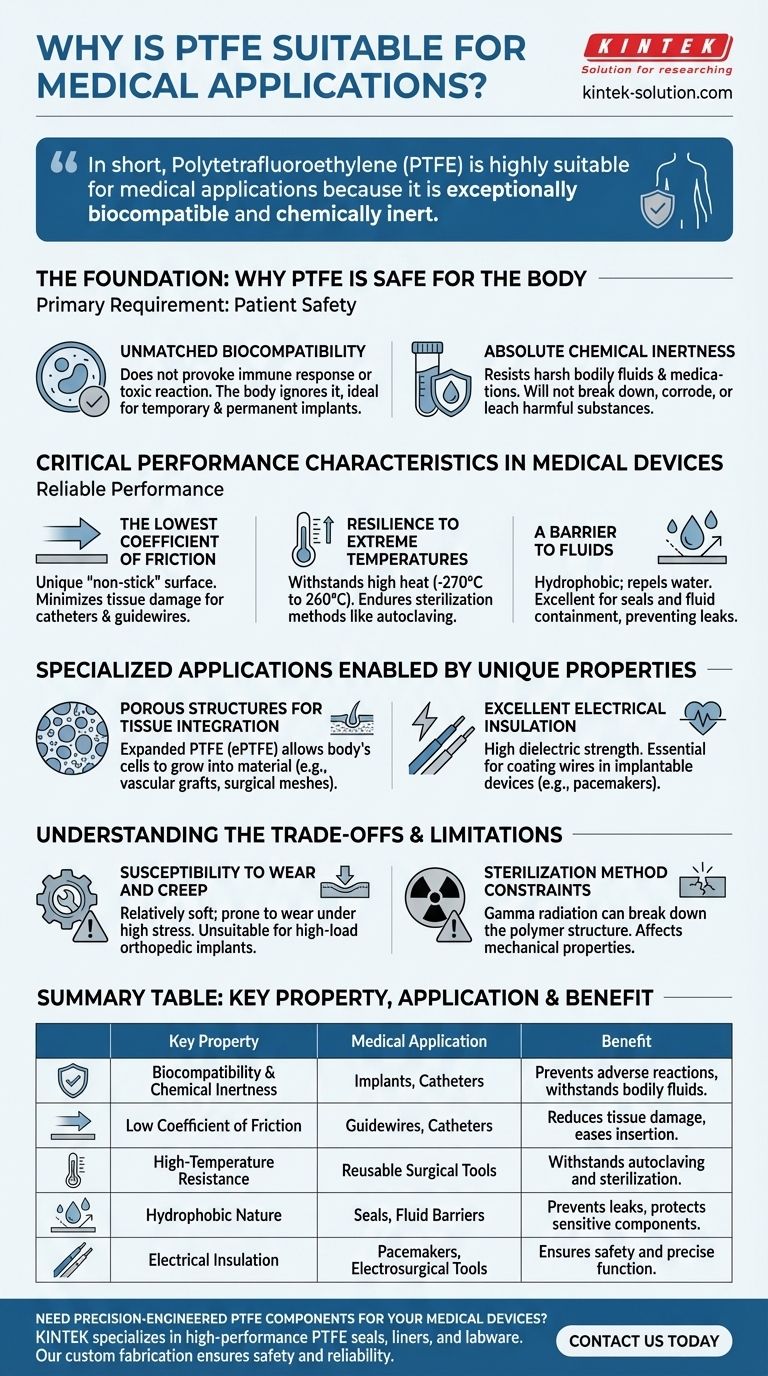
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is highly suitable for medical applications because it is exceptionally biocompatible and chemically inert. This means it does not cause adverse reactions within the human body and does not degrade when exposed to bodily fluids or aggressive sterilization processes. Its unique combination of safety and high-performance properties makes it a trusted material for everything from simple syringes to life-saving implants.
The core reason for PTFE's widespread adoption in medicine is not a single feature, but its rare combination of biological safety, chemical stability, and an extremely low-friction surface. This trio of properties solves multiple critical challenges in medical device design simultaneously.
The Foundation: Why PTFE Is Safe for the Body
The primary requirement for any material used in medicine is that it must not harm the patient. PTFE excels in this area due to two fundamental characteristics.
Unmatched Biocompatibility
Biocompatibility means the material does not provoke an immune response or toxic reaction when it comes into contact with living tissue.
PTFE is one of the most inert materials known. The body largely ignores its presence, making it ideal for both temporary devices and permanent implants.
Absolute Chemical Inertness
Medical devices are exposed to a harsh environment, including bodily fluids, medications, and powerful cleaning agents.
PTFE’s chemical resistance ensures it will not break down, corrode, or leach harmful substances over its intended lifespan, guaranteeing the material's stability and the patient's safety.
Critical Performance Characteristics in Medical Devices
Beyond being safe, a medical material must perform its function reliably. PTFE's physical properties are perfectly suited for many demanding medical roles.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid, giving it a uniquely slippery, "non-stick" surface.
This property is critical for devices like catheters and guidewires, which must pass through blood vessels and other sensitive tissues with minimal irritation or damage. It also reduces the chance of blockages.
Resilience to Extreme Temperatures
Medical equipment must be sterilized to prevent infection, a process that often involves high heat or harsh chemicals.
PTFE can withstand an extremely wide thermal range (from -270°C to 260°C), allowing it to endure common sterilization methods like autoclaving (steam sterilization) without losing its integrity.
A Barrier to Fluids
PTFE is hydrophobic, meaning it repels water and other fluids.
This makes it an excellent material for seals and containment vessels, preventing leaks and protecting sensitive components from fluid damage.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly versatile, PTFE is not the solution for every medical challenge. Understanding its limitations is key to its proper application.
Susceptibility to Wear and Creep
PTFE is a relatively soft material. In applications involving high mechanical stress or abrasive forces, it can be prone to wear. It can also "creep" or slowly deform under a constant load, making it unsuitable for certain high-load-bearing orthopedic implants.
Sterilization Method Constraints
While its temperature resistance is excellent for steam autoclaving, PTFE can be degraded by other sterilization methods. Gamma radiation, a common technique for single-use devices, can break down the polymer's structure and compromise its mechanical properties.
Specialized Applications Enabled by Unique Properties
The base properties of PTFE have been adapted to create advanced materials for specific medical needs.
Porous Structures for Tissue Integration
PTFE can be processed into a microporous form known as expanded PTFE (ePTFE).
This structure allows the body's own cells to grow into the material, which is invaluable for applications like vascular grafts, surgical meshes, and ligament replacements where integration with the body is desired.
Excellent Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an exceptional electrical insulator, a property known as high dielectric strength.
This makes it essential for coating wires and components in electrosurgical tools and implantable electronic devices like pacemakers, where precise electrical isolation is critical for safety and function.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The suitability of PTFE depends entirely on the specific requirements of the medical device or application.
- If your primary focus is patient-contact devices (catheters, sutures): Its biocompatibility and low-friction surface are the most critical factors to prevent tissue irritation and ensure smooth delivery.
- If your primary focus is implantable devices (vascular grafts): Its chemical inertness and ability to be formed into porous structures for tissue integration are paramount for long-term safety and performance.
- If your primary focus is reusable equipment (surgical tools, vessels): Its resistance to chemicals and high temperatures makes it ideal for withstanding repeated, harsh sterilization cycles.
Ultimately, PTFE's unique combination of safety and high-performance characteristics has established it as a cornerstone material for modern medical innovation.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Medical Application | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Biocompatibility & Chemical Inertness | Implants, catheters | Prevents adverse reactions, withstands bodily fluids |
| Low Coefficient of Friction | Guidewires, catheters | Reduces tissue damage, eases insertion |
| High-Temperature Resistance | Reusable surgical tools | Withstands autoclaving and sterilization |
| Hydrophobic Nature | Seals, fluid barriers | Prevents leaks, protects sensitive components |
| Electrical Insulation | Pacemakers, electrosurgical tools | Ensures safety and precise function |
Need precision-engineered PTFE components for your medical devices? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE seals, liners, and labware for the medical, semiconductor, and laboratory industries. Our custom fabrication services—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensure your devices meet the highest standards of safety and reliability. Contact us today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Magnetic Stirring Bar
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















