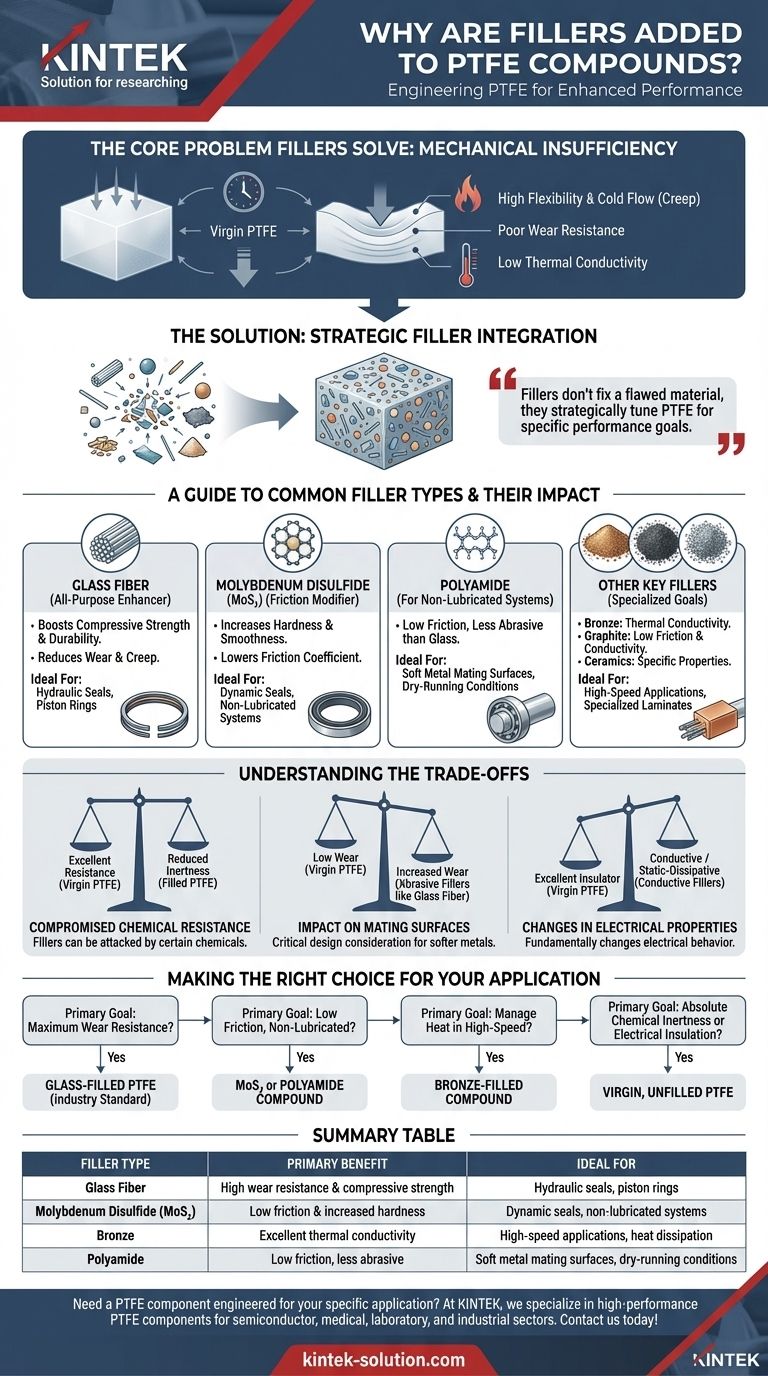
In short, fillers are added to Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) to overcome its inherent mechanical weaknesses. While virgin PTFE has remarkable low-friction and chemical-resistant properties, it is relatively soft and prone to deforming under load—a phenomenon known as "creep" or "cold flow." Adding fillers creates a composite material that enhances critical properties like wear resistance, compressive strength, and thermal conductivity, transforming PTFE into a robust engineering-grade material for demanding applications.
The core purpose of adding fillers is not to fix a flawed material, but to strategically tune PTFE for specific performance goals. This process turns a general-purpose polymer into a specialized compound engineered to withstand mechanical stress, abrasion, and thermal loads that virgin PTFE cannot handle alone.

The Core Problem Fillers Solve: Mechanical Insufficiency
Virgin PTFE is an exceptional material, but its utility is limited by a few key physical characteristics. Fillers are introduced specifically to counteract these limitations.
High Flexibility and Cold Flow (Creep)
Unfilled PTFE will deform permanently when subjected to a sustained compressive load, even at room temperature. This makes it unsuitable for high-load seals or structural components.
Fillers act as a reinforcing matrix within the PTFE, significantly increasing its stiffness and resistance to creep.
Poor Wear Resistance
Despite its famously low coefficient of friction, PTFE is not inherently durable against abrasion. In dynamic applications like bearings or piston rings, it can wear away quickly.
Fillers like glass fiber or molybdenum disulfide drastically improve the material's ability to withstand frictional wear, extending the service life of the component.
Low Thermal Conductivity
PTFE is an excellent thermal insulator. In high-speed applications, friction generates heat that cannot easily escape, which can lead to premature failure.
Thermally conductive fillers like bronze powder help dissipate this heat away from the wearing surface, maintaining mechanical integrity.
A Guide to Common Filler Types and Their Impact
The choice of filler is driven entirely by the demands of the application. Each type imparts a different set of properties to the final compound.
Glass Fiber: The All-Purpose Enhancer
Glass fiber is the most common filler used in PTFE. It provides a significant boost in compressive strength and overall durability.
It is particularly valued for its ability to reduce wear and creep, making it an industry standard for components like hydraulic piston rings.
Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS₂): The Friction Modifier
Often used in combination with other fillers like glass or bronze, MoS₂ increases the hardness and smoothness of the PTFE compound.
Crucially, it accomplishes this while also lowering the coefficient of friction, making it ideal for high-pressure dynamic seals and other low-friction applications.
Polyamide: For Non-Lubricated Systems
Polyamide is a synthetic polymer filler that offers a low friction coefficient and is less abrasive than glass.
This makes it an excellent choice for applications running against softer metal surfaces like aluminum or brass, especially in stop-start or dry-running conditions where lubrication is absent.
Other Key Fillers
Several other fillers are used for specialized purposes. Bronze is added for excellent thermal conductivity, graphite enhances both low friction and conductivity, and ceramics are used to engineer specific thermal or electromagnetic properties in laminates.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Adding fillers is an engineering compromise. Enhancing one property can often come at the expense of another.
Compromised Chemical Resistance
While filled PTFE compounds still offer excellent chemical resistance, they are not as universally inert as virgin PTFE. Certain fillers can be attacked by chemicals that pure PTFE would resist.
Impact on Mating Surfaces
Abrasive fillers, particularly glass fiber, can increase the wear on the mating surface the PTFE component runs against. This is a critical design consideration when working with softer metals.
Changes in Electrical Properties
Virgin PTFE is one of the best electrical insulators available. The addition of conductive fillers like graphite, bronze, or stainless steel will fundamentally change this property, making the compound conductive or static-dissipative.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct PTFE compound requires matching the filler's benefits to your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance in hydraulic systems: Glass-filled PTFE is the industry standard due to its high compressive strength and durability.
- If your primary focus is low friction in a non-lubricated, dynamic seal: A compound with Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS₂) or Polyamide will improve hardness without increasing friction.
- If your primary focus is managing heat in a high-speed application: Consider a bronze-filled compound to improve thermal conductivity and dissipate frictional heat.
- If your primary focus is absolute chemical inertness or electrical insulation: Virgin, unfilled PTFE remains the superior choice, as any filler can compromise these specific properties.
By understanding these strategic enhancements, you can select a PTFE compound engineered precisely for your operational demands.
Summary Table:
| Filler Type | Primary Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Glass Fiber | High wear resistance & compressive strength | Hydraulic seals, piston rings |
| Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS₂) | Low friction & increased hardness | Dynamic seals, non-lubricated systems |
| Bronze | Excellent thermal conductivity | High-speed applications, heat dissipation |
| Polyamide | Low friction, less abrasive | Soft metal mating surfaces, dry-running conditions |
Need a PTFE component engineered for your specific application? At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—from custom seals and liners to specialized labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, our precision production ensures your PTFE parts meet exact performance demands. Contact us today to discuss your project and let our expertise enhance your design!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Crucibles for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers



















