In essence, resistance to chemical and physical corrosion is the defining characteristic that makes PTFE a premier gasket material. This resistance is critical because it ensures the gasket maintains its structural integrity and sealing capability when exposed to aggressive media. Without it, the gasket would degrade, leading to leaks, equipment failure, and potential safety hazards.
The importance of corrosion resistance in PTFE gaskets goes beyond simple material longevity. It is the foundation of operational reliability, ensuring a stable, inert seal that prevents costly failures and maintains system purity in the most demanding chemical environments.

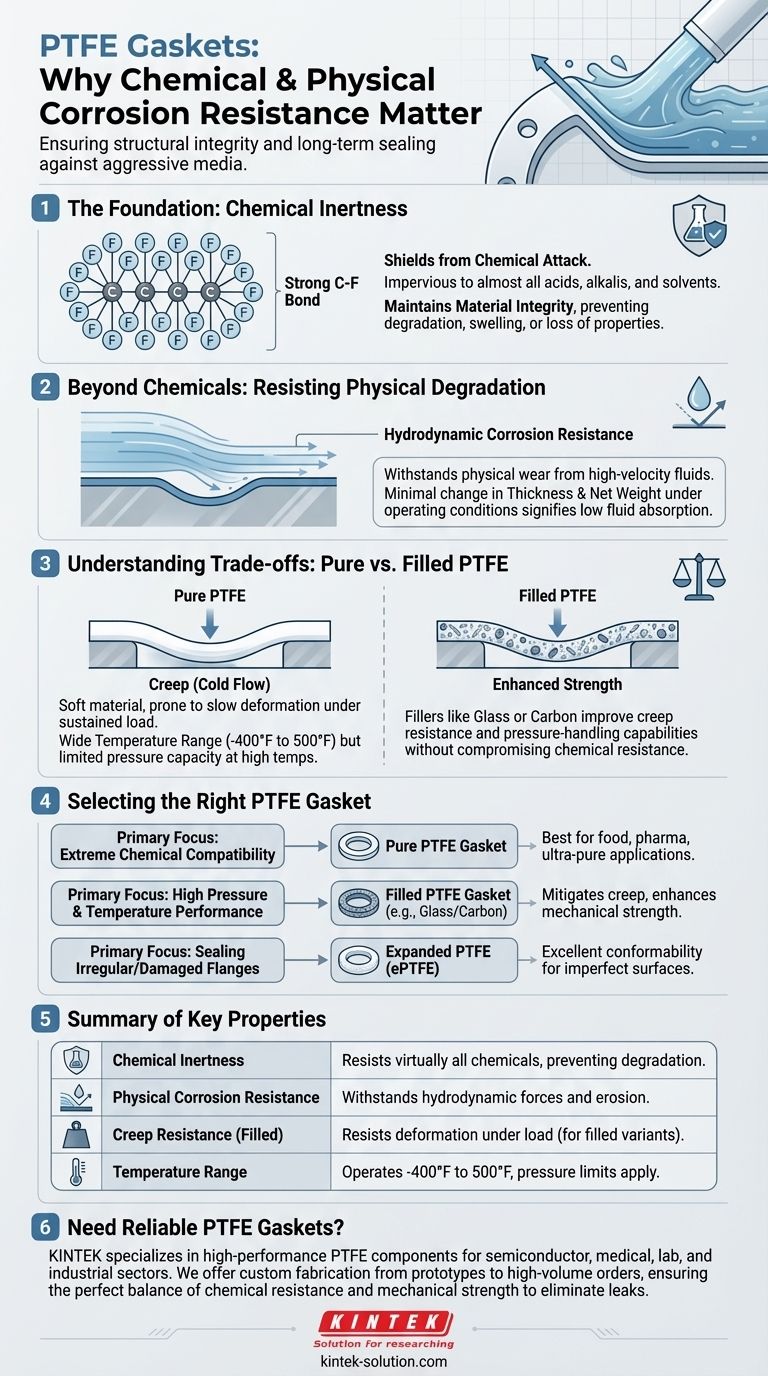
The Foundation of PTFE's Resilience: Chemical Inertness
The remarkable performance of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) stems from its unique molecular structure, which makes it one of the most chemically inert polymers available.
The Fluorocarbon Bond
At its core, PTFE consists of a chain of carbon atoms completely surrounded by fluorine atoms. The carbon-fluorine bond is exceptionally strong and stable.
This structure creates a non-reactive surface that effectively shields the material from chemical attack.
Impervious to Aggressive Media
PTFE is virtually impervious to almost all industrial chemicals, including strong acids, aggressive alkalis, corrosive gases, and solvents.
Its non-reactive nature means it will not degrade, swell, or lose its essential properties even after continuous exposure to these substances. This makes it superior to many other high-performance plastics.
Maintaining Material Integrity
This chemical resistance ensures the gasket retains its plasticity and mechanical properties over time.
A material that degrades becomes brittle or soft, compromising its ability to maintain a seal. PTFE's inertness prevents this from happening.
Beyond Chemicals: Resisting Physical Degradation
While chemical attack is a primary concern, physical forces within a system can also contribute to a gasket's failure. PTFE's properties provide a robust defense against this as well.
Understanding Hydrodynamic Corrosion
Hydrodynamic corrosion refers to the physical wear and material loss caused by the force and flow of fluids within a system.
High-velocity or turbulent fluids can slowly erode a gasket material, leading to a loss of sealing pressure and eventual leaks.
Measuring Physical Resistance
A key indicator of a material's resistance to this physical infiltration is its change in thickness and net weight after being submerged in the operating liquid.
A high-quality PTFE raw material will show minimal to no increase, signifying that it is not absorbing the fluid or being physically compromised by it.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Pure PTFE Limitations
While its chemical resistance is nearly absolute, it is critical to understand the mechanical limitations of pure, or "virgin," PTFE, especially in demanding applications.
The Challenge of Creep (Cold Flow)
Pure PTFE is a relatively soft material. Under sustained mechanical load, especially at elevated temperatures, it can be prone to creep, also known as cold flow.
This is a slow deformation of the material, which can cause the gasket to thin out and lose its sealing force, resulting in a leak.
Temperature and Pressure Boundaries
Although PTFE has an exceptionally wide operating temperature range (from -400°F to 500°F), its ability to handle pressure decreases significantly at higher temperatures.
The Pr value, which combines pressure and temperature ratings, must be carefully considered during selection, as pure PTFE is generally not suitable for simultaneous high-pressure and high-temperature service.
The Role of Fillers
To overcome the mechanical limitations of pure PTFE, manufacturers often add fillers like glass, carbon, or graphite.
These fillers significantly improve the gasket's resistance to creep and increase its pressure-handling capabilities without substantially compromising its chemical resistance.
Selecting the Right PTFE Gasket for Your Application
Choosing the correct gasket material involves matching its properties to the specific demands of your operational environment.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical compatibility: Pure, virgin PTFE is often the best choice for its unparalleled chemical inertness, especially in food, pharmaceutical, or ultra-pure applications.
- If your primary focus is performance under high pressure and temperature: Select a filled PTFE gasket (e.g., glass or carbon-filled) to mitigate creep and enhance mechanical strength.
- If your primary focus is sealing irregular or damaged flanges: Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) provides excellent corrosion resistance with superior conformability to create a tight seal on imperfect surfaces.
Ultimately, understanding these properties empowers you to select a gasket that ensures both safety and long-term operational reliability.
Summary Table:
| Property | Importance for PTFE Gaskets |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists virtually all acids, alkalis, and solvents, preventing degradation. |
| Physical Corrosion Resistance | Withstands hydrodynamic forces and erosion, maintaining seal integrity. |
| Creep Resistance (with fillers) | Filled PTFE variants resist deformation under sustained load for high-pressure applications. |
| Temperature Range | Operates effectively from -400°F to 500°F, with pressure limits considered. |
Need a PTFE gasket that guarantees reliability in your specific application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including seals and gaskets, tailored for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your gasket provides the perfect balance of chemical resistance and mechanical strength, whether you require pure PTFE for extreme chemical compatibility or a filled formulation for enhanced pressure and temperature performance.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, prioritizing precision to meet your exact specifications. Let us help you eliminate leaks and ensure long-term system integrity.
Contact our experts today for a consultation to discuss your requirements and receive a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















