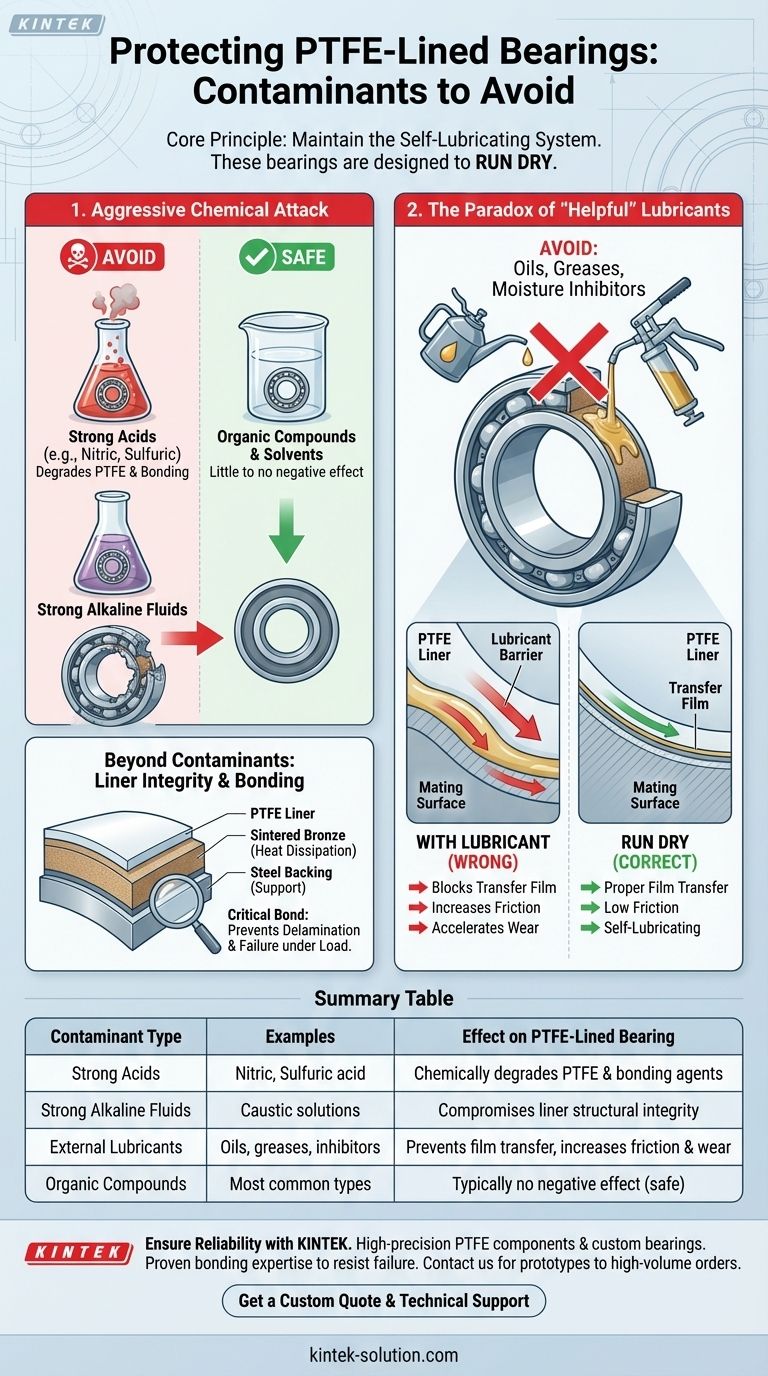
To ensure performance and longevity, you must avoid contaminating PTFE-lined bearings with strong acids, such as nitric and sulfuric acid, and strong alkaline fluids. Equally important, and often counter-intuitive, is the avoidance of adding external lubricants like oil or grease, as these substances interfere with the bearing's self-lubricating mechanism.
The core principle for maintaining PTFE-lined bearings is to protect the integrity of the self-lubricating system. These bearings are designed to run dry, and any contamination—whether from aggressive chemicals or seemingly helpful lubricants—disrupts the critical transfer film, leading to accelerated wear and premature failure.

The Two Primary Threats to PTFE Liners
Understanding how PTFE liners function reveals why certain substances are so detrimental. The bearing's performance relies entirely on the liner's ability to transfer a thin, self-lubricating film onto the mating surface through a process called burnishing.
Aggressive Chemical Attack
The primary chemical threats are potent and corrosive agents. Strong acids like nitric and sulfuric acid can chemically degrade the PTFE material and the bonding agents that secure the liner.
Similarly, strong alkaline fluids should be strictly avoided as they can also compromise the liner's structural integrity.
It is worth noting that most common organic compounds and solvents have little to no negative effect on PTFE liners, making them suitable for a wide range of applications where these substances are present.
The Paradox of "Helpful" Lubricants
A common mistake is treating a PTFE-lined bearing like a traditional metal bearing by adding lubrication. This is highly detrimental.
Substances like oil, grease, or even moisture inhibitors create a barrier on the contact surfaces. This barrier prevents the PTFE liner from properly burnishing and transferring its lubricating film to the mating component.
Without this critical transfer film, direct contact occurs, leading to a significant increase in friction and a rapid acceleration of wear. The bearing effectively loses its low-friction, self-lubricating properties.
Beyond Contaminants: The Importance of Liner Integrity
External contamination is not the only risk. The internal construction and manufacturing quality of the bearing are paramount to its survival, especially under load.
The Critical Role of the Bonding Process
A PTFE-lined bearing consists of multiple layers: the PTFE liner, a sintered bronze layer for heat dissipation, and a steel backing for structural support. The bond between these layers is critical.
An improper or weak bond can lead to liner separation or delamination during operation. This is a catastrophic failure mode that causes rapid degradation of the bearing.
Therefore, selecting a manufacturer with extensive and proven experience in the specialized process of bonding PTFE liners is a critical step in ensuring system reliability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Protecting your PTFE-lined bearings requires a focus on both preventing contamination and ensuring initial quality.
- If your primary focus is chemical compatibility: Rigorously avoid strong acids and strong alkalis, but feel confident using most common organic solvents.
- If your primary focus is mechanical performance: Always run the bearings dry as intended and never introduce external oils, greases, or other additives.
- If your primary focus is overall system reliability: Source your bearings from a reputable manufacturer with documented expertise in the liner bonding process to prevent catastrophic failure.
Ultimately, preserving the delicate, dry, self-lubricating system is the key to maximizing the life and performance of your PTFE-lined bearings.
Summary Table:
| Contaminant Type | Examples | Effect on PTFE-Lined Bearing |
|---|---|---|
| Strong Acids | Nitric acid, Sulfuric acid | Chemically degrades PTFE and bonding agents |
| Strong Alkaline Fluids | Caustic solutions | Compromises liner structural integrity |
| External Lubricants | Oils, greases, moisture inhibitors | Prevents proper film transfer, increases friction and wear |
| Organic Compounds/Solvents | Most common types | Typically no negative effect (safe for use) |
Ensure your PTFE-lined bearings perform reliably and last longer. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom bearings for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in the critical bonding process ensures your bearings resist delamination and failure under load.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements—from prototypes to high-volume orders—and let our precision production deliver the reliability your application demands.
Get a Custom Quote & Technical Support
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support



















