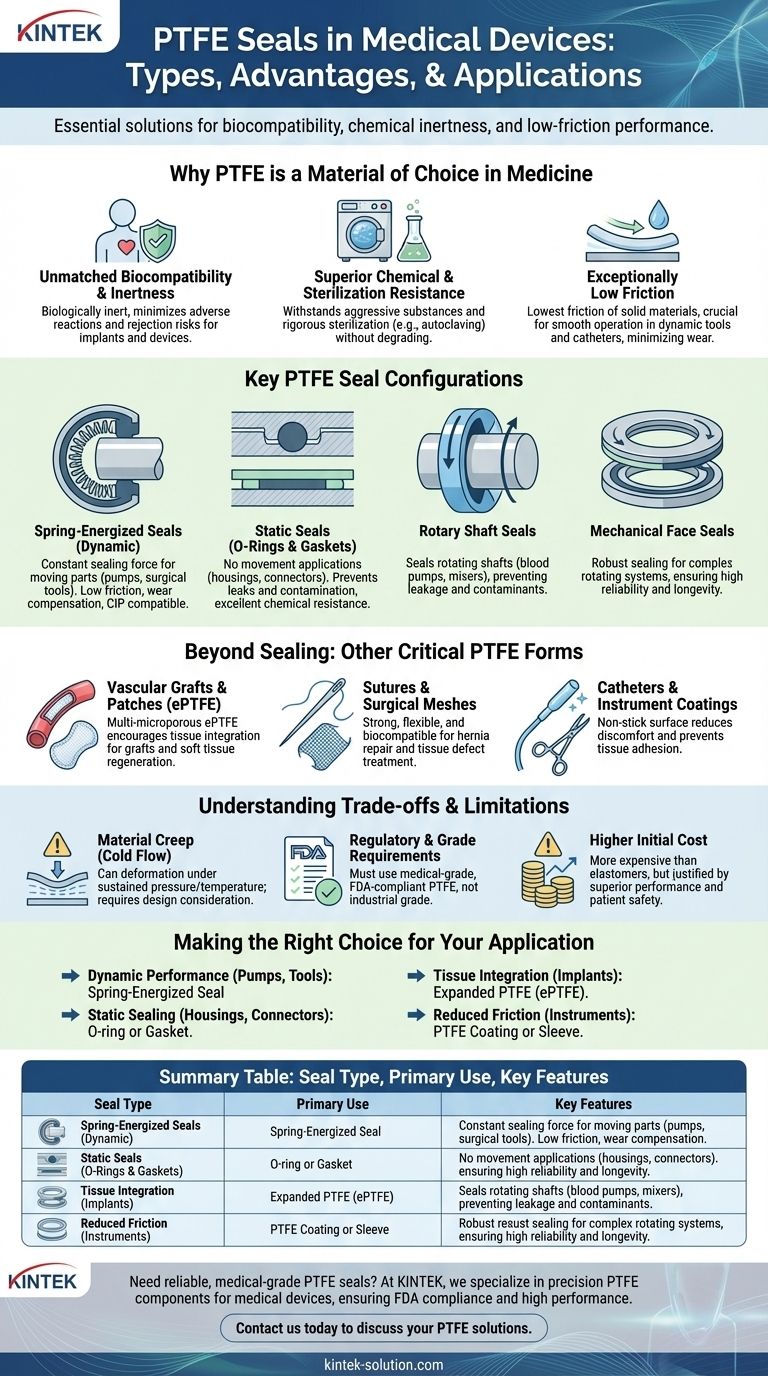
In the medical field, the most common PTFE seals range from simple static O-rings to highly specialized spring-energized seals for dynamic equipment and mechanical face seals for complex rotating systems. These components are chosen for their unique combination of biocompatibility, chemical inertness, and low-friction properties, which are critical for patient safety and device reliability.
The selection of a PTFE seal in a medical context is driven by the application's demands—whether it is static or dynamic, implantable or external—but is always governed by PTFE's fundamental ability to perform reliably without reacting to bodily fluids or harsh sterilization processes.

Why PTFE is a Material of Choice in Medicine
The use of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) in medical devices is not accidental. Its distinct molecular structure gives rise to a set of properties that are uniquely suited for demanding healthcare environments.
Unmatched Biocompatibility and Inertness
PTFE is biologically inert, meaning it has a very low potential to cause an adverse reaction when in contact with human tissue or fluids.
This property is crucial for both short-term devices and long-term implants, as it minimizes the risk of rejection or other physiological side effects.
Superior Chemical and Sterilization Resistance
Medical devices must withstand aggressive substances and rigorous sterilization protocols. PTFE is resistant to virtually all chemicals and can be sterilized by any common method, including autoclaving.
This ensures the material maintains its integrity and purity, which is essential for preventing contamination and ensuring device longevity.
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, often compared to wet ice on wet ice.
This "non-stick" characteristic is vital for dynamic applications, reducing wear on moving parts and minimizing discomfort in devices like catheters.
Key PTFE Seal Configurations in Medical Devices
While the material properties are foundational, the seal's physical design is what enables it to perform a specific function within a medical device.
Spring-Energized Seals (For Dynamic Applications)
These are advanced seals used in equipment with moving parts, such as pumps, surgical tools, and analytical instruments.
A metallic spring energizer provides a constant, uniform sealing force, which compensates for material wear and temperature fluctuations. Their low friction is critical for smooth operation, and many are designed for Clean-in-Place (CIP) protocols.
Static Seals (O-Rings and Gaskets)
For applications with no movement between sealing surfaces, simple static seals like O-rings and gaskets are used.
They are typically found in device housings, fluid connectors, and analytical equipment to prevent leaks and protect internal components from contamination.
Rotary Shaft Seals
These seals are essential for any medical device with a rotating shaft, such as a blood pump or medical mixer.
They prevent leakage of fluids along the shaft while blocking external contaminants. Designs can include single, dual, or custom lip configurations depending on the pressure and fluid environment.
Mechanical Face Seals
In more complex rotating equipment, mechanical face seals provide a robust solution. They are used where two flat surfaces rotate against each other, offering a durable seal for critical applications that demand high reliability and longevity.
Beyond Sealing: Other Critical Forms of PTFE
The same properties that make PTFE an excellent sealing material also make it suitable for other direct-contact medical applications.
Vascular Grafts and Patches
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) features a multi-microporous structure that encourages natural tissue integration.
This makes it an ideal material for manufacturing artificial blood vessels, heart patches, and components for soft tissue regeneration.
Sutures and Surgical Meshes
PTFE's combination of strength, flexibility, and biocompatibility makes it a preferred material for surgical sutures and meshes used to repair hernias and other tissue defects.
Catheters and Instrument Coatings
The low-friction, non-stick surface of PTFE is used to coat medical instruments like catheters and forceps. This reduces patient discomfort and prevents tissue adhesion during medical procedures.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, PTFE is not without its limitations. A clear understanding of these trade-offs is essential for proper device engineering.
Material Creep (Cold Flow)
Under sustained pressure and temperature, PTFE can slowly deform or "creep." This must be accounted for in the design of high-pressure seals to prevent failure over time.
Regulatory and Grade Requirements
Not all PTFE is suitable for medical use. Materials must comply with stringent FDA regulations and safety standards. Using industrial-grade PTFE in a medical device is a critical error.
Higher Initial Cost
Compared to common elastomers, medical-grade PTFE and complex seal designs like spring-energized seals represent a higher initial component cost. However, this is often justified by superior performance, reliability, and patient safety.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct PTFE seal or component requires a clear understanding of the device's primary function and operating environment.
- If your primary focus is dynamic performance in pumps or surgical tools: A spring-energized seal is the standard choice for ensuring a reliable, low-friction seal over millions of cycles.
- If your primary focus is static sealing in a device housing or connector: A simpler and more cost-effective PTFE O-ring or custom gasket will provide excellent chemical resistance and reliability.
- If your primary focus is tissue integration for an implantable device: Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) is the required material for applications like vascular grafts and surgical patches.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction on an instrument: A PTFE coating or sleeve offers a proven method for creating a non-stick, biocompatible surface.
Ultimately, leveraging PTFE successfully in the medical field depends on matching its exceptional properties to the specific demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Seal Type | Primary Use | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Spring-Energized Seals | Dynamic applications (pumps, surgical tools) | Low friction, compensates for wear, ideal for CIP protocols |
| Static Seals (O-rings, Gaskets) | Non-moving parts (device housings, connectors) | Excellent chemical resistance, prevents leaks and contamination |
| Rotary Shaft Seals | Rotating equipment (blood pumps, mixers) | Prevents fluid leakage, blocks contaminants, durable for high-reliability systems |
| Mechanical Face Seals | Complex rotating systems | Robust sealing for flat surfaces, high longevity and performance |
| Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) | Implantable devices (vascular grafts, patches) | Encourages tissue integration, multi-microporous structure |
Need reliable, medical-grade PTFE seals for your device?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—from seals and liners to custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your devices meet stringent FDA regulations and performance demands, with custom fabrication available from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact us today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance your medical device's safety, reliability, and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















