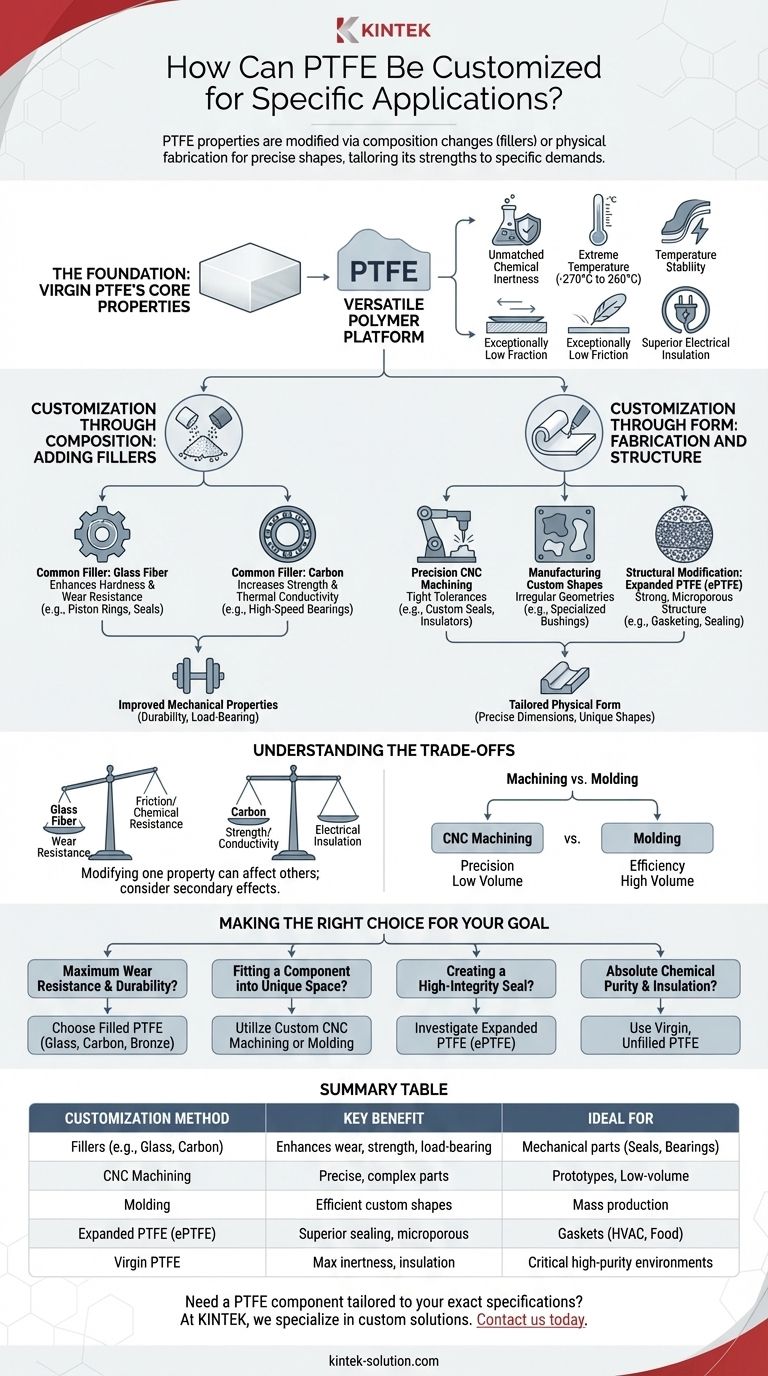
To customize PTFE for a specific application, its properties are modified in two primary ways: by altering its chemical composition with fillers like glass or carbon to enhance characteristics such as wear resistance, or by physically fabricating it into precise, custom shapes and structures through methods like CNC machining. This dual approach allows engineers to tailor PTFE's inherent strengths to meet highly specific performance demands.
The key takeaway is that Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) should not be viewed as a single, static material. Instead, it is a versatile polymer platform that can be precisely engineered through additives and advanced fabrication to solve unique challenges in friction, wear, sealing, and insulation.
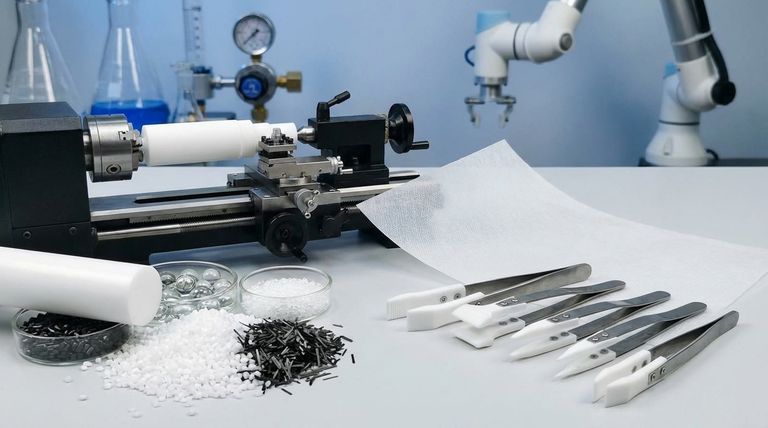

The Foundation: Virgin PTFE's Core Properties
Before exploring customization, it is essential to understand the baseline characteristics of pure, or "virgin," PTFE. These inherent properties are the reason it is selected for high-performance applications in the first place.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually inert, resisting almost all industrial chemicals and solvents. This makes it an ideal material for seals, linings, and components in aggressive chemical processing environments.
Extreme Temperature Stability
The material performs reliably across an exceptionally wide thermal range, from cryogenic conditions (-270°C) up to high-heat applications (260°C), without degrading.
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, making it a premier choice for self-lubricating bearings, bushings, and non-stick surfaces.
Superior Electrical Insulation
With high dielectric strength and electrical resistance, PTFE is a top-tier insulator. It is frequently used for wire insulation and critical components in transformers and electronics where performance cannot be compromised.
Customization Through Composition: Adding Fillers
While virgin PTFE is impressive, its mechanical properties, particularly its resistance to wear and deformation under load, can be significantly improved by compounding it with fillers.
Enhancing Hardness and Wear Resistance
The most common reason to add fillers is to overcome PTFE's relative softness. Additives create a composite material that is far more durable for demanding mechanical applications.
Common Filler: Glass Fiber
Adding glass fiber is a cost-effective way to dramatically increase compressive strength and wear resistance. It is often used in applications like piston rings and seals.
Common Filler: Carbon
Carbon, often in fiber or powder form, is added to increase compressive strength, hardness, and load-bearing capabilities. It also improves thermal conductivity, helping to dissipate heat in high-speed applications.
Customization Through Form: Fabrication and Structure
Beyond its chemical makeup, PTFE's physical form can be precisely controlled to fit unique application requirements.
Precision Machining for Custom Parts
Using CNC machining, stock rods, sheets, and tubes of PTFE can be fabricated into highly specific components. This is ideal for creating custom seals, washers, insulators, and linings with tight tolerances.
Manufacturing Custom Shapes
For components with irregular geometries, PTFE can be molded into custom shapes. This allows for the creation of specialized bushings and bearings that fit perfectly into non-standard housings.
Structural Modification: Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
PTFE can be physically altered to create expanded PTFE (ePTFE), a strong, microporous material. This form is exceptionally well-suited for gasketing and sealing applications across HVAC, chemical, and food processing industries, often replacing older materials like neoprene or asbestos composites.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Customizing PTFE is not without compromise. Modifying the material to enhance one property can have a secondary effect on others, which is a critical consideration for any engineering team.
The Impact of Fillers
While a filler like glass fiber improves wear resistance, it can slightly increase the coefficient of friction and may be less resistant to certain aggressive chemicals, like strong alkalis. Similarly, adding carbon increases strength but also raises electrical conductivity, making it unsuitable for applications requiring high insulation.
Machining vs. Molding
CNC machining offers incredible precision and is ideal for prototyping or low-volume production of complex parts. However, it generates material waste and can be less cost-effective for high-volume runs.
Molding, on the other hand, is highly efficient for mass production but requires significant upfront investment in tooling and is less practical for creating one-off or intricate designs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct PTFE formulation and form depends entirely on the primary goal of your application.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance and durability: Choose a PTFE compound filled with glass, carbon, or bronze.
- If your primary focus is fitting a component into a unique physical space: Utilize custom CNC machining or molding to create a part with precise dimensions.
- If your primary focus is creating a high-integrity seal in a demanding system: Investigate expanded PTFE (ePTFE) for its superior conformity and resilience.
- If your primary focus is absolute chemical purity and electrical insulation: Use virgin, unfilled PTFE to retain its inherent inertness and dielectric properties.
By understanding these customization levers, you can engineer a PTFE solution that precisely matches the demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Customization Method | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Fillers (e.g., Glass, Carbon) | Enhances wear resistance, compressive strength, and load-bearing capacity. | Mechanical parts like seals, bearings, and piston rings. |
| CNC Machining | Creates precise, complex custom parts with tight tolerances. | Prototypes, low-volume orders, and intricate components. |
| Molding | Efficiently produces custom shapes for high-volume runs. | Mass-produced specialized bushings, bearings, and non-standard parts. |
| Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) | Provides a strong, microporous structure for superior sealing. | Gaskets and seals in HVAC, chemical, and food processing industries. |
| Virgin PTFE | Maintains maximum chemical inertness and electrical insulation. | Critical components in aggressive chemical or high-purity environments. |
Need a PTFE component tailored to your exact specifications?
At KINTEK, we specialize in custom PTFE solutions for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require virgin PTFE for unmatched chemical resistance or a filled compound for enhanced durability, our precision manufacturing and custom fabrication services—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensure your components meet the highest performance standards.
Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how our expertise can solve your unique challenges in friction, wear, sealing, and insulation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials



















