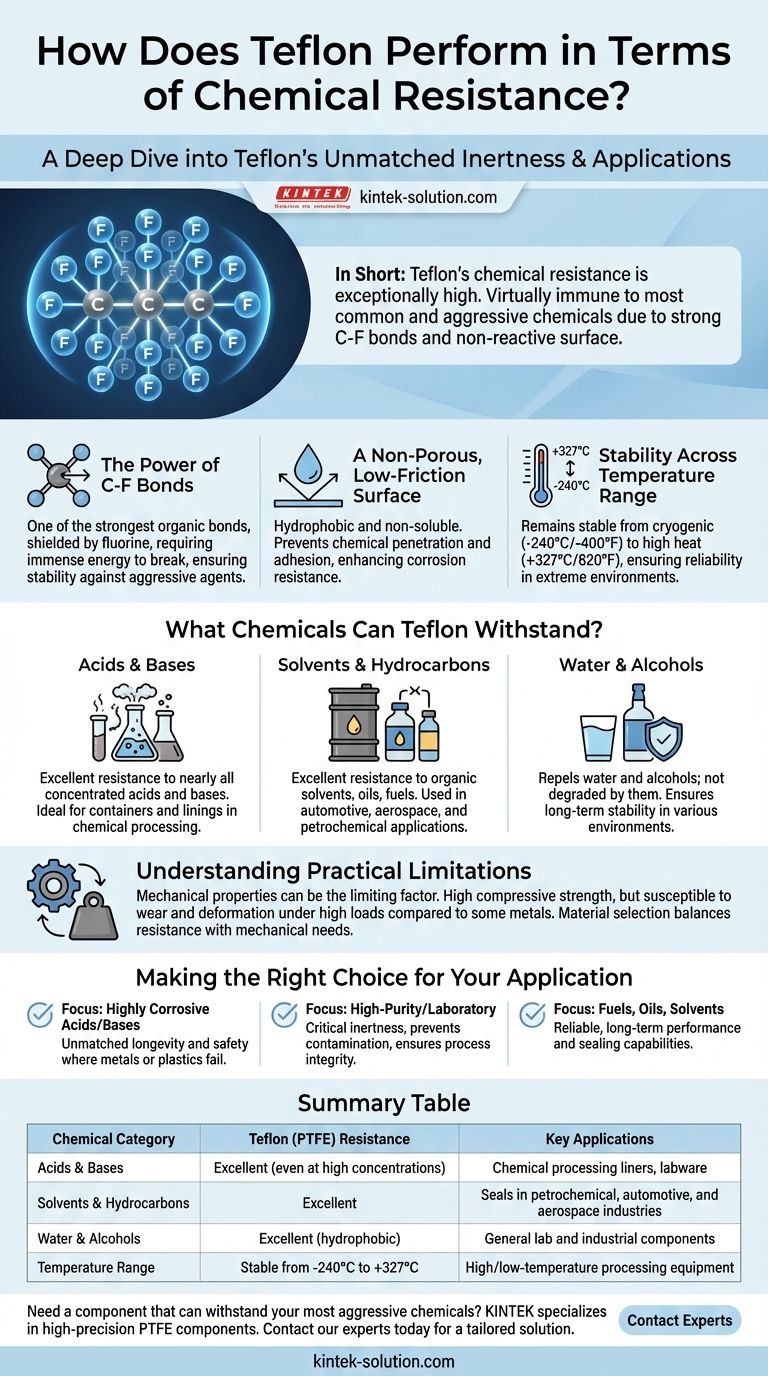
In short, Teflon's chemical resistance is exceptionally high. It is one of the most chemically inert materials known, making it virtually immune to degradation from the vast majority of common and aggressive chemicals, including strong acids, bases, solvents, and hydrocarbons.
The core reason for Teflon's unparalleled chemical performance lies in its molecular structure. The incredibly strong bond between its carbon and fluorine atoms creates a non-reactive, non-porous surface that most chemicals simply cannot break down or penetrate.

The Source of Teflon's Chemical Inertness
To understand why Teflon (PTFE) is a material of choice for demanding environments, we must look at its fundamental chemistry and physical properties.
The Power of Carbon-Fluorine Bonds
The molecular structure of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) consists of a long chain of carbon atoms completely shielded by a layer of fluorine atoms. The carbon-fluorine (C-F) bond is one of the strongest known in organic chemistry.
This immense bond strength means it takes a tremendous amount of energy to break the molecule apart. As a result, Teflon remains stable and does not react when exposed to aggressive chemical agents that would destroy other materials like metals or rubber.
A Non-Porous, Low-Friction Surface
Teflon is not soluble in water and effectively blocks chemical penetration. Its famously low coefficient of friction is a surface-level expression of its non-reactive nature.
This property means that even corrosive substances have difficulty adhering to its surface, further contributing to its resistance to chemical attack and corrosion.
Stability Across a Wide Temperature Range
Teflon’s chemical resistance is not compromised by temperature extremes. It remains stable and inert from cryogenic temperatures around -240°C (-400°F) up to its melting point of approximately 327°C (620°F).
This thermal stability ensures its chemical resistance properties are reliable across a vast range of industrial and laboratory applications.
What Chemicals Can Teflon Withstand?
Teflon’s inertness makes it compatible with an extensive list of substances that are destructive to lesser materials.
Acids and Bases
Teflon remains completely unaffected by exposure to nearly all concentrated acids and bases. This makes it a standard material for containers, seals, and linings in chemical processing.
Solvents and Hydrocarbons
It demonstrates excellent resistance to organic solvents, oils, fuels, and other hydrocarbons. This allows for its use in automotive, aerospace, and petrochemical applications where such exposures are constant.
Water and Alcohols
As a hydrophobic material, Teflon repels water and is not degraded by it or by alcohols. This ensures long-term stability in a wide variety of environments.
Understanding the Practical Limitations
While Teflon's chemical resistance is nearly universal, its selection for an application often depends on its physical properties, which can present trade-offs.
Mechanical Properties as the Limiting Factor
In some applications, the limiting factor is not Teflon's chemical inertness but its mechanical strength. While it has high compressive strength, it can be susceptible to wear and deformation under very high loads or abrasive conditions compared to certain metals.
Assessing Performance with Standard Metrics
In engineering, material selection is a precise process. For components like Teflon-encapsulated O-rings, chemical resistance is sometimes rated on a scale (e.g., 1 to 10) to quantify performance against specific chemicals under specific conditions. This ensures the correct grade and type of material are chosen for the intended purpose.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting Teflon is about leveraging its unique strengths for the right challenge. Consider your primary goal to determine if it is the optimal choice.
- If your primary focus is handling highly corrosive acids and bases: Teflon is a top-tier material that will provide unmatched longevity and safety where metals or plastics would fail.
- If your primary focus is a high-purity or laboratory environment: Teflon's inertness is critical, as it will not react with or contaminate the substances it contains, ensuring process integrity.
- If your primary focus is resistance to fuels, oils, and solvents: Teflon offers reliable, long-term performance and sealing capabilities in environments that would degrade other polymers and elastomers.
Ultimately, relying on Teflon is a decision to prioritize chemical inertness above all else.
Summary Table:
| Chemical Category | Teflon (PTFE) Resistance | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Acids & Bases | Excellent (even at high concentrations) | Chemical processing liners, labware |
| Solvents & Hydrocarbons | Excellent | Seals in petrochemical, automotive, and aerospace industries |
| Water & Alcohols | Excellent (hydrophobic) | General lab and industrial components |
| Temperature Range | Stable from -240°C to +327°C | High/low-temperature processing equipment |
Need a component that can withstand your most aggressive chemicals?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in custom fabrication ensures you get a part that delivers unmatched chemical resistance and reliability, from prototype to high-volume production.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific chemical resistance challenge and receive a tailored solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
People Also Ask
- In which industries is PTFE commonly used? Key Applications for Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- Why is chemical compatibility important when choosing a PTFE-coated septum? Avoid Sample Contamination and Data Loss
- What are the primary applications of PTFE? Unlocking High-Performance Solutions
- What material is the PTFE bottle made from? Discover the Benefits of 100% Virgin PTFE
- Why are PTFE vials considered environmentally friendly? Reduce Lab Waste with Durable Reusables



















