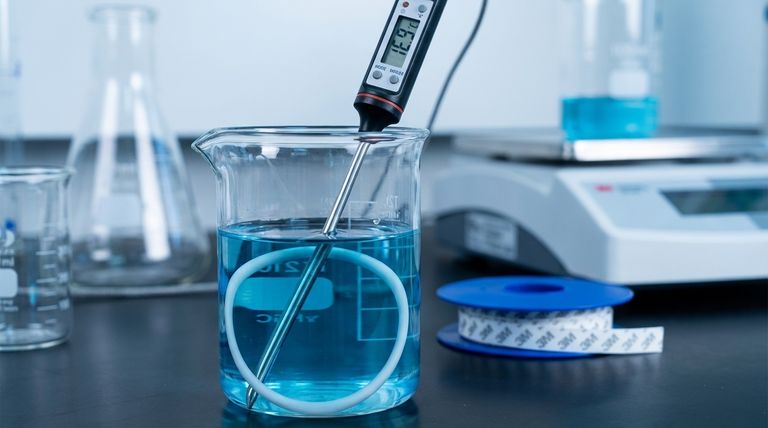
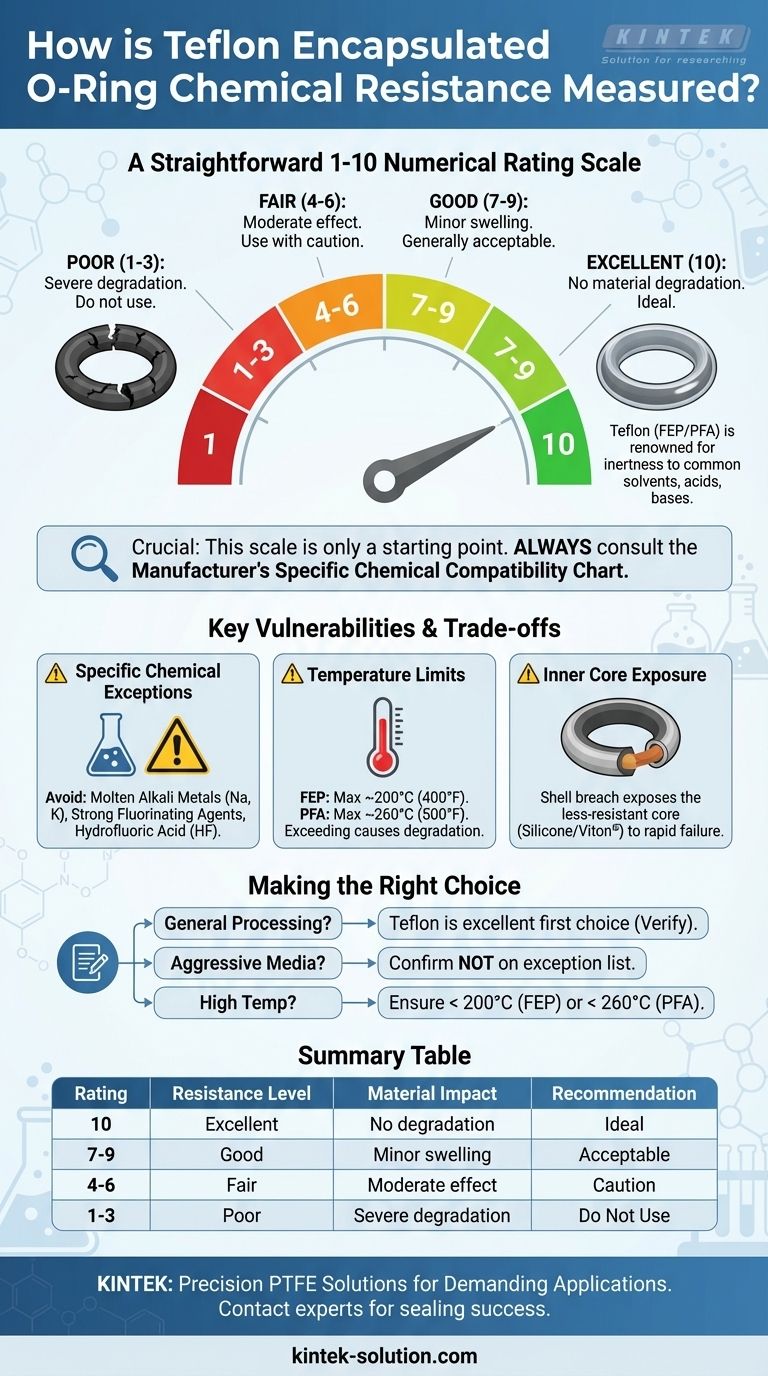
To put it simply, the chemical resistance of Teflon encapsulated O-rings is measured using a straightforward numerical rating scale. This scale typically runs from 1 to 10, where a rating of 10 signifies excellent resistance with no material degradation, and a rating of 1 indicates poor resistance where the material is severely affected and should not be used.
While the 1-10 rating scale provides a quick reference, it's only the starting point. True material selection requires a deeper understanding of the specific chemicals, operating temperatures, and known limitations of the Teflon encapsulation itself.

Deconstructing the 1-10 Resistance Scale
How the Scale Works
This numerical guide offers a standardized way to quickly assess the compatibility of an O-ring material with a specific chemical. A higher number means a better, more reliable seal in that chemical environment.
A rating of 10 generally means the material is inert and experiences no volume swell or degradation. As the number decreases, the degree of chemical attack, swelling, or loss of physical properties increases.
What "Excellent" Resistance (Rating 10) Looks Like
Teflon (FEP or PFA) encapsulation is renowned for its inertness. It typically carries a top rating for its resistance to a vast array of chemicals.
This includes common solvents like water, ethanol, acetone, and toluene, as well as aggressive acids, bases, and petroleum spirits. This broad compatibility is why these seals are chosen for demanding applications in chemical processing and semiconductor manufacturing.
The Importance of Manufacturer Data
The 1-10 scale is a valuable industry guideline, but it is not a universal standard. The ultimate authority is always the manufacturer's specific chemical compatibility chart.
These documents provide detailed ratings for their exact materials against hundreds of chemicals, ensuring you are making a decision based on tested data for that specific product.
Key Vulnerabilities and Trade-offs
Even with their exceptional resistance, Teflon encapsulated O-rings have critical limitations. Acknowledging these is essential for preventing catastrophic seal failure.
Specific Chemical Exceptions
Certain highly reactive chemicals can attack the Teflon encapsulation. You must avoid using these seals with:
- Molten alkali metals, such as sodium and potassium.
- Extremely strong fluorinating agents, like elemental fluorine, especially at high temperatures.
- Hydrofluoric acid (HF) is a known agent that can compromise performance.
The Impact of High Temperatures
Chemical resistance is not absolute; it is dependent on temperature. The encapsulation material has a strict operating ceiling.
For FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene), this limit is approximately 200°C (400°F). For PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy), the limit is higher at around 260°C (500°F). Exceeding these temperatures will cause material degradation, even with a compatible chemical.
The Role of the Inner Core
Remember that an encapsulated O-ring consists of two parts: the outer Teflon shell and an inner energizing core (typically silicone or Viton®). The shell provides the chemical barrier.
If the shell is breached by mechanical damage or chemical attack, the less-resistant inner core becomes exposed, leading to rapid seal failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct seal involves looking beyond a single rating and evaluating the entire system.
- If your primary focus is general chemical processing: Teflon's broad resistance to acids, bases, and organic solvents makes it an excellent first choice, but always verify your specific media against a manufacturer's chart.
- If you are working with aggressive or unusual media: Specifically confirm that your chemical is not on the list of known exceptions, such as molten alkali metals or high-temperature fluorinating agents.
- If your application involves high temperatures: Ensure your maximum operating temperature remains safely below the specified limit for the encapsulation material (200°C for FEP or 260°C for PFA).
A reliable seal is achieved by matching the material's known capabilities to the complete chemical, thermal, and mechanical demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Rating | Resistance Level | Material Impact | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | Excellent | No degradation or swelling | Ideal for use |
| 7-9 | Good | Minor swelling or effect | Generally acceptable |
| 4-6 | Fair | Moderate effect; property loss | Use with caution |
| 1-3 | Poor | Severe degradation | Do not use |
Need a Chemically Resistant Seal for Demanding Applications?
Teflon encapsulated O-rings offer superior resistance to a vast range of aggressive chemicals, including acids, bases, and solvents. However, selecting the right seal requires expert knowledge of specific media, temperatures, and mechanical demands.
KINTEK manufactures precision PTFE components, including custom O-rings, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring you get a seal perfectly matched to your application's unique challenges.
Let our experts help you navigate chemical compatibility and ensure sealing success.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How do FEP and PTFE encapsulated O-rings contribute to equipment longevity? Prevent Costly Downtime with Superior Seals
- What are the primary characteristics of PTFE seals? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Conditions
- Why are PTFE seals preferred over traditional rubber seals? Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the five outstanding characteristics of PTFE seals? Engineered for Extreme Performance
- What are the advantages of PTFE-based seals? Unmatched Performance in Extreme Conditions



















