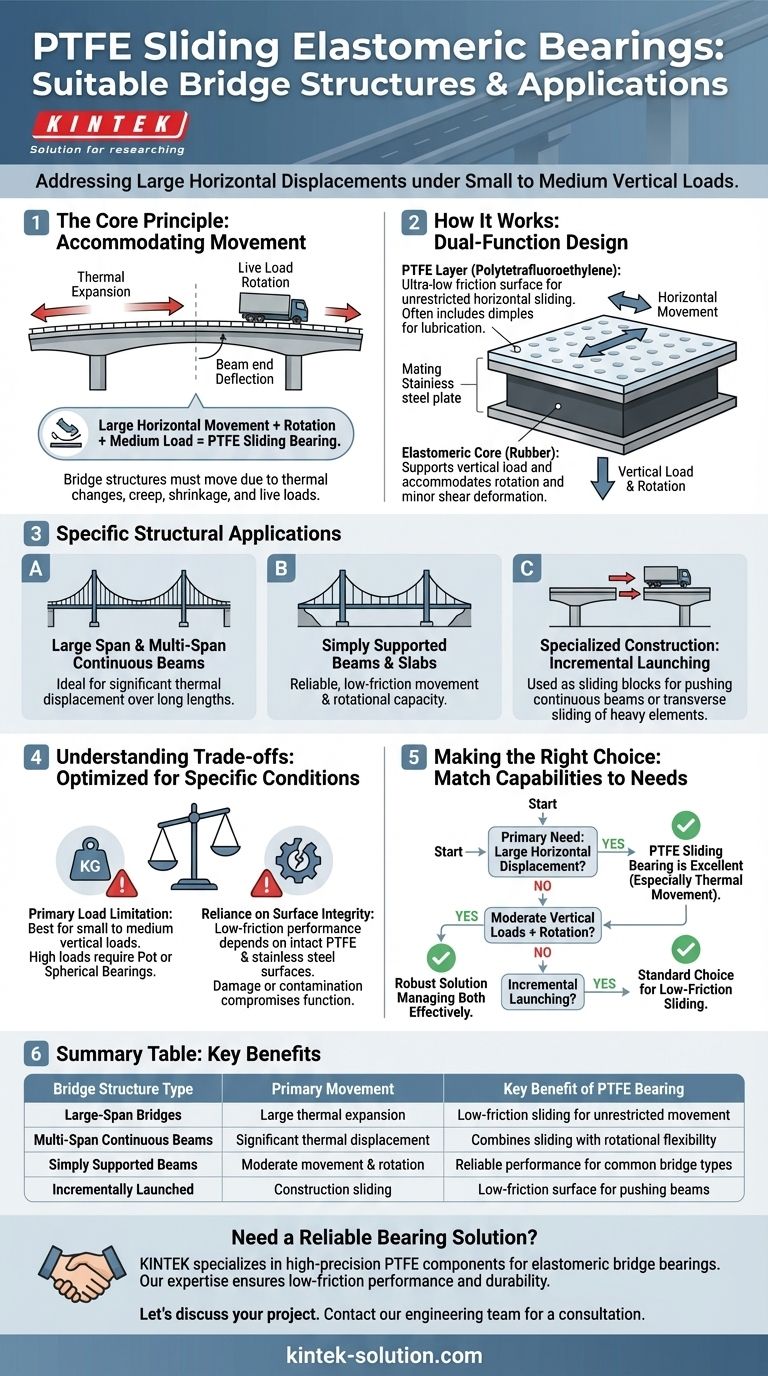
To be precise, PTFE sliding elastomeric bearings are suitable for bridge structures that experience large horizontal displacements under small to medium vertical loads. This includes a wide range of common structures such as large-span bridges, multi-span continuous beams, simply supported beams, and continuous slabs where significant movement from thermal changes, creep, or shrinkage must be accommodated without inducing harmful stress.
The core principle is simple: adding a low-friction PTFE surface to a standard elastomeric bearing allows the structure to slide freely and rotate as needed. This makes them the ideal solution for bridges that must manage significant horizontal movement without being restricted by bearing friction.

The Core Problem: Accommodating Bridge Movement
Bridges are not static structures. They must be designed to move in response to a variety of forces, and bearings are the critical interface that allows this movement to occur safely.
Thermal Expansion and Contraction
The most significant source of movement in many bridges is thermal fluctuation. As materials heat up, they expand, and as they cool, they contract, causing the bridge deck to lengthen and shorten.
Rotational and Live Load Demands
As vehicles (live loads) cross a bridge, the ends of the beam sections deflect and rotate slightly. The bearing must be flexible enough to adapt to this constant rotational movement without degrading.
How PTFE Bearings Provide a Solution
A PTFE sliding elastomeric bearing intelligently combines two materials to solve two different problems simultaneously: horizontal movement and vertical load/rotation.
The Role of the PTFE Layer
The top layer of the bearing is made of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), a material with an exceptionally low coefficient of friction. This layer allows the bridge superstructure to slide back and forth with minimal resistance.
Often, this PTFE surface will have dimples pressed into it which act as reservoirs for a long-lasting silicone lubricant, further reducing friction and ensuring smooth movement over the life of the bearing.
The Function of the Elastomer Core
Beneath the PTFE is the elastomeric pad (typically a high-quality neoprene or natural rubber). This rubber core supports the vertical load from the bridge and provides the flexibility needed to absorb beam-end rotations.
The elastomer's ability to deform under shear also allows it to accommodate some horizontal displacement itself, working in tandem with the sliding PTFE layer.
Combining Sliding with Flexibility
This combination is what makes the design so effective. The PTFE layer handles the large, unrestricted horizontal sliding, while the elastomer core handles the vertical loads, rotation, and minor shear deformations. This separation of functions creates a highly efficient and durable bearing.
Specific Structural Applications
This design makes PTFE bearings a versatile choice for many common bridge types and even specialized construction methods.
Large Span and Multi-Span Continuous Beams
These structures accumulate significant thermal movement over their long lengths. PTFE bearings are ideal because they can easily accommodate these large expansion and contraction displacements.
Simply Supported Beams and Slabs
While the displacement needs may be less than in very long spans, PTFE bearings are still an excellent choice for simply supported structures, providing reliable, low-friction movement and rotational capacity.
Specialized Construction Uses
During construction, these bearings can be used as sliding blocks for incrementally launched bridges (pushing continuous beams into place) or for the transverse sliding of heavy T-shaped beams into their final position.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, it's critical to recognize that PTFE elastomeric bearings are not the solution for every scenario. Their design is optimized for a specific set of conditions.
Primary Load Limitation
The most significant factor is their suitability for small to medium vertical loads. The elastomer pad itself is the primary load-bearing component. For bridges with extremely high vertical reactions, other bearing types like Pot Bearings or Spherical Bearings are generally required.
Reliance on Surface Integrity
The low-friction performance is entirely dependent on the integrity of the PTFE and its mating stainless steel surface. Any significant damage or contamination of these sliding surfaces can compromise the bearing's primary function.
Making the Right Choice for Your Structure
Selecting the correct bearing requires a clear understanding of your primary structural demand.
- If your primary focus is accommodating large horizontal displacement: These bearings are an excellent and cost-effective choice, especially where thermal movement is the dominant design factor.
- If you have moderate vertical loads combined with rotation: The flexible elastomer core and sliding top surface provide a robust solution that manages both movements effectively.
- If your design involves incremental launching or transverse sliding: Their low-friction properties make them a standard choice for these specialized construction techniques.
By correctly matching the bearing's capabilities to the bridge's specific needs for movement and load, you ensure the long-term health and durability of the entire structure.
Summary Table:
| Bridge Structure Type | Primary Movement Accommodated | Key Benefit of PTFE Bearing |
|---|---|---|
| Large-Span Bridges | Large thermal expansion/contraction | Low-friction sliding for unrestricted movement |
| Multi-Span Continuous Beams | Significant thermal displacement | Combines sliding with rotational flexibility |
| Simply Supported Beams/Slabs | Moderate movement and rotation | Reliable performance for common bridge types |
| Incrementally Launched Bridges | Construction sliding | Low-friction surface for pushing beams into place |
Need a Reliable Bearing Solution for Your Bridge Project?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including the critical sliding surfaces for elastomeric bridge bearings. Our expertise ensures your bearings deliver the low-friction performance and durability required for long-span, multi-span, and simply supported bridge structures.
We provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, prioritizing precision for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
Let's discuss how our PTFE components can enhance your next project. Contact our engineering team today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















