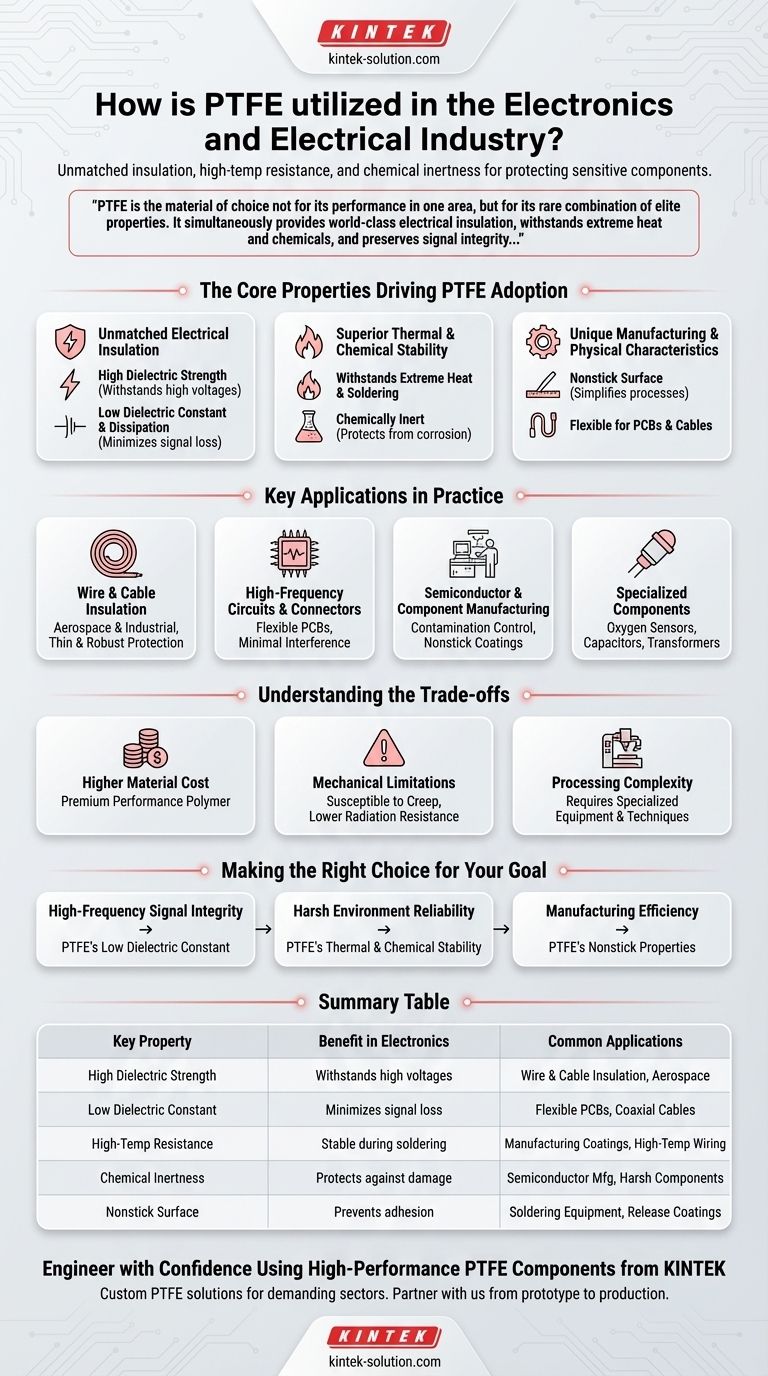
In the electronics and electrical industry, PTFE is primarily used for high-performance wire and cable insulation, connectors, flexible printed circuit boards, and as a nonstick coating in manufacturing processes. Its value stems from a unique combination of exceptional electrical insulating properties, high-temperature resistance, and chemical inertness, making it indispensable for protecting sensitive components.
PTFE is the material of choice not for its performance in one area, but for its rare combination of elite properties. It simultaneously provides world-class electrical insulation, withstands extreme heat and chemicals, and preserves signal integrity in high-frequency applications where other materials would fail.

The Core Properties Driving PTFE Adoption
The widespread use of PTFE in electronics isn't accidental. It is a direct result of several key material properties that solve critical engineering challenges.
Unmatched Electrical Insulation
PTFE is one of the best electrical insulators known. This performance is defined by several distinct characteristics.
Its high dielectric strength allows it to withstand very high voltages without breaking down, making it a reliable insulator for everything from micro-motors to aerospace components.
It also possesses a low dielectric constant and a low dissipation factor. This means it minimizes signal energy loss, which is absolutely critical for maintaining signal integrity in high-frequency applications like flexible printed circuits and coaxial cables.
Superior Thermal and Chemical Stability
Electronics often operate in or are manufactured under harsh conditions. PTFE provides a robust shield against these threats.
It can withstand the high temperatures required for processes like soldering and heat sealing without degrading. This thermal stability also ensures reliable performance in high-temperature operating environments.
Furthermore, PTFE is almost completely chemically inert. This protects delicate wires and semiconductor parts from moisture, corrosion, and other chemical damage during both manufacturing and a product's operational life.
Unique Manufacturing and Physical Characteristics
Beyond its core protective qualities, PTFE's physical nature makes it invaluable during the assembly process.
Its famous nonstick surface prevents solder and other materials from adhering to manufacturing equipment, simplifying processes and protecting components.
Its flexibility also allows it to be used in applications like flexible printed circuit boards and cable jackets that must bend and move without compromising electrical performance.
Key Applications in Practice
These fundamental properties translate directly into specific, high-value applications across the industry.
Wire and Cable Insulation
PTFE is the gold standard for insulating wires and cables in demanding sectors like aerospace and industrial controls. It provides a thin, lightweight, yet incredibly robust layer of protection against high voltages, extreme temperatures, and chemical exposure.
High-Frequency Circuits and Connectors
For high-frequency systems, preserving the purity of a signal is paramount. PTFE is used in flexible printed circuit boards and high-performance connectors specifically because its low dielectric constant ensures minimal interference and signal loss.
Semiconductor and Component Manufacturing
In the manufacturing of sensitive electronics, contamination is a major concern. PTFE's non-reactive nature protects delicate semiconductor parts, while its nonstick properties are used to coat equipment for soldering and component assembly.
Specialized Components
PTFE's unique attributes extend to niche applications. Its selective permeability is leveraged in specialized oxygen sensors, while its electrical properties make it suitable for parts within capacitors, transformers, microphones, and loudspeakers.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its performance is exceptional, PTFE is not the default choice for every application. Its selection requires a clear understanding of its limitations.
Higher Material Cost
PTFE is a premium performance polymer. It is significantly more expensive than common insulators like PVC or polyethylene, making it best suited for applications where its specific properties are a strict requirement, not a preference.
Mechanical Limitations
PTFE is a relatively soft material and can be susceptible to "creep" or cold flow, meaning it can deform over time when under a sustained mechanical load. It also has lower resistance to high-energy radiation compared to some other polymers.
Processing Complexity
Compared to common thermoplastics, PTFE can be more difficult to process. Its high melting point and viscosity require specialized equipment and techniques, which can add to the overall manufacturing cost and complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE is about matching its unique strengths to a specific engineering need.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency signal integrity: PTFE's low dielectric constant and low loss factor are non-negotiable for ensuring performance in advanced PCBs and coaxial cables.
- If your primary focus is reliability in harsh environments: PTFE's unmatched thermal stability and chemical inertness provide robust protection for wiring and components exposed to extreme conditions.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing process efficiency: PTFE's nonstick properties are invaluable for creating durable, reusable coatings on soldering and heat-sealing equipment.
Ultimately, understanding PTFE's elite combination of properties empowers you to engineer more reliable and higher-performing electronic systems.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit in Electronics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| High Dielectric Strength | Withstands high voltages without breakdown | Wire & cable insulation, aerospace components |
| Low Dielectric Constant | Minimizes signal loss in high-frequency apps | Flexible PCBs, coaxial cables, connectors |
| High-Temperature Resistance | Stable during soldering/heat sealing; reliable in hot environments | Manufacturing equipment coatings, high-temp wiring |
| Chemical Inertness | Protects against moisture, corrosion, and chemical damage | Semiconductor manufacturing, harsh environment components |
| Nonstick Surface | Prevents material adhesion in manufacturing processes | Soldering equipment, release coatings |
Engineer with Confidence Using High-Performance PTFE Components from KINTEK
Do you require the unmatched electrical insulation, signal integrity, and thermal stability that PTFE provides for your critical electronics applications? KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, labware, and complex fabricated parts—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We partner with you from prototype to high-volume production, ensuring your components meet exact specifications for performance in demanding environments.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project needs and discover how our expertise in PTFE can enhance the reliability and performance of your products.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















