| PTFE Element | Held in place by the cases to utilize hoop stress for dynamic sealing. |
| Gasket/Spacers | Compressed between cases to prevent internal leakage and position the lip. |
Need a Teflon seal that won't fail under pressure? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom lip seals, for the semiconductor, medical, and laboratory industries. Our expertise in custom fabrication ensures your seals are perfectly secured for maximum performance and longevity. Contact us today to discuss your application requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Crucibles for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















