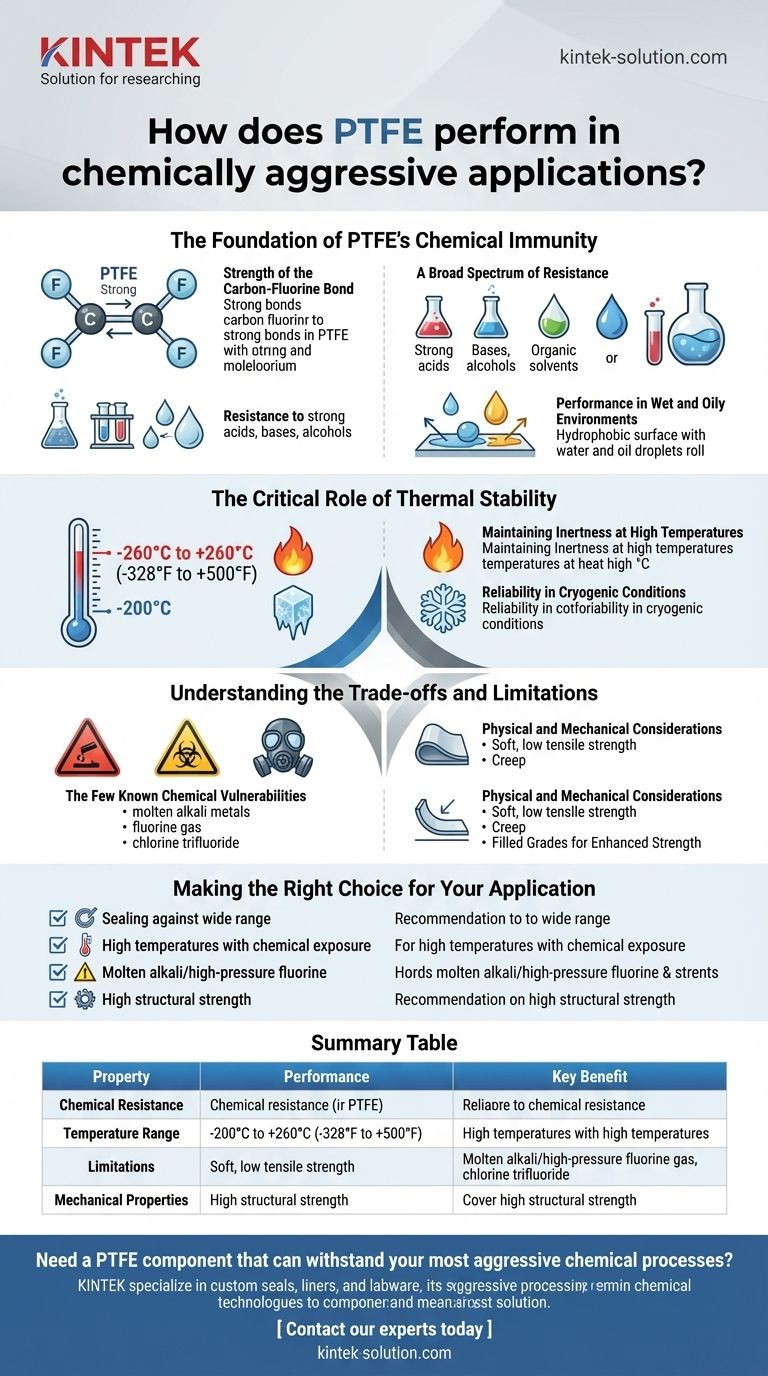
In chemically aggressive applications, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) performs exceptionally well. It is one of the most chemically inert polymers known, making it a default material choice for components like seals, gaskets, and linings that are exposed to corrosive substances. This extreme resistance stems from its powerful carbon-fluorine bonds, which are incredibly stable and difficult for chemicals to attack.
PTFE's near-universal chemical inertness, combined with its high thermal stability, makes it one of the most reliable materials for aggressive chemical applications. Its performance is not absolute, however, as it has known—albeit rare—vulnerabilities that must be considered in extreme conditions.

The Foundation of PTFE's Chemical Immunity
PTFE’s remarkable performance is not an accident; it is a direct result of its unique molecular structure. This structure gives it a level of resistance that few other materials can match.
The Strength of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
The backbone of the PTFE polymer consists of carbon atoms, each completely shielded by a sheath of fluorine atoms.
The bond between carbon and fluorine is exceptionally strong and stable. This molecular shield prevents virtually all chemicals from reacting with the carbon chain.
A Broad Spectrum of Resistance
Because of its inert structure, PTFE is resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals.
This includes strong acids, bases, alcohols, detergents, and organic solvents. It also holds up against aggressive cleaning and disinfecting agents like chlorine dioxide.
Performance in Wet and Oily Environments
PTFE exhibits very poor water absorption (hydrophobicity) and repels oils (oleophobicity).
This makes it an ideal material for washers and seals in piping or process systems that move water, oil, or oil-containing fluids, as it will not swell or degrade.
The Critical Role of Thermal Stability
A material's chemical resistance is only useful if it can survive the operating temperatures of the application. PTFE excels in this regard, maintaining its integrity across a vast temperature range.
Maintaining Inertness at High Temperatures
PTFE remains stable and retains its chemical resistance at continuous service temperatures up to 260°C (500°F).
Its high melting point of approximately 327°C (621°F) provides a significant safety margin in industrial processes, baking, and other high-heat environments.
Reliability in Cryogenic Conditions
Just as it resists high temperatures, PTFE also maintains its properties at very low, cryogenic temperatures. This makes it a versatile choice for applications that cycle between thermal extremes.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. While PTFE’s chemical resistance is legendary, it is critical to understand its specific vulnerabilities and physical properties to ensure successful application.
The Few Known Chemical Vulnerabilities
PTFE is virtually inert, but it can be attacked by a very small group of highly reactive substances.
These exceptions include molten alkali metals (like sodium), fluorine gas, and potent halogenated compounds such as chlorine trifluoride, particularly at high temperatures and pressures.
Physical and Mechanical Considerations
While chemically robust, PTFE is a relatively soft material with low tensile strength and a susceptibility to creep (deformation under sustained load).
In applications requiring high mechanical loads or abrasion resistance, virgin PTFE may not be suitable. In these cases, filled grades of PTFE (which include additives like glass or carbon) are often used to enhance physical strength.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires balancing chemical needs with mechanical and thermal demands. PTFE is often the best choice, but only when its full profile is considered.
- If your primary focus is sealing against a wide range of acids, bases, or solvents: PTFE is an industry-standard choice due to its near-universal inertness.
- If your application involves high temperatures alongside chemical exposure: PTFE's thermal stability up to 260°C (500°F) ensures its chemical resistance remains intact.
- If you are working with molten alkali metals or high-pressure fluorine compounds: You must seek an alternative material, as these are the few known substances that can attack PTFE.
- If the component requires high structural strength or abrasion resistance: Consider using a filled grade of PTFE or another high-performance polymer to meet mechanical requirements.
By understanding both its profound chemical resilience and its specific limitations, you can confidently deploy PTFE in the most demanding environments.
Summary Table:
| Property | Performance | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Resists nearly all acids, bases, solvents | Near-universal inertness for reliable sealing |
| Temperature Range | -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F) | Stable performance from cryogenic to high heat |
| Limitations | Vulnerable to molten alkali metals, fluorine gas | Critical to know for extreme conditions |
| Mechanical Properties | Soft, low tensile strength, can creep | Filled grades available for enhanced strength |
Need a PTFE component that can withstand your most aggressive chemical processes?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including custom seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your components deliver unmatched chemical resistance and thermal stability, from prototype to high-volume production.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application requirements and receive a custom solution quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications



















