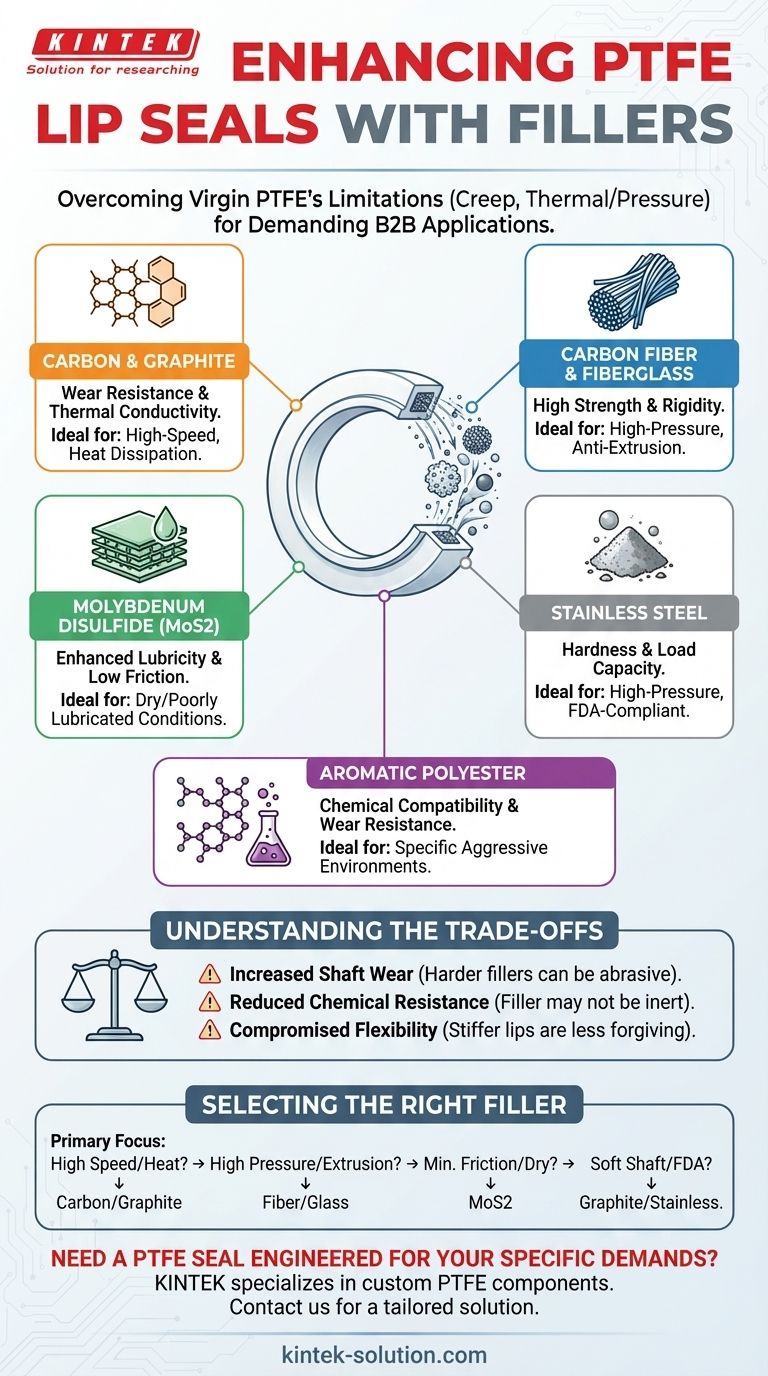
To enhance the performance of PTFE lip seals, a variety of specialized fillers are compounded into the base material. The most common fillers include carbon, graphite, carbon fiber, fiberglass, stainless steel, molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), mineral powders, and aromatic polyesters. Each filler is chosen to improve specific properties of the seal, overcoming the natural limitations of pure, or "virgin," PTFE.
The core reason for using fillers in PTFE seals is to overcome the material's inherent softness and tendency to "creep" or deform under load. Fillers act as a reinforcing matrix, significantly improving the seal's wear resistance, dimensional stability, and thermal conductivity for demanding applications.

Why Virgin PTFE Needs Reinforcement
While Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is known for its extremely low friction and broad chemical compatibility, its pure form has significant mechanical weaknesses. Understanding these limitations is key to appreciating the role of fillers.
The Challenge of Cold Flow (Creep)
Virgin PTFE is mechanically soft and exhibits a phenomenon known as creep or cold flow. This means that under sustained pressure and temperature, the material will slowly deform and lose its original shape. For a seal, this leads to a loss of sealing force and eventual failure.
Limited Thermal and Pressure Ratings
Unfilled PTFE has a relatively narrow operating window for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Fillers are essential for increasing the material's load-carrying capacity and its ability to dissipate heat generated at the sealing lip.
A Breakdown of Common PTFE Fillers
Each filler imparts a unique set of characteristics to the final seal material. The choice is a deliberate engineering decision based on the application's specific demands, such as speed, pressure, temperature, and media.
For General-Purpose Wear Resistance
Graphite and Carbon-Graphite are among the most common fillers. They significantly increase wear resistance and thermal conductivity, helping to draw heat away from the seal's contact point on the shaft. This makes them ideal for higher-speed applications.
For High Strength and Rigidity
Carbon Fiber and Fiberglass are used to dramatically improve the seal's stiffness and resistance to creep. These fibrous fillers create a strong internal structure, making the seal highly resistant to extrusion under high pressure.
For Enhanced Lubricity
Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS2) is a dry-film lubricant. When added to PTFE, it lowers the coefficient of friction even further, which is especially beneficial in applications with poor lubrication or high breakaway torque requirements.
For Hardness and Food-Grade Applications
Stainless Steel powder increases the hardness and load capacity of the seal, making it suitable for high-pressure service. It is also a common choice for food, beverage, and pharmaceutical applications where FDA-compliant materials are required.
For Specific Chemical Environments
Aromatic Polyester and other specialized polymer fillers can offer a unique balance of wear resistance and chemical compatibility. They are often selected for service where other common fillers might be chemically attacked by the system media.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Adding fillers is an engineering compromise. While they solve the primary weaknesses of virgin PTFE, they also introduce new considerations that must be managed.
Increased Shaft Wear
A harder, filled seal material can be more abrasive than virgin PTFE. Fillers like fiberglass or mineral powders can increase wear on softer shaft materials. This requires careful consideration of shaft hardness and surface finish to ensure long system life.
Reduced Overall Chemical Resistance
While PTFE itself is nearly chemically inert, the filler material may not be. Adding a filler reduces the universal chemical compatibility of the seal. The chosen filler must be compatible with the specific fluids or gases in the application.
Compromised Flexibility
Fillers increase the stiffness of the seal lip. This can make the seal less forgiving of shaft imperfections, runout, or dynamic misalignment compared to a more flexible, unfilled PTFE seal.
Selecting the Right Filler for Your Application
Choosing the correct filled PTFE compound is critical to achieving reliable, long-term seal performance. Your decision should be guided by the most demanding aspect of your operating environment.
- If your primary focus is high rotational speed or heat dissipation: Carbon and graphite-filled compounds offer the best thermal conductivity.
- If your primary focus is high pressure and preventing extrusion: Carbon fiber or fiberglass-filled compounds provide the necessary rigidity and creep resistance.
- If your primary focus is minimizing friction in dry or poorly lubricated conditions: Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) is the most effective choice.
- If your primary focus is protecting a soft shaft or ensuring FDA compliance: Consider graphite or stainless steel-filled compounds.
By understanding the role of each filler, you can specify a PTFE seal that is precisely engineered for your equipment's demands.
Summary Table:
| Filler Type | Primary Benefit(s) | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon/Graphite | Wear resistance, thermal conductivity | High-speed applications, heat dissipation |
| Carbon Fiber/Fiberglass | High strength, rigidity, creep resistance | High-pressure service, preventing extrusion |
| Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS2) | Enhanced lubricity, low friction | Dry or poorly lubricated conditions |
| Stainless Steel | Hardness, load capacity | High-pressure, FDA-compliant applications |
| Aromatic Polyester | Wear resistance, chemical compatibility | Specific, aggressive chemical environments |
Need a PTFE Seal Engineered for Your Specific Demands?
Choosing the right filler compound is critical for reliable performance in high-pressure, high-speed, or chemically aggressive environments. The experts at KINTEK specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom lip seals, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We work with you to select or formulate the perfect filled PTFE material to overcome challenges like creep, wear, and thermal limitations. From prototypes to high-volume production, our custom fabrication ensures your seals meet exact specifications.
Contact us today to discuss your application and receive a tailored solution: Get in Touch
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















