In essence, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a premier sealing material for ball valves due to its unique combination of chemical inertness, extremely low friction, and physical flexibility. These properties allow it to form a tight, durable, and low-maintenance seal that remains effective even when exposed to corrosive media, high pressures, or frequent cycling.
The critical insight is that PTFE doesn't just passively block leaks. Its distinct properties actively work together to create a dynamic, resilient, and self-lubricating seal that adapts to operating conditions and resists degradation over the valve's service life.

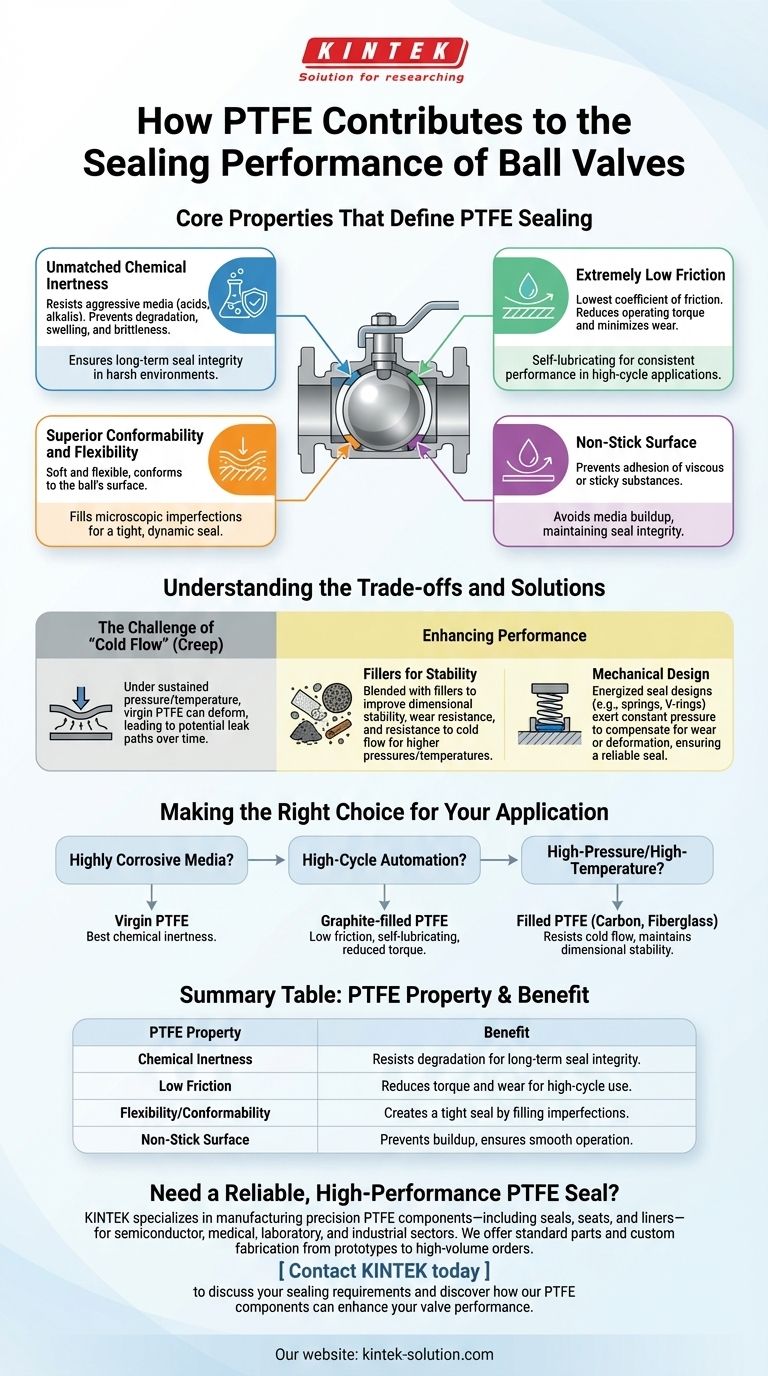
The Core Properties That Define PTFE Sealing
To understand PTFE's effectiveness, we must look at how its fundamental characteristics contribute directly to the function of a valve seal.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is one of the most chemically resistant polymers known. It remains stable when exposed to a vast range of aggressive media, including strong acids and alkalis.
This chemical corrosion resistance ensures the seal material does not degrade, swell, or become brittle. This directly prevents leaks and extends the service life of the valve in harsh chemical processing applications.
Extremely Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, often compared to wet ice on wet ice. This self-lubricating property is critical in a ball valve.
It significantly reduces the torque required to open and close the valve, which is especially important for automated or frequently actuated systems. This low friction also minimizes wear on both the ball and the seat, ensuring a consistent sealing performance over thousands of cycles.
Superior Conformability and Flexibility
Virgin PTFE is a relatively soft and highly flexible material. This allows the valve seats to conform perfectly to the spherical surface of the ball.
This plasticity ensures an exceptionally tight seal by filling microscopic imperfections on the sealing surfaces. Even in dynamic applications, this flexibility allows the seal to maintain constant contact and prevent leakage.
Non-Stick Surface
The non-stick nature of PTFE prevents process media, especially viscous or sticky substances, from adhering to the sealing surfaces.
This is vital for maintaining the integrity of the seal, as buildup could otherwise create a potential leak path or interfere with the valve's operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Solutions
While PTFE's core properties are excellent, it is not without limitations. Understanding these trade-offs is key to specifying the right material for an application.
The Challenge of "Cold Flow"
The primary weakness of virgin PTFE is its tendency to "cold flow," or creep. Under sustained pressure and temperature, the material can slowly deform, which may lead to a loss of sealing integrity over time.
The Role of Fillers
To counteract cold flow and enhance mechanical properties, PTFE is often blended with fillers. Materials like carbon, fiberglass, bronze, or graphite are added to the base PTFE.
These fillers dramatically improve the material's dimensional stability, wear resistance, and resistance to cold flow. This makes filled PTFE grades suitable for higher pressure and temperature applications where virgin PTFE would fail.
The Importance of Mechanical Design
Valve design also plays a crucial role. Many high-performance valves use spring-loaded or other energized seal designs.
These mechanisms, such as a spring or V-ring packing, exert constant pressure on the PTFE seal. This ensures it remains in tight contact with the ball even if minor wear or material deformation occurs, providing a reliable, maintenance-free seal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct type of PTFE seal depends entirely on the specific demands of your system.
- If your primary focus is handling highly corrosive media: Virgin PTFE is often the best choice due to its unmatched chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is high-cycle automation: The low friction and self-lubricating properties of a graphite-filled PTFE will minimize torque and extend operational life.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure or high-temperature service: A filled PTFE, such as one with carbon or fiberglass, is essential to resist cold flow and maintain dimensional stability.
Ultimately, understanding how PTFE's properties align with your operational demands is the key to achieving superior valve performance and long-term system reliability.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Property | Benefit for Ball Valve Sealing |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists degradation from corrosive media, ensuring long-term seal integrity. |
| Low Friction | Reduces operating torque and minimizes wear for high-cycle applications. |
| Flexibility/Conformability | Creates a tight seal by filling microscopic imperfections on the ball surface. |
| Non-Stick Surface | Prevents media buildup that could interfere with sealing or valve operation. |
Need a Reliable, High-Performance PTFE Seal for Your Ball Valves?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, seats, and liners—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require standard parts or custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, our expertise ensures a solution that meets your specific application demands for chemical resistance, pressure, and cycle life.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your sealing requirements and discover how our PTFE components can enhance your valve performance and system reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the overall advantages of using PTFE balls in fluid management systems? Enhance Reliability & Efficiency
- In which industries are Teflon (PTFE) balls commonly used? Key Applications & Benefits
- Why are PTFE balls particularly suitable for high-performance applications? Key Properties & Selection Guide
- What temperature range can Teflon (PTFE) balls withstand? -200°C to +260°C Performance Guide
- What are the advantages of PTFE balls over metals or alloys? Superior Chemical & Friction Resistance



















