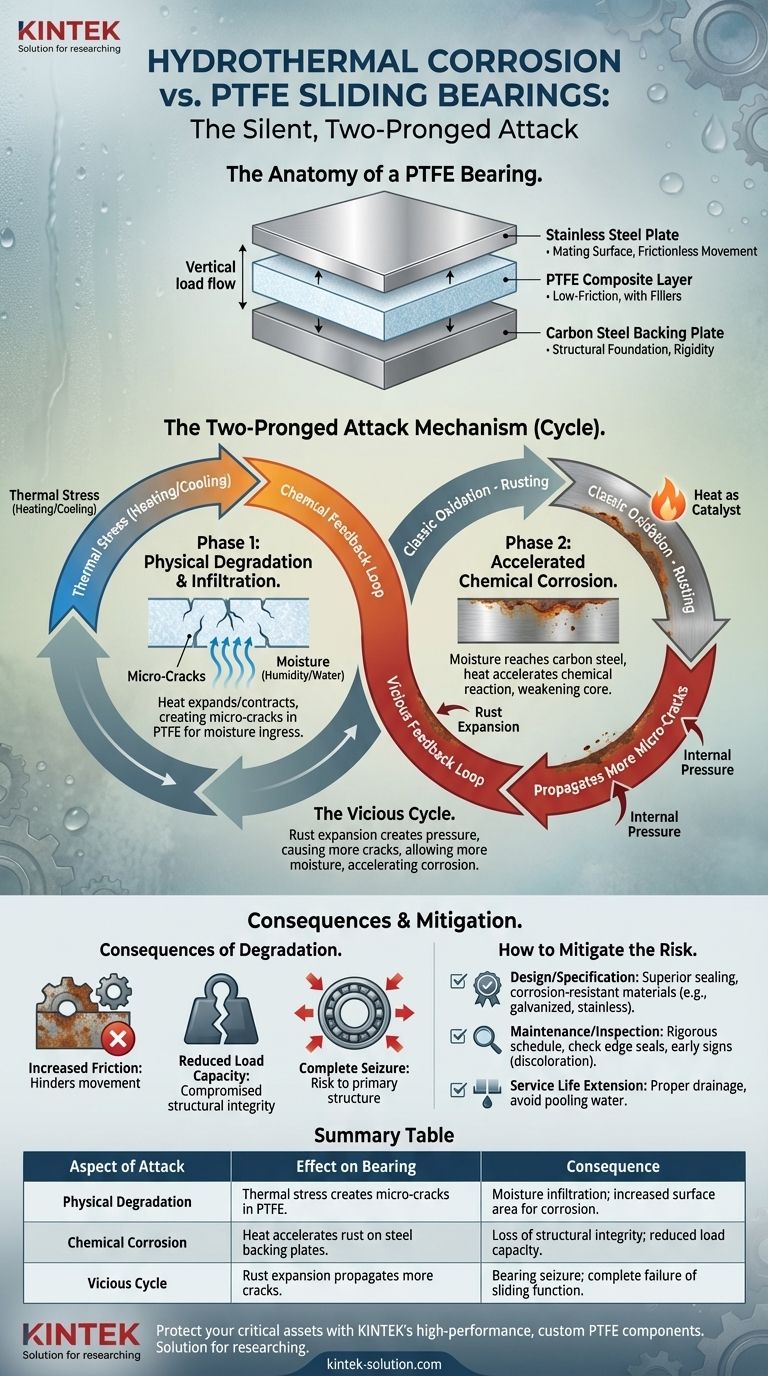
Hydrothermal corrosion attacks PTFE sliding bearings on two fronts. It instigates traditional rust on the structural steel components while simultaneously causing physical degradation of the PTFE composite material itself. The combination of heat and moisture creates a destructive feedback loop where each element accelerates the damage caused by the other.
The primary threat of hydrothermal corrosion isn't from heat or moisture alone, but from their powerful synergistic effect. Thermal stress creates microscopic pathways for moisture to penetrate, while heat accelerates the corrosive chemical reactions, leading to a rapid decline in the bearing's structural integrity and performance.

The Anatomy of a PTFE Bearing
To understand the attack, you must first understand the target. A typical PTFE sliding bearing is a layered assembly, with each part playing a distinct role.
The Steel Backing Plates
These plates, typically made of carbon steel, form the structural foundation of the bearing. Their primary function is to provide rigidity and transfer the vertical load from the structure to the foundation.
The PTFE Composite Layer
This is the key functional layer, providing an extremely low-friction surface. It is rarely pure PTFE; it includes fillers to improve mechanical properties like resistance to "creep" under load.
The Polished Stainless Steel Plate
A highly polished stainless steel plate mates with the PTFE layer. The interaction between these two surfaces is what allows for near-frictionless translational movement.
The Two-Pronged Attack Mechanism
Hydrothermal corrosion is not a single process but a vicious cycle where physical and chemical degradation reinforce one another.
Phase 1: Physical Degradation and Infiltration
Repeated heating and cooling cause the different materials in the bearing to expand and contract at different rates. This thermal stress creates micro-cracks, particularly within the PTFE composite layer.
Moisture, in the form of humidity or direct water contact, then infiltrates these newly created cracks. This dramatically increases the surface area vulnerable to attack.
Phase 2: Accelerated Chemical Corrosion
Once moisture penetrates the PTFE layer and reaches the carbon steel backing plates, classic oxidation—rusting—begins.
Heat acts as a catalyst for this chemical reaction. The warmer the environment, the faster the steel will corrode, weakening the bearing's structural core.
The Vicious Cycle
As rust forms on the backing plate, it expands in volume. This expansion exerts internal pressure on the PTFE layer from behind, creating even more stress and propagating more micro-cracks.
These new cracks allow more moisture to enter, which in turn accelerates the corrosion of the steel. This feedback loop is the primary driver of rapid bearing failure in harsh environments.
The Consequences of Degradation
The end results of this cycle directly compromise the bearing's ability to perform its function.
Increased Friction
Corrosion byproducts (rust) and the physically degraded PTFE surface are no longer smooth. This contamination dramatically increases the coefficient of friction, hindering or preventing the intended sliding motion.
Reduced Load Capacity
The structural integrity of the bearing comes from its steel plates. As corrosion eats away at this steel, the bearing's ability to support its designed vertical load is dangerously compromised.
Complete Seizure
In advanced stages, the combination of high friction and the "jacking" effect of rust expansion can cause the bearing to seize completely. This prevents any movement, transferring immense stress to the primary structure (e.g., bridge girders or building columns) it was designed to protect.
How to Mitigate the Risk
Understanding the failure mechanism allows for targeted strategies in design, inspection, and maintenance.
- If your primary focus is design and specification: Prioritize bearings with superior sealing systems and consider specifying corrosion-resistant materials for the backing plates, such as galvanized or stainless steel.
- If your primary focus is maintenance and inspection: Implement a rigorous inspection schedule focused on checking the integrity of edge seals and looking for early signs of moisture ingress or discoloration (rust staining).
- If your primary focus is extending service life: Ensure proper drainage around the bearing installation to prevent water from pooling, as standing water is a major accelerator of hydrothermal corrosion.
Ultimately, managing hydrothermal corrosion is about controlling the environment and recognizing that the interplay between heat and moisture is the most critical factor in a bearing's long-term durability.
Summary Table:
| Aspect of Attack | Effect on Bearing | Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Degradation | Thermal stress creates micro-cracks in PTFE. | Moisture infiltration; increased surface area for corrosion. |
| Chemical Corrosion | Heat accelerates rust on steel backing plates. | Loss of structural integrity; reduced load capacity. |
| Vicious Cycle | Rust expansion propagates more cracks. | Bearing seizure; complete failure of sliding function. |
Protect your critical assets from hydrothermal corrosion. The failure of a single PTFE sliding bearing can lead to costly downtime and significant structural risk. At KINTEK, we understand the demanding environments faced by the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We manufacture high-performance, custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—engineered for superior corrosion resistance and long-term durability. Whether you need a prototype for testing or a high-volume production run, our precision production ensures reliability.
Don't let corrosion compromise your operations. Contact our experts today to discuss a custom solution tailored to your specific challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















