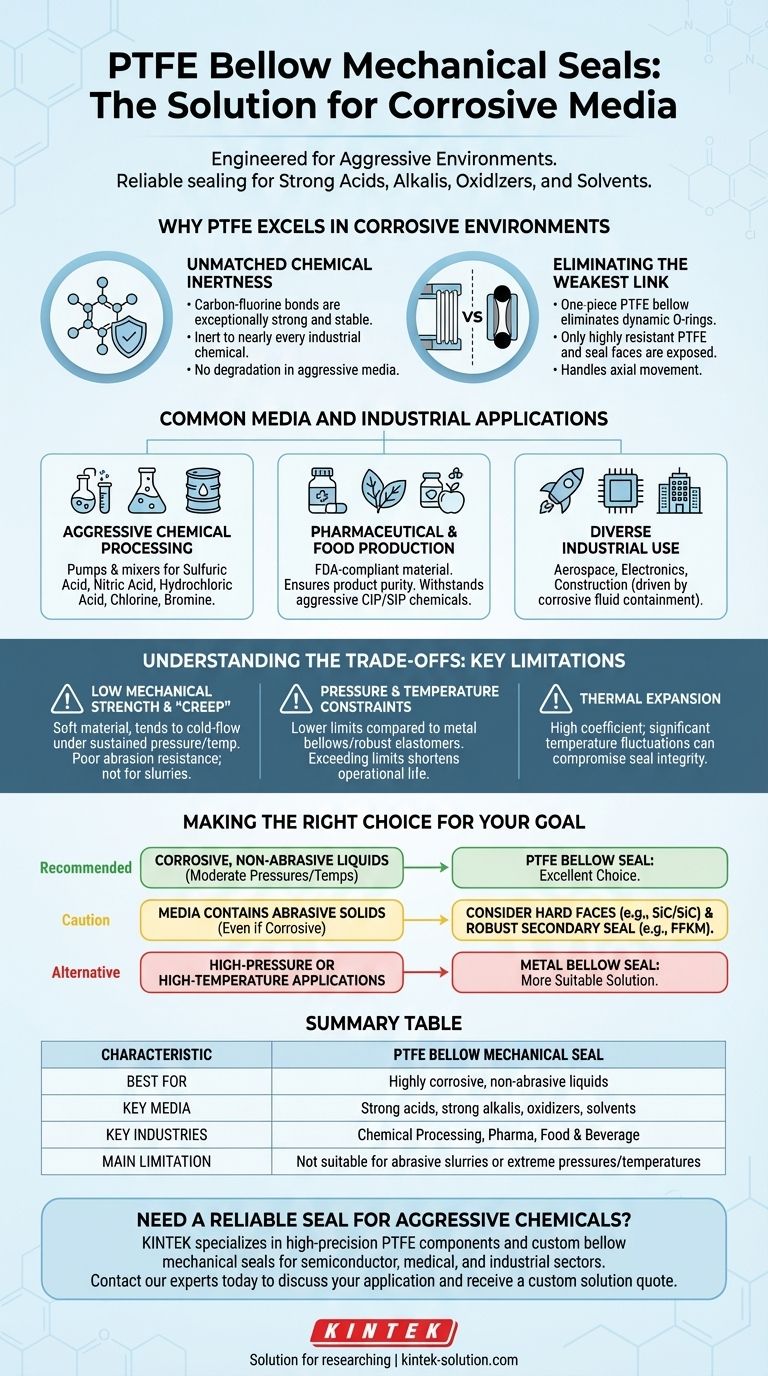
At its core, a PTFE Bellow Mechanical Seal is a specialized solution engineered for the most chemically aggressive environments you can encounter. They are the go-to choice for reliably sealing strong acids, strong oxidizing agents, caustics, and a wide range of other highly corrosive media that would quickly destroy standard seal materials.
A PTFE Bellow Mechanical Seal leverages the near-total chemical inertness of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) to provide a reliable seal in applications where other materials would fail. Its primary purpose is to handle extreme chemical corrosion, not high pressures or abrasive solids.
Why PTFE Excels in Corrosive Environments
Understanding the material science behind PTFE clarifies why it is reserved for such demanding duties. Its performance is a direct result of its unique molecular structure and the clever engineering of the bellow design.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
Often called the "king of plastic," Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is one of the most non-reactive materials known. Its carbon-fluorine bonds are exceptionally strong and stable.
This structure makes it inert to nearly every industrial chemical, including concentrated acids, alkalis, solvents, and oxidizing agents. It can be used in any of these media for extended periods without degrading.
Eliminating the Weakest Link
In many conventional mechanical seals, a secondary seal (typically an O-ring) must slide along the shaft to compensate for wear and movement. This dynamic O-ring is often the first component to fail from chemical attack.
The PTFE bellow seal’s one-piece design eliminates the need for a separate dynamic O-ring. The flexible bellow itself handles axial movement, ensuring that the only material exposed to the aggressive media is the highly resistant PTFE and the seal faces.
Common Media and Industrial Applications
While the primary qualification is "highly corrosive," these seals are found wherever chemical resistance and purity are paramount.
Aggressive Chemical Processing
This is the most common application. PTFE bellow seals are used on pumps and mixers handling substances like sulfuric acid, nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, chlorine, and bromine.
Pharmaceutical and Food Production
In these industries, product purity is non-negotiable. PTFE is an FDA-compliant material that will not contaminate the process fluid.
Furthermore, it can withstand the aggressive Clean-in-Place (CIP) and Sterilize-in-Place (SIP) chemicals used to sanitize equipment between batches.
Diverse Industrial Use
Due to its unique properties, PTFE as a material is found in aerospace, electronics, and construction. However, in the context of a bellow mechanical seal, its application is almost always driven by the need to contain a corrosive fluid.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Key Limitations
No single material is perfect for every situation. The exceptional chemical resistance of PTFE comes with clear mechanical trade-offs that you must consider.
Low Mechanical Strength and "Creep"
PTFE is a relatively soft material. It has a tendency to "creep" or cold-flow under sustained pressure and temperature, which can lead to a loss of seal face flatness and subsequent leakage.
This softness also means it has poor abrasion resistance. It is not a suitable choice for media containing hard, abrasive solids or slurries.
Pressure and Temperature Constraints
Compared to seals made with metal bellows or more robust elastomers, PTFE bellow seals have lower pressure and temperature ratings. Exceeding these limits will accelerate creep and drastically shorten the seal's operational life.
Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a high coefficient of thermal expansion. Significant temperature fluctuations can cause dimensional changes that may compromise the seal's integrity, making stable operating temperatures preferable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a seal requires matching its specific strengths against the demands of your application. A PTFE bellow seal is a powerful tool, but only when used in the right context.
- If your primary focus is sealing highly corrosive, non-abrasive liquids at moderate pressures and temperatures: A PTFE bellow seal is an excellent, and often the only viable, choice.
- If your media contains abrasive solids, even if corrosive: You must consider a seal with hard faces (like Silicon Carbide vs. Silicon Carbide) and a more robust secondary seal material (like a perfluoroelastomer, or FFKM).
- If you are sealing high-pressure or high-temperature applications: A metal bellow seal is likely a more suitable and reliable solution.
Ultimately, proper seal selection is about applying this specialized technology precisely where its unique chemical resilience is the critical factor for success.

Summary Table:
| Characteristic | PTFE Bellow Mechanical Seal |
|---|---|
| Best For | Highly corrosive, non-abrasive liquids |
| Key Media | Strong acids, strong alkalis, oxidizers, solvents |
| Key Industries | Chemical Processing, Pharma, Food & Beverage |
| Main Limitation | Not suitable for abrasive slurries or extreme pressures/temperatures |
Need a reliable seal for aggressive chemicals? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom bellow mechanical seals. Our expertise in custom fabrication for the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors ensures you get a solution engineered for your specific corrosive media and operating conditions.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and receive a custom solution quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE compare to other low-friction plastics like UHMW-PE and Nylon? A Guide to Material Selection
- How is PTFE used in industrial processes? Maximize Safety and Efficiency
- Why is PTFE considered a significant discovery? A Material That Revolutionized Industry
- Why is dimensional stability a concern when machining PTFE? Ensure Accurate, Stable PTFE Components
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation



















