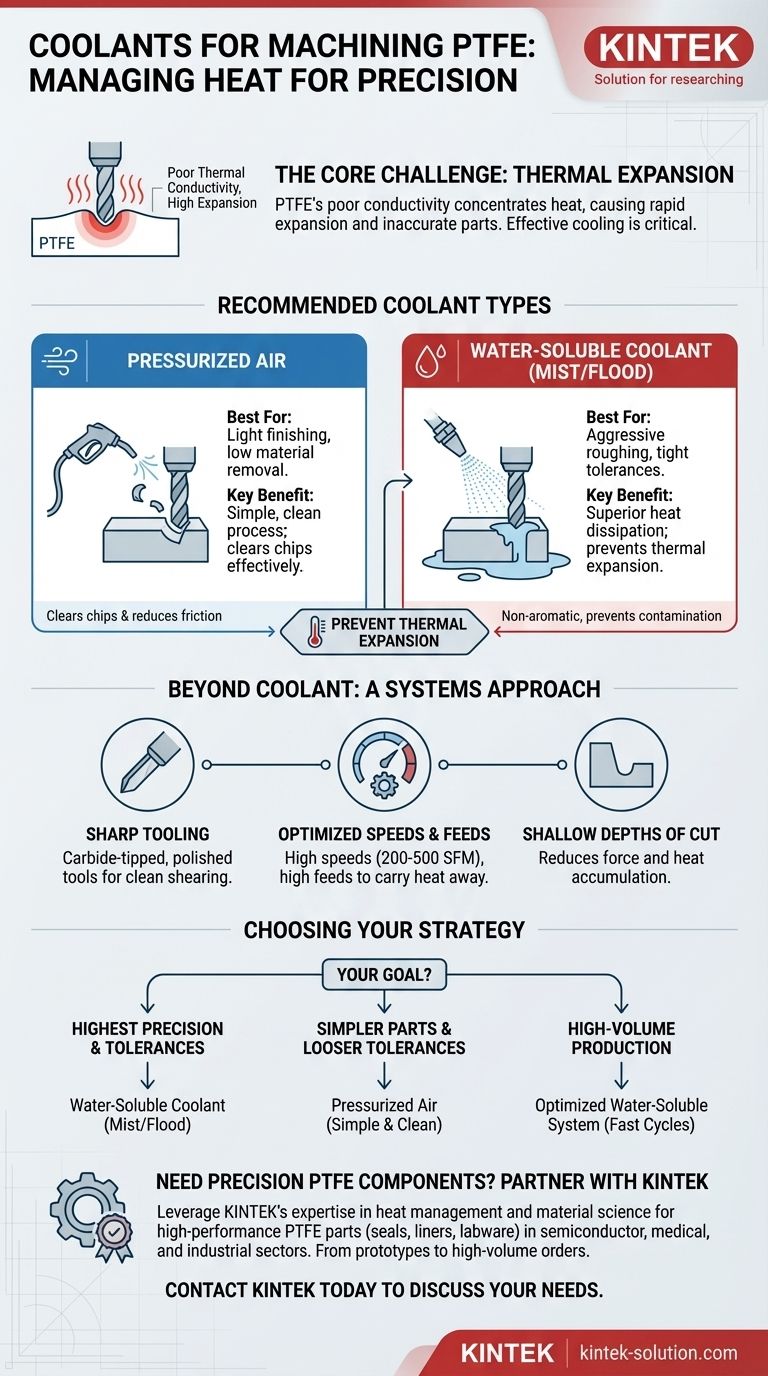
For machining Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), the best coolants are those that effectively manage heat without chemically reacting with the material. The most commonly recommended options are non-aromatic, water-soluble coolants, often applied as a spray mist, or simply pressurized air for lighter cuts. These choices are critical for preventing thermal expansion, which is the primary challenge when machining PTFE.
The core challenge in machining PTFE is not the material's hardness, but its poor thermal conductivity and high rate of thermal expansion. Your choice of coolant is a critical part of a broader strategy to manage heat at the cutting edge, ensuring dimensional stability and a quality surface finish.

The Core Challenge: Managing Heat in PTFE
PTFE is an excellent thermal insulator. While this is a benefit in many applications, it creates significant problems during machining.
Why Heat is the Enemy
Friction from the cutting tool generates heat that does not dissipate quickly through the material. Instead, it concentrates at the cutting zone.
This localized heat causes the PTFE to expand rapidly. If not controlled, this thermal expansion will result in inaccurate dimensions, poor tolerances, and a compromised surface finish once the part cools down.
The Role of an Effective Coolant
A proper coolant serves two primary functions. First, it dissipates heat directly from the tool and the workpiece, preventing thermal expansion. Second, it helps clear chips from the cutting area, which is crucial for preventing friction and heat buildup.
Recommended Coolant Types and Their Application
Your choice of coolant depends on the intensity of the machining operation.
Pressurized Air
For light finishing passes or operations with low material removal rates, pressurized air is an excellent choice. It effectively blows chips away from the cutting zone, preventing them from being recut and generating more friction. It also provides a modest cooling effect.
Spray Mists & Water-Soluble Coolants
For more aggressive roughing or when holding very tight tolerances, a liquid coolant is necessary. Non-aromatic, water-soluble coolants are the standard.
These fluids provide superior cooling capacity compared to air, directly counteracting thermal expansion. Applying them as a fine mist is often sufficient to keep temperatures stable without flooding the machine.
Beyond Coolant: A Systems Approach to Machining PTFE
Effective cooling is just one piece of the puzzle. To achieve consistent, high-quality results, you must integrate your coolant strategy with the right tooling and machine parameters.
The Importance of Sharp Tooling
Use extremely sharp, polished tools, with carbide-tipped tools being a preferred choice. A sharp edge shears the material cleanly rather than plowing through it, which drastically reduces the amount of frictional heat generated in the first place.
Optimizing Speeds and Feeds
The goal is to remove material efficiently without creating excess heat. Recommendations can vary, but the underlying principle is consistent.
Use high cutting speeds (in the range of 200-500 SFM, or Surface Feet per Minute) paired with high feed rates (0.002 to 0.010 inches per revolution). This combination allows the tool to move through the material quickly, carrying heat away with the chip before it can soak into the workpiece.
Shallow Depths of Cut
To minimize stress and heat accumulation, use shallow depths of cut. This reduces the cutting forces and the volume of material being deformed at any given moment, further aiding in temperature control.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right approach involves balancing efficiency with process simplicity.
Dry Machining (Air Only) vs. Wet Machining
Dry machining with pressurized air is cleaner and simpler, with no coolant to manage or dispose of. However, it limits your material removal rates and may not be suitable for parts requiring the highest precision.
Wet machining with a liquid coolant allows for more aggressive cycles and is essential for maintaining tight dimensional stability. The trade-off is the added complexity of managing the coolant system and ensuring part cleanliness.
Material Integrity and Contamination
PTFE is often used in medical, food-grade, or high-purity applications. In these cases, you must ensure your chosen coolant is non-reactive and does not contaminate the final part. This is why non-aromatic, water-soluble fluids are specified.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your cooling strategy based on the specific requirements of the component you are producing.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest precision and tightest tolerances: Use a non-aromatic, water-soluble coolant mist or flood to aggressively manage thermal expansion.
- If your primary focus is on simpler components with looser tolerances: Pressurized air is often sufficient and provides a cleaner, simpler process.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: An optimized system using a water-soluble coolant is necessary to achieve the fast cycle times and tool life required.
Ultimately, mastering the machining of PTFE comes down to a comprehensive strategy for controlling heat at every stage of the process.
Summary Table:
| Coolant Type | Best For | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Pressurized Air | Light finishing, low material removal | Simple, clean process; clears chips effectively |
| Water-Soluble Coolant (Mist/Flood) | Aggressive roughing, tight tolerances | Superior heat dissipation; prevents thermal expansion |
Need Precision PTFE Components? Partner with KINTEK
Machining PTFE to exact specifications requires expertise in heat management and material science. As a leading manufacturer of high-performance PTFE components (including seals, liners, and custom labware) for the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors, KINTEK has the experience to ensure your parts meet the highest standards of precision and purity.
We specialize in custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, leveraging optimal machining strategies for superior results. Let us apply our expertise to your project.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your PTFE component needs and request a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Crucibles for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers



















