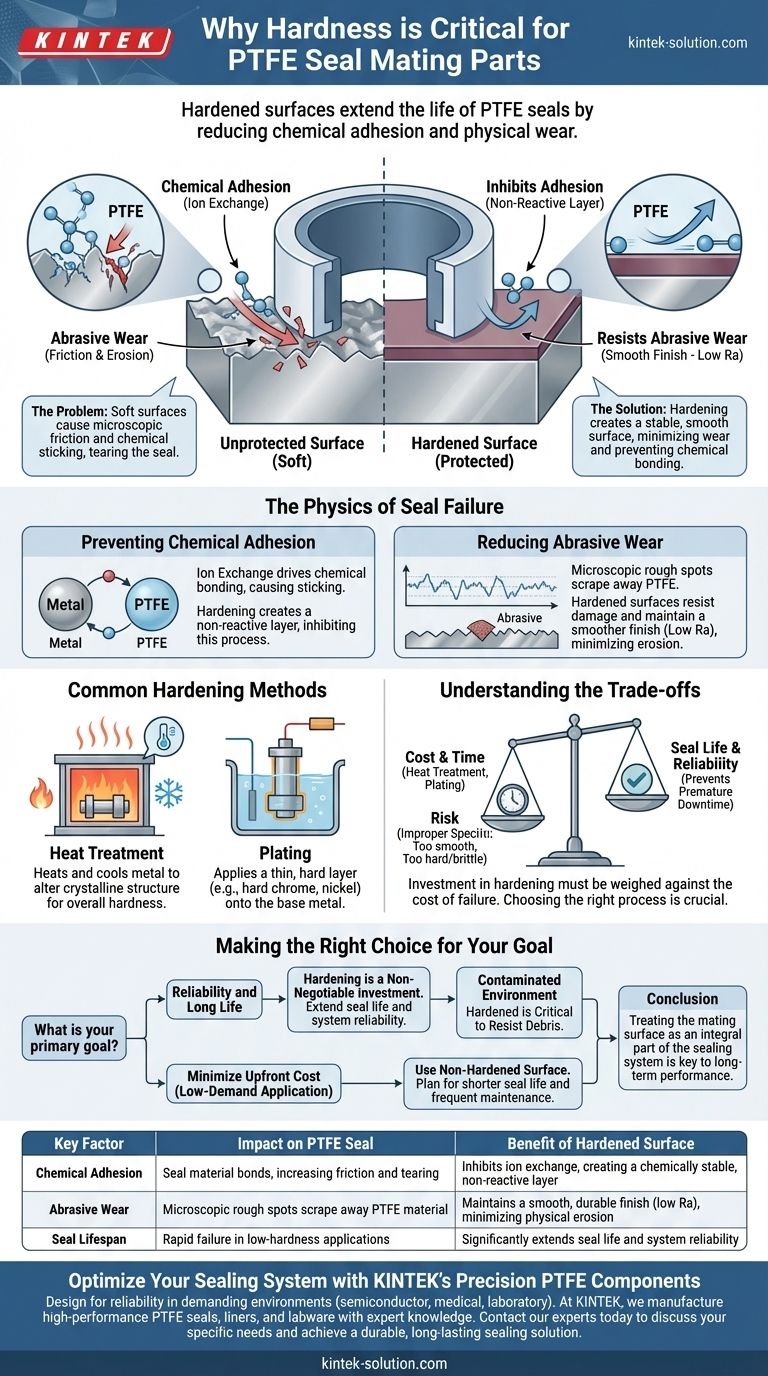
In short, hardness is critical for PTFE seal mating parts because it directly extends the life of the seal. A hardened surface significantly reduces the two primary causes of seal failure: chemical adhesion and physical wear. This ensures a more reliable and durable sealing system over time.
The core problem isn't just about preventing scratches. A harder mating surface creates a more stable environment, minimizing both the microscopic friction that causes abrasive wear and the chemical ion exchange that makes the seal stick to the surface and tear itself apart.

The Physics of Seal Failure
A seal's performance is fundamentally tied to the quality of the surface it runs against. While PTFE is a low-friction material, it is also relatively soft. A mating surface that is not properly prepared can rapidly destroy it through two distinct mechanisms.
Preventing Chemical Adhesion
Adhesion is a subtle but destructive process where the seal material chemically bonds to the mating surface.
This is often driven by ion exchange, a process where molecules are shared between the softer metal of an unhardened part and the seal material. This creates a microscopic "sticking" effect that increases friction and can cause the seal to tear.
Hardening a surface, either through heat treatment or plating, creates a more chemically stable and non-reactive layer. This stable surface inhibits ion exchange, preventing the root cause of adhesion.
Reducing Abrasive Wear
Abrasive wear is the physical erosion of the seal material. It's like rubbing an eraser against sandpaper.
A soft mating surface is prone to scratches and imperfections. Under pressure, these microscopic rough spots act like cutting tools, physically scraping away the PTFE material with every cycle.
A hardened surface is much more resistant to damage and can maintain a smoother finish (measured in Ra, or Roughness average). This smooth, durable surface provides an ideal path for the seal, minimizing physical wear.
Common Hardening Methods
Achieving the necessary surface hardness is a standard manufacturing step for high-performance sealing applications. The goal is to create a durable surface without making the entire component brittle.
Heat Treatment
This process involves heating and then cooling a metal under tightly controlled conditions. It alters the crystalline structure of the material itself, increasing its overall hardness and durability.
Plating
Plating involves applying a thin layer of a much harder material, such as hard chrome or nickel, onto the base metal of the component. This creates an extremely hard and smooth external surface specifically for the seal to run against, while the underlying component retains its original properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While hardening is highly beneficial, it's an engineering decision that involves balancing performance requirements with other factors.
The Impact of Cost
Both heat treatment and plating are additional manufacturing processes that add cost and time to production. This investment must be weighed against the cost of premature seal failure and system downtime.
The Risk of Improper Specification
Choosing the wrong hardening process or surface finish can be counterproductive. For example, some plating can be too smooth, preventing a necessary lubrication film from forming. A surface that is too hard but also brittle can crack under high loads.
When Maximum Hardness Isn't Necessary
In very low-speed, low-pressure, or non-critical applications, the added expense of hardening may not provide a proportional return on investment. However, these situations are the exception, not the rule for dynamic seals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to harden a mating surface should be based on the demands of the application and the desired lifespan of the system.
- If your primary focus is reliability and long life: Hardening the mating surface to the recommended specification is a non-negotiable investment.
- If your primary focus is minimizing upfront cost for a low-demand application: You may use a non-hardened surface, but you must plan for a significantly shorter seal life and more frequent maintenance.
- If your system operates in a contaminated environment: A hardened surface is absolutely critical to resist the abrasive wear caused by debris.
Ultimately, treating the mating surface as an integral part of the sealing system is key to achieving reliable, long-term performance.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Impact on PTFE Seal | Benefit of Hardened Surface |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Adhesion | Seal material bonds to surface, increasing friction and tearing | Inhibits ion exchange, creating a chemically stable, non-reactive layer |
| Abrasive Wear | Microscopic rough spots scrape away PTFE material | Maintains a smooth, durable finish (low Ra), minimizing physical erosion |
| Seal Lifespan | Rapid failure in low-hardness applications | Significantly extends seal life and system reliability |
Optimize Your Sealing System with KINTEK's Precision PTFE Components
Are you designing for reliability in demanding environments like semiconductor, medical, or laboratory equipment? The right surface hardness for your mating parts is critical to prevent PTFE seal failure.
At KINTEK, we manufacture high-performance PTFE seals, liners, and labware with an expert understanding of material science and application requirements. We can help you select or custom-fabricate components that ensure optimal performance, from prototypes to high-volume production.
Don't let seal failure compromise your system. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and achieve a durable, long-lasting sealing solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the overall operating temperature range for PTFE seals, gaskets, and O-rings? Achieve Sealing Integrity from -200°C to +260°C
- What are the benefits of using PTFE seals? Unmatched Chemical & Temperature Resistance
- What are some common PTFE seal types used in industrial applications? Explore Solutions for Every Motion & Environment
- What are the key properties of PTFE that make it suitable for seals? Unlock Reliability in Extreme Conditions
- What are the key advantages of PTFE rotary seals over traditional rubber seals? Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions



















