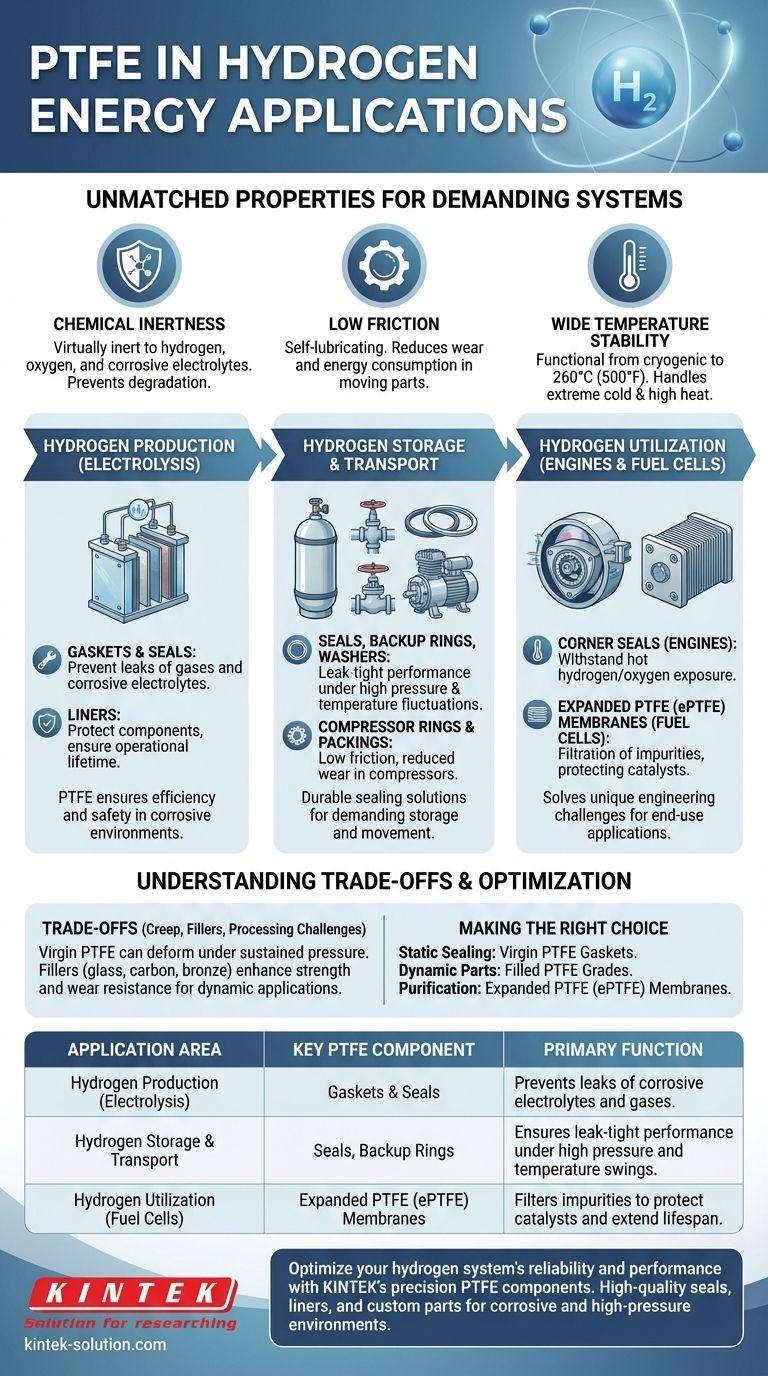
In hydrogen energy systems, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a critical enabling material used primarily for seals, gaskets, membranes, and low-friction components. Its unique combination of extreme chemical resistance and a wide operating temperature range allows it to ensure the safety, reliability, and efficiency of hydrogen production, storage, and utilization equipment where other materials would fail.
The core reason PTFE is indispensable in the hydrogen economy is its ability to withstand highly corrosive conditions and maintain physical integrity across a vast temperature spectrum. This makes it one of the few materials capable of handling everything from cryogenic liquid hydrogen to the pure oxygen byproducts of electrolysis.

Why PTFE is Essential for Hydrogen Systems
The challenges within hydrogen systems—purity, pressure, temperature, and material compatibility—create a demanding environment. PTFE's fundamental properties directly address these core challenges.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually inert to all chemicals, including the pure hydrogen and oxygen gases present in hydrogen applications. This prevents the corrosion and degradation that can compromise system integrity.
This property is vital in components like electrolyzers, where materials are exposed to corrosive electrolytes and gases, ensuring long-term reliability.
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, making it self-lubricating.
This is critical for moving parts within the hydrogen value chain, such as in compressors or pumps, where it reduces wear, lowers energy consumption, and minimizes maintenance requirements.
Wide Temperature Stability
The material remains stable and functional across an enormous temperature range, from cryogenic conditions up to 260°C (500°F).
This allows it to be used for sealing applications in both liquid hydrogen storage (which is extremely cold) and in high-temperature environments like hydrogen combustion engines or fuel cells.
Key Applications Across the Hydrogen Value Chain
PTFE's properties allow it to be deployed in various forms—from solid gaskets to microporous membranes—at every stage of the hydrogen lifecycle.
In Hydrogen Production (Electrolysis)
In electrolyzer stacks that split water into hydrogen and oxygen, PTFE is used for gaskets and seals. These components prevent leaks of gas and corrosive electrolytes, ensuring the efficiency and safety of the process.
It is also used to line components in some electrolyzer designs to prevent corrosion, directly contributing to the system's operational lifetime.
In Hydrogen Storage and Transport
High-pressure tanks, valves, and compressors required for storing and moving hydrogen rely on durable sealing solutions.
PTFE seals, backup rings, and washers are used in this equipment to provide leak-tight performance under high pressure and across wide temperature fluctuations. For compressors, its low-friction properties are also leveraged in components like piston rings and packings.
In Hydrogen Utilization (Engines & Fuel Cells)
PTFE components are used to solve unique engineering challenges in end-use applications. For example, it has been successfully used for corner seals in Wankel hydrogen engines, withstanding direct exposure to hot hydrogen and oxygen gases.
In fuel cells, expanded PTFE (ePTFE) membranes are used for filtration. These membranes can filter impurities from the air or hydrogen stream, protecting the sensitive catalyst and improving the fuel cell's lifespan and performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, PTFE is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to proper application.
Mechanical Strength and Creep
Virgin PTFE is a relatively soft material and can deform under sustained pressure, a phenomenon known as creep. It is not suitable for high-load structural applications on its own.
The Importance of Fillers
To enhance its mechanical properties, PTFE is often blended with fillers like glass, carbon, or bronze. These compounds improve strength, wear resistance, and resistance to creep, making them better suited for dynamic applications like bearings or high-pressure seals.
Processing Challenges
Compared to common thermoplastics, PTFE can be more difficult and costly to process into complex shapes, which can influence component design and manufacturing choices.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct form of PTFE is dependent on the specific engineering challenge you are trying to solve within your hydrogen system.
- If your primary focus is sealing and corrosion prevention: Virgin PTFE gaskets and seals are the ideal choice for static applications in electrolyzers, tanks, and fittings where chemical resistance is paramount.
- If your primary focus is efficiency in moving parts: A filled PTFE grade is necessary for compressor rings, bearings, or dynamic seals to reduce friction while providing superior wear resistance and mechanical strength.
- If your primary focus is purification and separation: Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) membranes with controlled porosity are essential for critical filtration tasks in fuel cells and gas purification systems.
Ultimately, PTFE's unique material profile makes it a foundational component for building a safe, durable, and efficient hydrogen infrastructure.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key PTFE Component | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen Production (Electrolysis) | Gaskets & Seals | Prevents leaks of corrosive electrolytes and gases. |
| Hydrogen Storage & Transport | Seals, Backup Rings | Ensures leak-tight performance under high pressure and temperature swings. |
| Hydrogen Utilization (Fuel Cells) | Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) Membranes | Filters impurities to protect catalysts and extend lifespan. |
Optimize your hydrogen system's reliability and performance with KINTEK's precision PTFE components.
As a leading manufacturer of high-quality PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom fabricated parts, we serve the specialized needs of the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors—including the demanding hydrogen energy industry. Our expertise ensures your components meet the exacting standards required for safety and efficiency in corrosive and high-pressure environments.
Whether you need a prototype or are scaling up to high-volume production, we deliver the precision and material expertise your project demands.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications



















