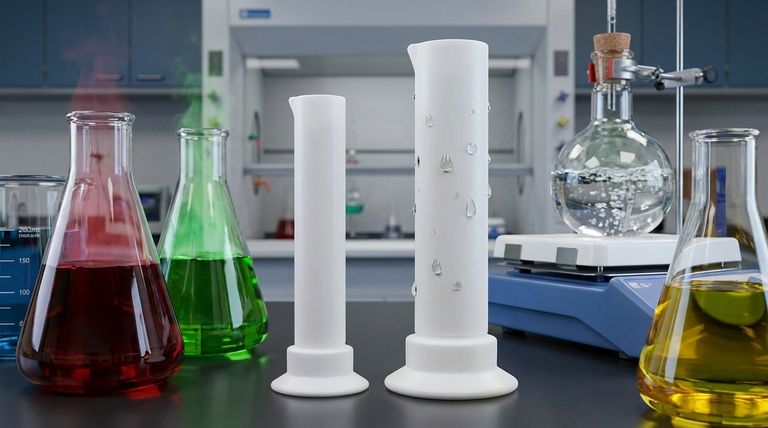
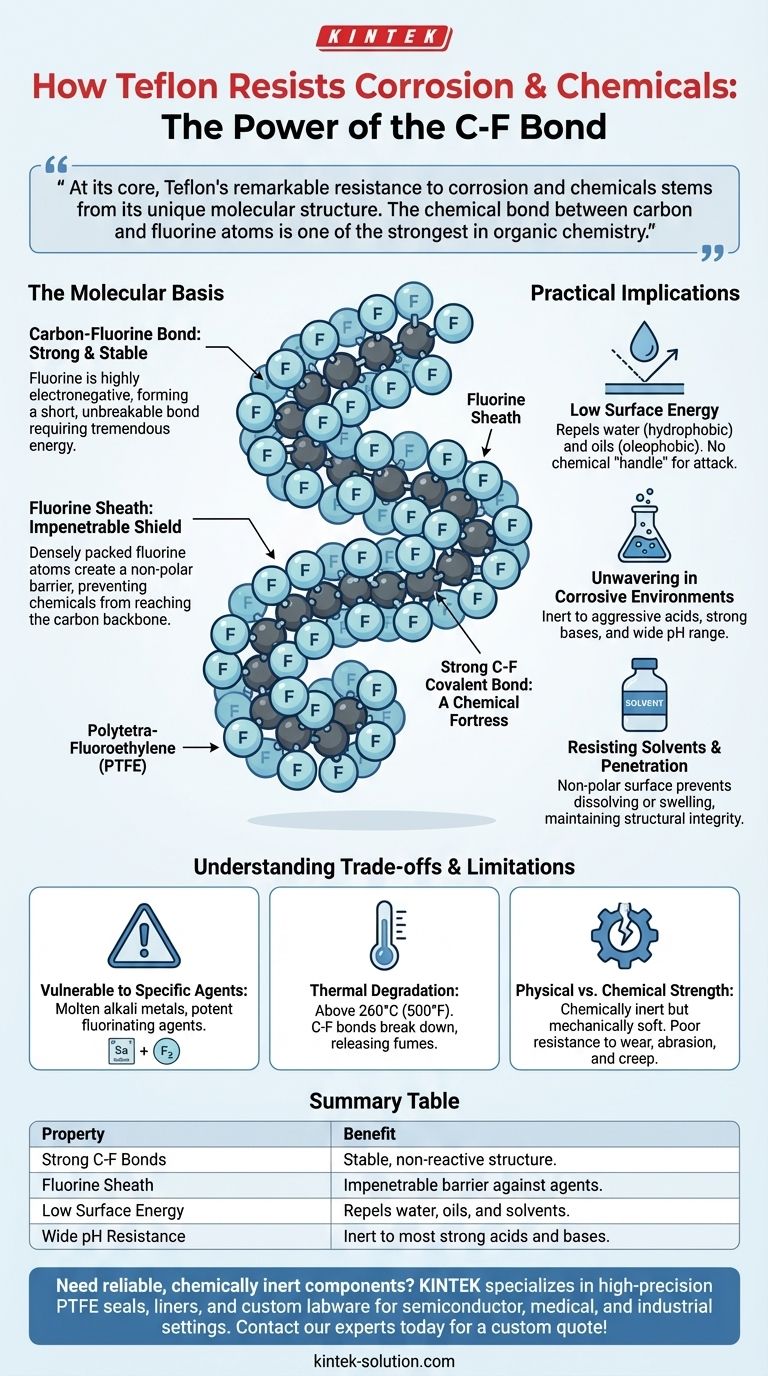
At its core, Teflon's remarkable resistance to corrosion and chemicals stems from its unique molecular structure. The chemical bond between carbon and fluorine atoms is one of the strongest in organic chemistry. This creates a highly stable, non-reactive surface that effectively forms a protective shield, preventing other chemicals from penetrating or reacting with the material.
The secret to Teflon's resilience isn't a complex additive or coating; it is the fundamental simplicity of its own structure. Fluorine atoms create a tight, impenetrable sheath around a carbon backbone, making the molecule chemically inert and physically resistant to attack.

The Molecular Basis of Teflon's Inertness
To truly understand Teflon's performance, we must look at its atomic-level construction. Its properties are not accidental; they are a direct result of its chemical makeup, specifically Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE).
The Carbon-Fluorine Bond: A Chemical Fortress
The bond between a carbon atom and a fluorine atom is exceptionally strong and stable. Fluorine is the most electronegative element, meaning it has an incredibly powerful pull on electrons.
When bonded to carbon, it forms a very short, very strong covalent bond. This bond requires a tremendous amount of energy to break, making the molecule highly resistant to chemical reactions.
The Fluorine Sheath: An Impenetrable Shield
In a PTFE molecule, the relatively small carbon atoms form a long chain, which serves as a backbone. This backbone is completely encased by larger fluorine atoms.
This creates a dense, uniform, and non-polar "sheath" of fluorine. This physical and electrical barrier prevents corrosive chemicals from ever reaching the vulnerable carbon backbone to initiate a reaction.
Low Surface Energy: Repelling All Invaders
The fluorine sheath gives Teflon an extremely low surface energy. This is why it is famous for being non-stick.
This same property means it is both hydrophobic (repels water) and oleophobic (repels oils). Because it repels nearly everything, there is no chemical "handle" for other molecules to grab onto, which is the first step required for a chemical attack.
Practical Implications of Chemical Resistance
This molecular stability translates directly into reliable performance in harsh industrial and laboratory environments.
Unwavering in Corrosive Environments
Because its bonds are so difficult to break, Teflon is inert to the vast majority of corrosive chemicals, including highly aggressive acids and strong bases.
It remains stable across a very wide pH range where many other materials, including high-grade metals, would quickly degrade.
Resisting Solvents and Chemical Penetration
The same principles make Teflon highly resistant to organic solvents. The dense molecular structure and non-polar surface prevent solvents from dissolving, swelling, or physically seeping into the material.
This ensures the structural integrity and purity of the Teflon component is maintained even with prolonged chemical exposure.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While its chemical resistance is world-class, Teflon is not an infallible solution for every engineering problem. Objectivity requires acknowledging its limitations.
Vulnerability to Specific Agents
Despite its inertness, Teflon can be attacked by a few highly reactive substances. These include molten alkali metals (like sodium), and potent fluorinating agents. These are niche exceptions but are critical to know for specialized applications.
Thermal Degradation
Teflon has a distinct service temperature limit, typically around 260°C (500°F). Above this temperature, the C-F bonds can begin to break down, which not only compromises the material but can also release toxic fumes.
Physical vs. Chemical Strength
It is critical to distinguish between chemical resistance and mechanical strength. Teflon is a relatively soft material with poor resistance to wear, abrasion, and "creep" (deformation under load). Its chemical inertness does not imply it is mechanically tough.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires matching its core properties to your primary challenge.
- If your primary focus is containing aggressive acids, bases, or solvents: Teflon is an exceptional first choice due to the unparalleled stability of its carbon-fluorine bond.
- If your application involves high mechanical stress or abrasion: You must recognize that Teflon's chemical inertness does not translate to physical durability, and a reinforced grade or a different material may be required.
- If you are operating near or above 260°C (500°F): You must account for Teflon's thermal degradation point and select a higher-temperature material if necessary.
Understanding the simple yet powerful molecular structure of Teflon is the key to correctly leveraging its remarkable chemical resistance in your project.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit for Chemical Resistance |
|---|---|
| Strong C-F Bonds | Provides a stable, non-reactive molecular structure. |
| Fluorine Sheath | Creates an impenetrable barrier against corrosive agents. |
| Low Surface Energy | Repels water, oils, and solvents, preventing chemical attack. |
| Wide pH Resistance | Remains inert to most strong acids and bases. |
Need reliable, chemically inert components for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components like seals, liners, and custom labware. Our expertise ensures your equipment is protected against the harshest chemicals in semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial settings.
Let us provide the durable, corrosion-resistant solution you need.
Contact our experts today for a custom quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
People Also Ask
- What are some exceptional properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Extreme Environments
- What material is the PTFE bottle made from? Discover the Benefits of 100% Virgin PTFE
- Why are PTFE vials considered environmentally friendly? Reduce Lab Waste with Durable Reusables
- What are the common characteristics of Teflon? Unlocking Extreme Chemical and Thermal Resistance
- What industrial applications does PTFE have? Unlock Performance in Extreme Environments



















