Simply put, PTFE O-Rings repel nearly all common fluids. Their chemical structure makes them one of the most inert and universally compatible sealing materials available. They are only affected by a very small and specific group of substances, such as molten alkali metals and a few rare fluorinated compounds.
The core consideration when selecting PTFE is not its chemical resistance, which is near-universal, but its physical properties. Its stiffness and potential for creep are the true limiting factors in most engineering applications.

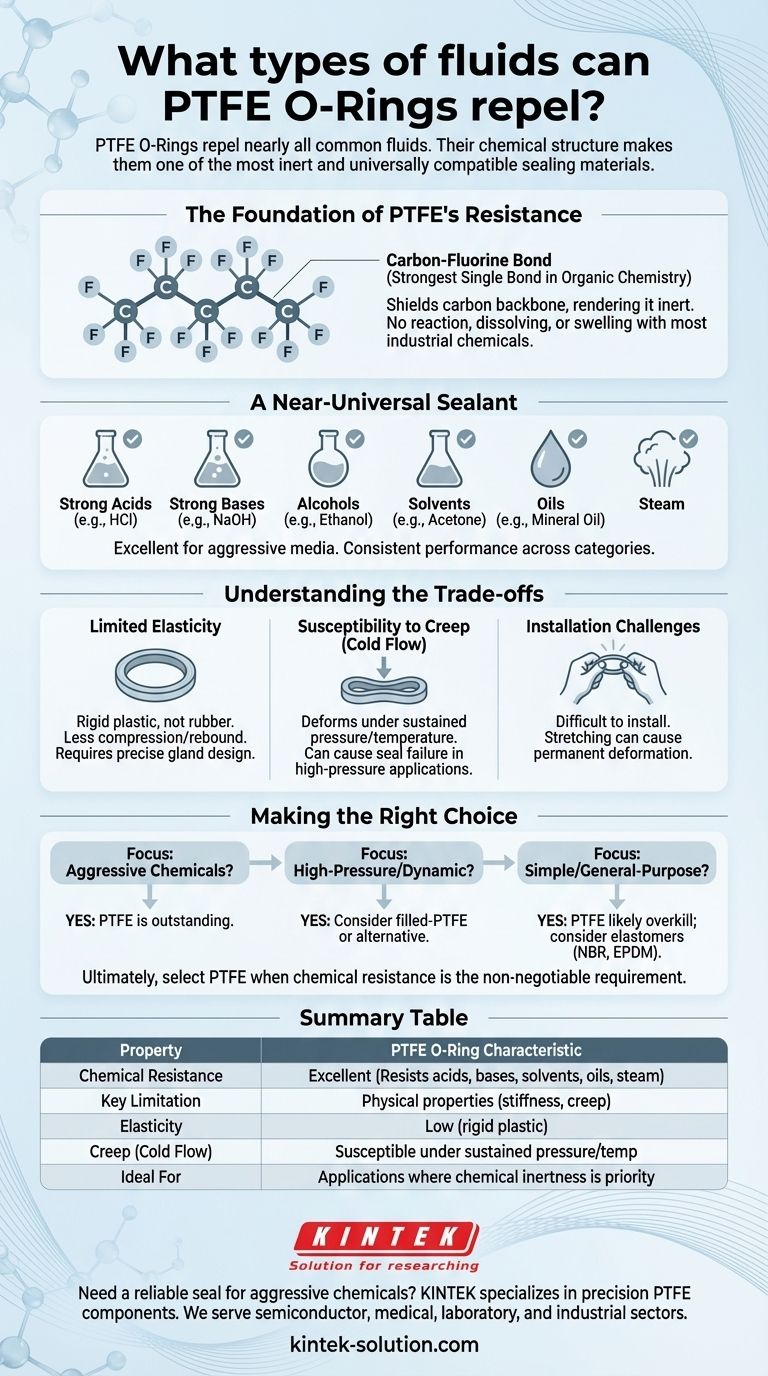
The Foundation of PTFE's Resistance
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a fluoropolymer with unique properties that stem directly from its molecular structure. Understanding this is key to trusting its performance in demanding environments.
The Power of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
The defining feature of PTFE is the bond between its carbon and fluorine atoms. This is one of the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry.
This incredibly stable bond shell shields the carbon backbone from chemical attack, rendering the material almost completely inert. It does not react, dissolve, or swell when exposed to the vast majority of industrial chemicals.
A Near-Universal Sealant
Because of its inert nature, PTFE is an excellent choice for sealing against a wide range of aggressive media.
This includes strong acids, bases, alcohols, solvents, oils, and steam. Its performance is consistent across these categories where other materials would quickly degrade.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While chemically robust, PTFE is not an elastomer like rubber. It is a rigid plastic, and this introduces critical physical limitations that must be considered.
Limited Elasticity
Unlike rubber O-rings, PTFE O-rings are not very flexible. They do not compress and rebound with the same effectiveness.
This means they require more precise gland design and surface finishes to create an effective seal. They offer very little "forgiveness" for imperfections.
Susceptibility to Creep (Cold Flow)
Under sustained pressure and temperature, PTFE can slowly deform over time, a phenomenon known as creep or cold flow.
This permanent deformation can lead to a loss of sealing pressure, eventually causing the seal to fail. This is a primary consideration in high-pressure applications.
Installation Challenges
The inherent stiffness of solid PTFE O-rings can make them difficult to install, especially in smaller sizes.
Stretching them over a shaft can cause permanent deformation, compromising the seal before it's even put into service.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a sealing material requires balancing chemical compatibility with the physical demands of the system.
- If your primary focus is sealing against aggressive chemicals: PTFE is an outstanding first choice due to its near-universal chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is a high-pressure or dynamic application: You must account for PTFE's limited elasticity and tendency to creep; a filled-PTFE or an alternative high-performance elastomer may be necessary.
- If your primary focus is a simple, general-purpose seal: PTFE is likely overkill and less practical than a standard elastomer like NBR or EPDM, which are more flexible and cost-effective.
Ultimately, you select PTFE when chemical resistance is the non-negotiable requirement of your design.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE O-Ring Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (Resists acids, bases, solvents, oils, steam) |
| Key Limitation | Physical properties (stiffness, creep) not chemical resistance |
| Elasticity | Low (rigid plastic, requires precise installation) |
| Creep (Cold Flow) | Susceptible under sustained pressure/temperature |
| Ideal For | Applications where chemical inertness is the top priority |
Need a reliable seal for aggressive chemicals?
PTFE's near-universal chemical resistance makes it the ideal choice for sealing against strong acids, bases, solvents, and oils in demanding environments. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including O-rings, seals, liners, and custom labware.
We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, providing custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders. Our expertise ensures you get a seal that meets your exact specifications for performance and durability.
Let's discuss your application requirements. Contact our experts today for a solution tailored to your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















