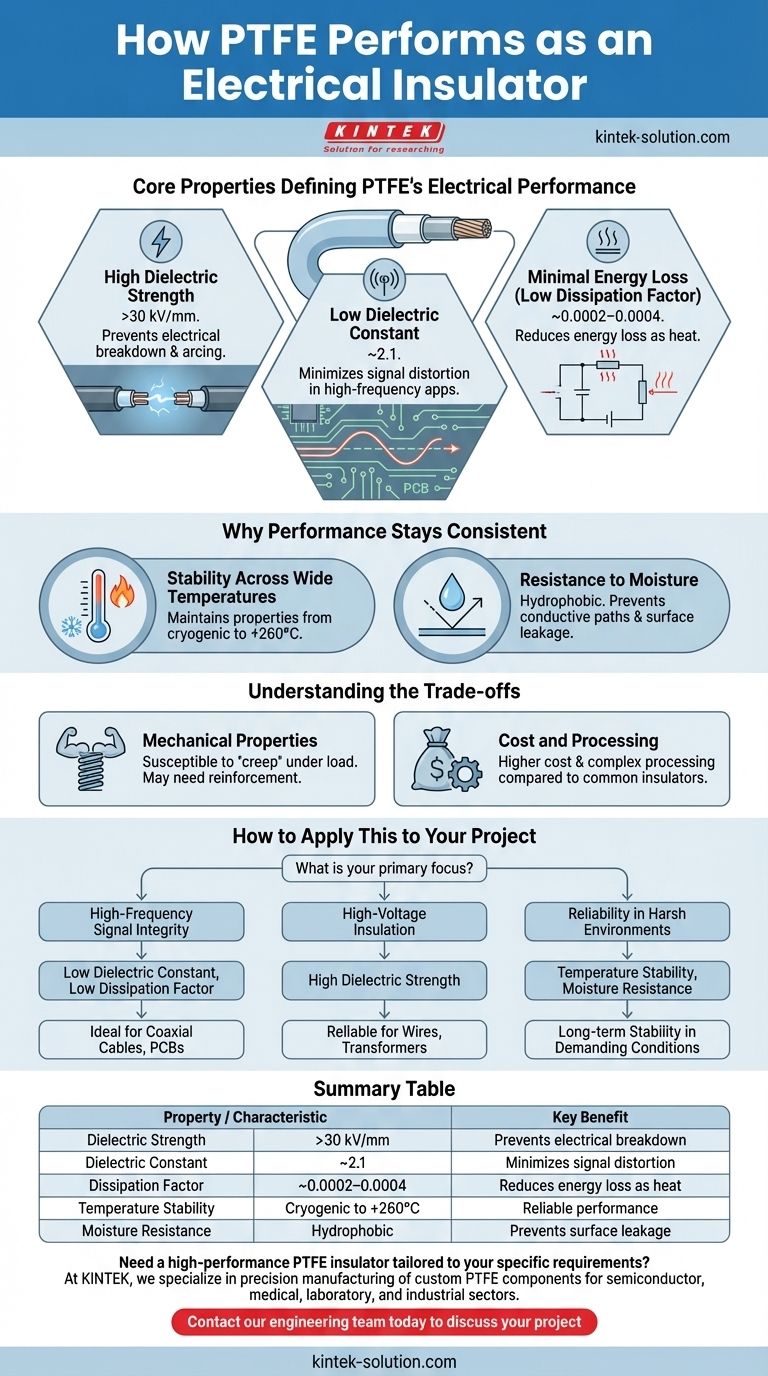
PTFE is an exceptional electrical insulator, valued for a unique combination of properties that ensure reliability in demanding applications. Its performance stems from its high dielectric strength, a very low dielectric constant, and its ability to maintain these characteristics across a wide range of temperatures and frequencies.
The core reason PTFE excels as an insulator is not just its ability to block current, but its capacity to do so with minimal signal distortion or energy loss, especially in high-frequency and high-voltage scenarios where other materials falter.
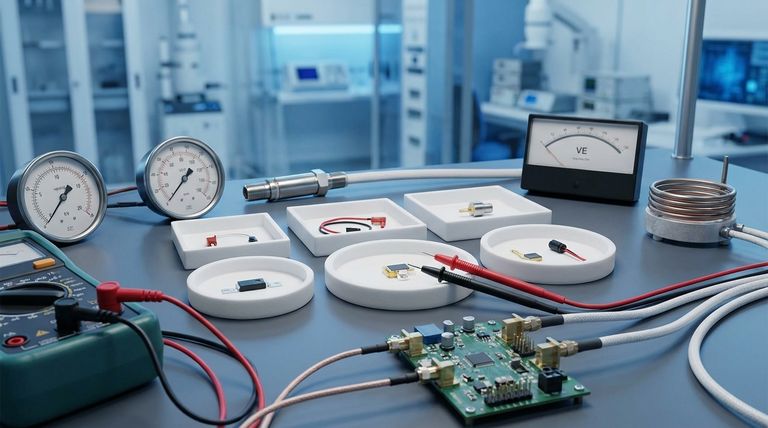

The Core Properties Defining PTFE's Electrical Performance
To understand why PTFE is so effective, we must look at three specific electrical characteristics. These properties work in concert to protect components, ensure signal integrity, and maintain safety.
High Dielectric Strength
Dielectric strength measures a material's ability to withstand a strong electric field without breaking down and conducting electricity.
PTFE possesses a very high dielectric strength, often exceeding 30 kV/mm. This means it can resist high voltages, preventing dangerous electrical arcing and short circuits, which is critical for coating wires and cables.
Low Dielectric Constant
The dielectric constant indicates how much electrical energy a material can store when subjected to an electric field.
With a low dielectric constant of 2.1, PTFE stores very little energy. This is a crucial advantage in high-frequency applications like printed circuit boards (PCBs) and coaxial cables, as it minimizes signal distortion and ensures clean, efficient transmission.
Minimal Energy Loss (Low Dissipation Factor)
The dissipation factor quantifies how much energy is lost as heat within an insulating material when an alternating electric field is applied.
PTFE has an extremely low dissipation factor (around 0.0002–0.0004). This means almost no energy is wasted, making it highly efficient for high-frequency circuits where minimizing heat buildup and energy loss is paramount.
Why Performance Stays Consistent
Beyond its core electrical properties, PTFE's reliability comes from its stability in challenging operating conditions.
Stability Across Wide Temperatures
Many insulators see their performance degrade significantly at high or low temperatures.
PTFE, however, maintains its excellent insulating properties over a very broad temperature range, ensuring consistent and predictable performance in electronics that operate in harsh environments.
Resistance to Moisture
Moisture can create conductive paths on the surface of an insulator, leading to failure.
PTFE's chemical structure makes it naturally hydrophobic, meaning it repels water. This property provides an added layer of protection, preventing moisture from compromising the insulation of electrical components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its electrical characteristics are top-tier, no material is perfect for every situation. A complete technical evaluation requires considering its practical limitations.
Mechanical Properties
PTFE is a relatively soft material and can be susceptible to "creep" or cold flow under sustained mechanical load. In applications where high abrasion resistance or structural rigidity is required, it may need to be reinforced or an alternative material may be more suitable.
Cost and Processing
Compared to common insulators like PVC or polyethylene, PTFE is generally more expensive and can be more complex to process and manufacture. Its use is typically justified in high-performance applications where its unique electrical and thermal benefits outweigh the higher cost.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Choosing an insulator depends entirely on your specific engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency signal integrity (e.g., coaxial cables, PCBs): PTFE's low dielectric constant and low dissipation factor are its most critical advantages, ensuring minimal signal loss and distortion.
- If your primary focus is high-voltage insulation: Its high dielectric strength makes it a profoundly reliable choice for safely coating wires, transformers, and other components to prevent electrical breakdown.
- If your primary focus is reliability in harsh environments: PTFE's consistent performance across wide temperature ranges and its resistance to moisture ensure long-term stability where other insulators might fail.
Ultimately, PTFE's unique combination of electrical properties makes it a premier choice for demanding applications where performance and reliability cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value / Characteristic | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Strength | > 30 kV/mm | Prevents electrical breakdown and arcing under high voltage |
| Dielectric Constant | ~2.1 | Minimizes signal distortion in high-frequency applications |
| Dissipation Factor | ~0.0002–0.0004 | Reduces energy loss as heat, ensuring efficiency |
| Temperature Stability | Maintains properties from cryogenic to +260°C | Reliable performance in harsh environments |
| Moisture Resistance | Hydrophobic (water-repelling) | Prevents conductive paths and surface leakage |
Need a high-performance PTFE insulator tailored to your specific requirements?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise ensures your components deliver the unmatched electrical insulation, signal integrity, and reliability that PTFE is known for.
Contact our engineering team today to discuss how we can support your project with superior PTFE solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials



















