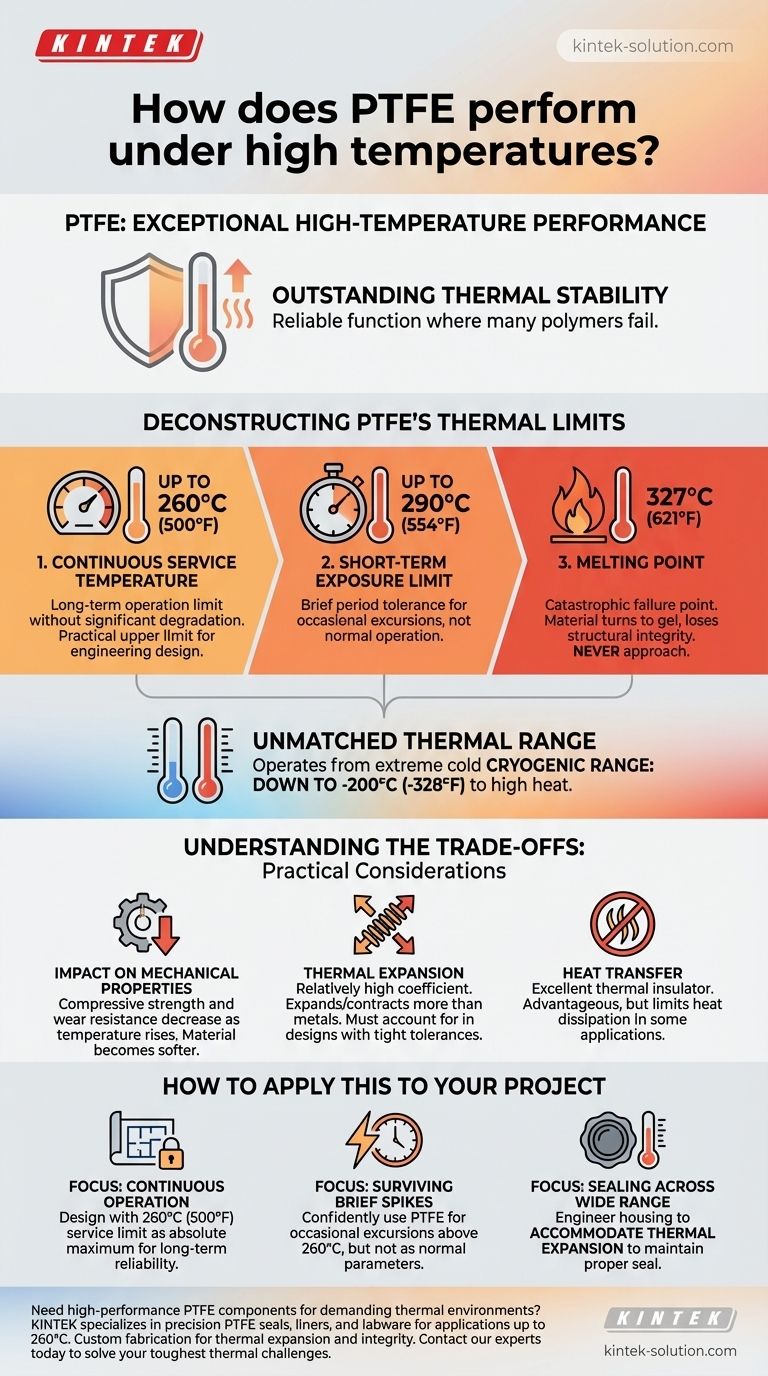
To be clear, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers exceptional performance at high temperatures. Its primary advantage is its outstanding thermal stability, allowing it to function reliably in environments where many other polymers would fail. The material has a continuous service temperature of up to 260°C (500°F) and a very high melting point of approximately 327°C (621°F).
The critical distinction for any high-temperature application is the difference between a material's continuous operating limit and its point of physical failure. PTFE's value is its ability to maintain its integrity and properties up to 260°C, providing a significant and reliable safety margin well below its actual melting point.

Deconstructing PTFE's Thermal Limits
To properly evaluate PTFE, you must understand three distinct temperature thresholds. Each one defines a different aspect of its performance and limitations under heat.
The Continuous Service Temperature
This is the most important number for engineering design. PTFE can operate continuously at temperatures up to 260°C (500°F) without significant degradation of its chemical or mechanical properties. This is the practical upper limit for long-term applications.
The Short-Term Exposure Limit
For brief periods, PTFE can withstand temperatures slightly higher than its continuous service limit, with some sources indicating tolerance up to 290°C (554°F). However, operating in this range should be considered an occasional excursion, not a normal condition.
The Melting Point
PTFE has a high melting point of 327°C (621°F). At this temperature, the material undergoes a phase transition from a solid to a gel-like state, losing all structural integrity. This is a point of catastrophic failure and should never be approached in an application.
Unmatched Thermal Range
It is also important to note that PTFE's thermal stability extends to extreme cold. It maintains its properties in cryogenic conditions, with an operational range down to -200°C (-328°F) and even lower, making it one of the few materials suitable for such a vast temperature spectrum.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its thermal stability is a primary benefit, there are practical considerations that must be factored into any design involving high temperatures.
Impact on Mechanical Properties
As PTFE approaches its upper service temperature, some of its mechanical properties, such as compressive strength and wear resistance, will naturally decrease. While it remains structurally stable, it will be softer than it is at room temperature.
Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it will expand and contract more than metals or other engineering plastics when subjected to temperature changes. This must be accounted for in designs with tight tolerances to avoid component failure.
Heat Transfer
PTFE is an excellent thermal insulator, which is often an advantage. However, in applications where heat dissipation is required, this property can be a limitation. It will not transfer heat away from a system effectively.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Understanding these characteristics allows you to leverage PTFE's strengths in the right context.
- If your primary focus is continuous operation in a high-heat environment: Design your application with the 260°C (500°F) service limit as your absolute maximum for long-term reliability.
- If your primary focus is surviving brief temperature spikes: You can be confident that PTFE will tolerate occasional excursions above 260°C, but this should not be the basis of your normal operating parameters.
- If your primary focus is sealing across a wide thermal range: PTFE is an excellent choice, but you must engineer your component housing to accommodate its thermal expansion to maintain a proper seal.
By respecting these thermal boundaries and design considerations, you can confidently leverage PTFE's remarkable stability in your most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Threshold | Temperature Range | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Service | Up to 260°C (500°F) | Long-term operation without significant degradation |
| Short-Term Exposure | Up to 290°C (554°F) | Tolerance for brief temperature spikes |
| Melting Point | 327°C (621°F) | Point of catastrophic failure (loss of structural integrity) |
| Cryogenic Range | Down to -200°C (-328°F) | Maintains properties in extreme cold, offering a vast thermal spectrum |
Need high-performance PTFE components for demanding thermal environments? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, liners, and labware that excel in high-temperature applications up to 260°C. Our custom fabrication services—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensure your components are engineered to handle thermal expansion and maintain integrity. Let us help you solve your toughest thermal challenges in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Cleaning Rack
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE that make it commercially valuable? Unlock Unmatched Performance
- What industrial applications does PTFE have? Unlock Performance in Extreme Environments
- Why is chemical compatibility important when choosing a PTFE-coated septum? Avoid Sample Contamination and Data Loss
- What are the common characteristics of Teflon? Unlocking Extreme Chemical and Thermal Resistance
- What makes the PTFE bottle durable? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability for Demanding Applications



















