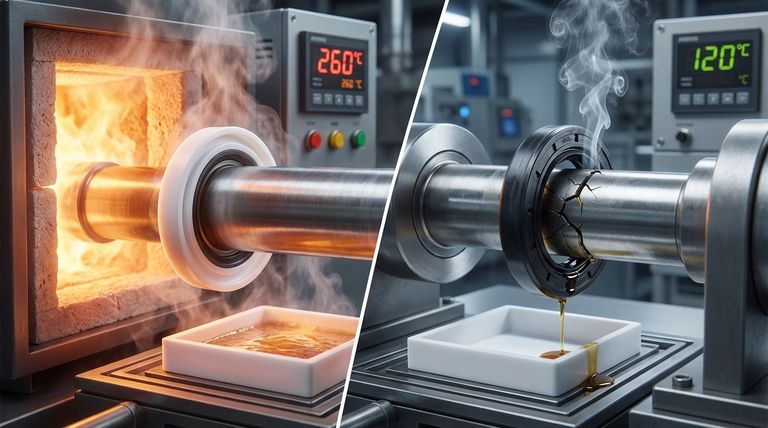
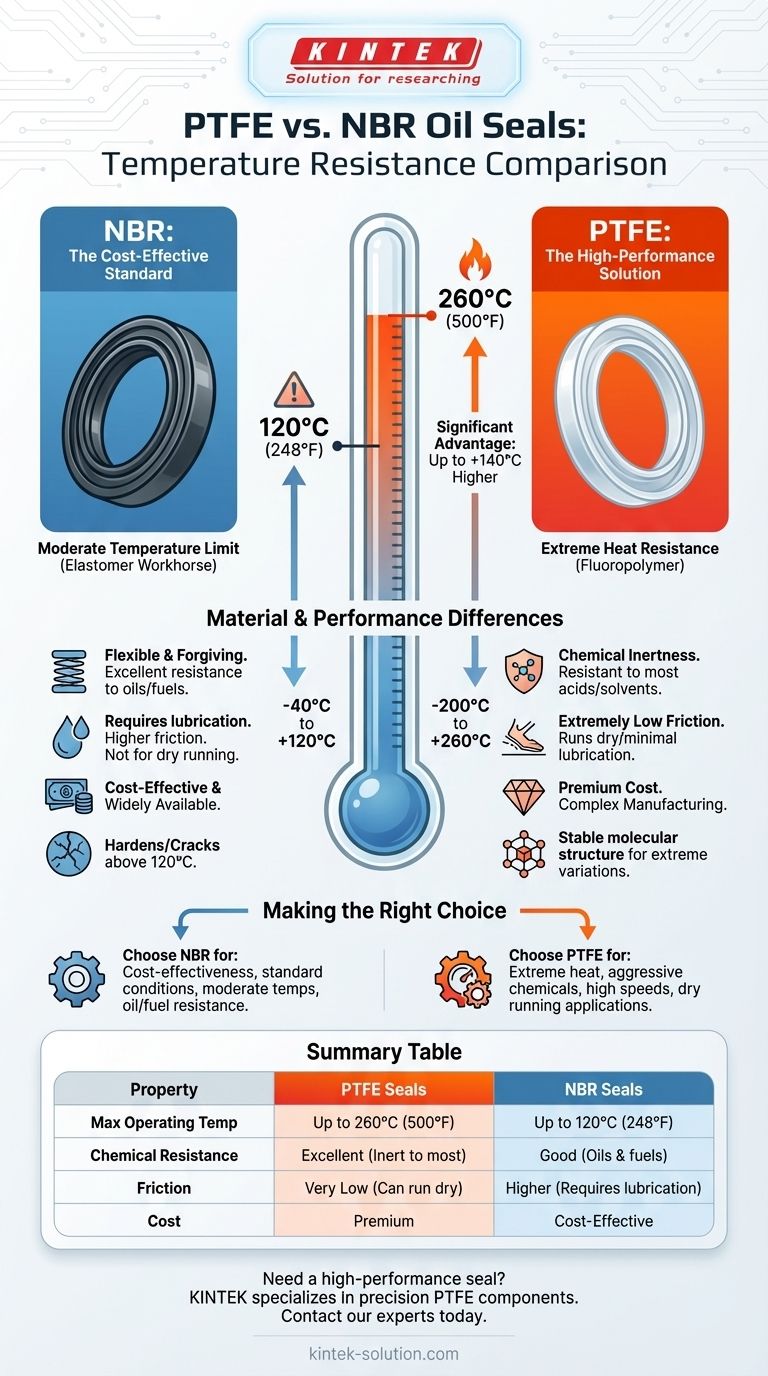
When comparing oil seals, PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) demonstrates significantly higher temperature resistance than NBR (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber). PTFE seals can reliably operate in temperatures up to 260°C (500°F), whereas NBR seals are generally limited to a maximum operating temperature of 120°C (248°F). This fundamental difference makes PTFE the necessary choice for high-heat applications where NBR would quickly fail.
The choice between PTFE and NBR is a classic engineering trade-off. NBR is the cost-effective standard for moderate conditions, while PTFE is the high-performance solution required for extreme temperatures, aggressive chemicals, and low-friction demands.

The Fundamental Material Difference
The performance gap between these two materials stems from their core composition. Understanding this is key to selecting the right seal for your needs.
NBR: The Elastomer Workhorse
NBR, also known as Nitrile rubber, is an elastomer. This gives it excellent flexibility and makes it very forgiving during installation.
It is the most common general-purpose oil seal material due to its excellent resistance to standard petroleum-based oils and fuels in moderate temperature ranges.
PTFE: The High-Performance Polymer
PTFE is a fluoropolymer, a type of plastic known for its exceptional chemical inertness and low coefficient of friction.
Its stable molecular structure is what allows it to withstand extreme temperature variations, from cryogenic lows to high-heat engine and industrial applications.
Performance Under Extreme Conditions
While both materials seal effectively, their operational windows are vastly different.
Temperature Range: PTFE's Clear Advantage
PTFE seals have an exceptionally wide operating temperature range, often cited from -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F).
This thermal stability means they do not harden or lose sealing capability in extreme heat, making them ideal for aerospace, automotive, and heavy industrial machinery.
Temperature Range: NBR's Limitations
NBR seals perform reliably within a more constrained range, typically -40°C to +120°C (-40°F to +248°F).
Exceeding this upper limit will cause the rubber to harden, crack, and lose its sealing ability, leading to inevitable leaks and component failure.
Chemical Resistance
PTFE's chemical inertness makes it resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals, solvents, and acids.
NBR, while robust against standard oils and fuels, can be degraded by more aggressive chemicals or certain additives, limiting its use in harsh chemical environments.
Friction and Lubrication
A key benefit of PTFE is its extremely low friction, which allows it to run dry or with minimal lubrication without generating excessive heat or wear.
In contrast, NBR requires consistent lubrication to prevent overheating and premature failure. It is not suitable for dry-running applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a material is not just about performance; it's also about cost and practicality. Ignoring these trade-offs is a common pitfall.
Cost
This is the most significant trade-off. NBR seals are significantly more affordable and widely available, making them the default choice for budget-conscious and standard applications.
PTFE seals are a premium product. Their complex manufacturing and superior material properties result in a much higher cost per unit.
Installation and Flexibility
The flexibility of NBR makes installation straightforward and less prone to damage. Its elasticity allows it to conform easily to minor imperfections in a shaft or bore.
PTFE is a more rigid material. It requires greater care and proper tools during installation to avoid scratching the sealing lip, which would compromise its performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be driven by the specific demands of the operating environment.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for standard conditions: Choose NBR. Its performance is more than sufficient for applications within its temperature and chemical resistance limits.
- If you are dealing with high temperatures, aggressive chemicals, or both: PTFE is the only reliable option. The higher initial cost prevents catastrophic failure and costly downtime.
- If your application involves high speeds or potential for dry running: Choose PTFE. Its low-friction properties provide a margin of safety that NBR cannot match.
Ultimately, choosing the right seal is about matching the material's capability to the application's true requirements.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE Seals | NBR Seals |
|---|---|---|
| Max Operating Temp | Up to 260°C (500°F) | Up to 120°C (248°F) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (Inert to most chemicals) | Good (Resistant to oils & fuels) |
| Friction | Very Low (Can run dry) | Higher (Requires lubrication) |
| Cost | Premium | Cost-Effective |
Need a high-performance seal for extreme temperatures or harsh chemicals?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our custom fabrication services ensure you get the exact seal you need, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application requirements and discover how our PTFE solutions can enhance your equipment's reliability and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions



















