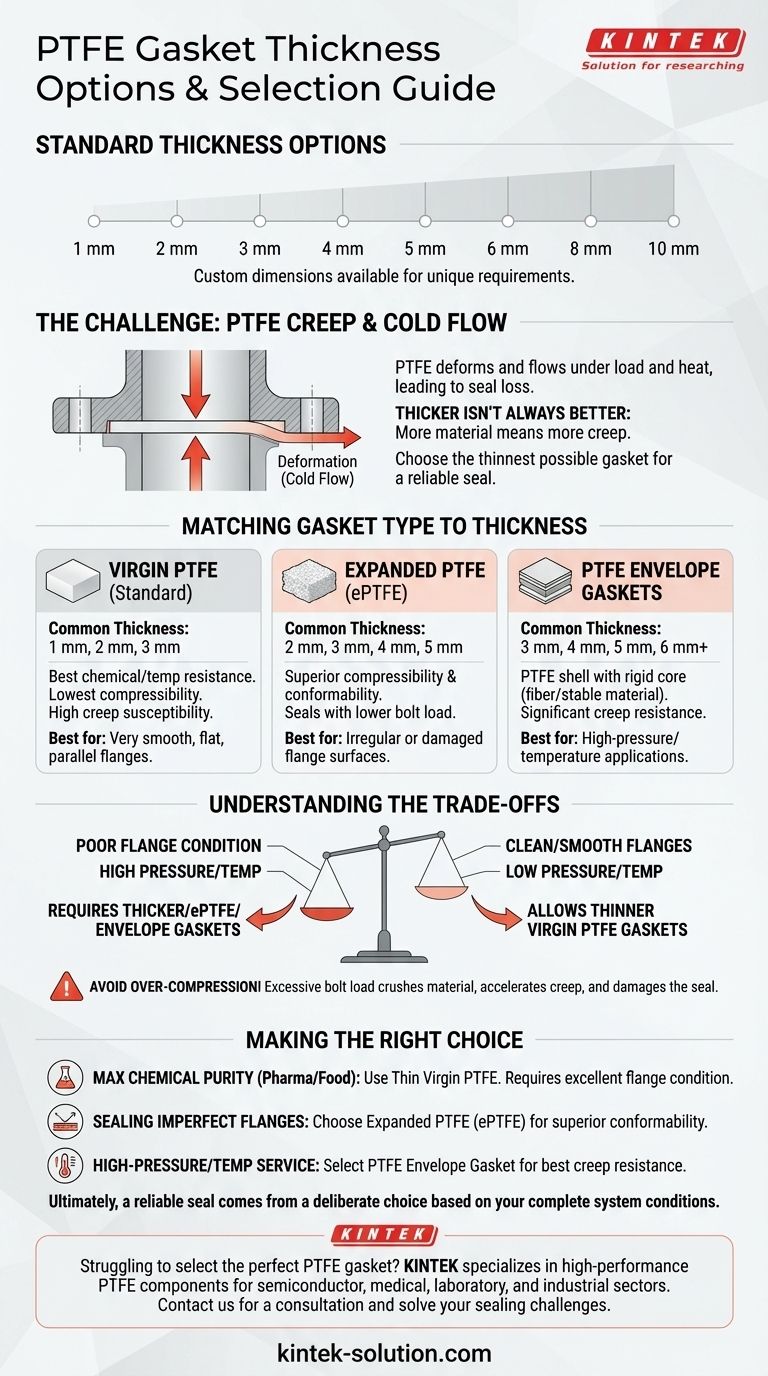
For PTFE gaskets, standard thickness options typically include 1 mm, 2 mm, 3 mm, 4 mm, 5 mm, 6 mm, 8 mm, and 10 mm. Beyond these common sizes, manufacturers can also produce custom dimensions to meet specific engineering requirements for unique flange or sealing applications.
The central challenge in selecting a gasket is not finding an available thickness, but choosing one that correctly balances the need to seal imperfect surfaces against PTFE's inherent tendency to deform under load and temperature over time.

Why Gasket Thickness is More Than Just a Number
Selecting the right gasket thickness is a critical engineering decision. The primary function of a gasket is to create a durable seal between two flange faces, compensating for any surface imperfections.
The Primary Goal: Conforming to the Flange
A gasket must be compressible enough to deform and fill the microscopic gaps, scratches, and misalignments present on flange surfaces.
A thicker gasket contains more material and can, in theory, fill larger imperfections. This is often necessary for older, warped, or damaged equipment.
The Challenge of PTFE: Creep and Cold Flow
While valued for its chemical resistance, PTFE has significant mechanical limitations. Its primary weakness is a phenomenon known as creep or cold flow.
This is the material's tendency to slowly deform and "flow" away from the point of compressive stress, especially under load and at elevated temperatures.
Thicker Isn't Always Better
A thicker gasket has more material that can be subject to creep. Under the same bolt load, a thicker gasket can deform more significantly over time, leading to a loss of sealing stress and eventual leakage.
This makes choosing the thinnest possible gasket that can still achieve a proper seal the most reliable engineering practice.
Matching Gasket Type to Thickness
The type of PTFE material fundamentally changes how it behaves at a given thickness. Understanding these variations is key to selecting the right product.
Virgin (Standard) PTFE
This is pure, unmodified PTFE. It offers the best chemical and temperature resistance but has the lowest compressibility and the highest susceptibility to creep.
It is best suited for applications with very smooth, flat, and parallel flange surfaces where a thinner gasket (e.g., 1 mm or 2 mm) can be used effectively.
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
ePTFE is a softer, more flexible form of PTFE. Its key advantage is superior compressibility and conformability.
This allows it to seal effectively on irregular or damaged flange surfaces, even with lower bolt loads. It is an excellent choice when you need a thicker gasket to compensate for flange imperfections.
PTFE Envelope Gaskets
These gaskets combine a chemically resistant PTFE outer shell with a mechanically robust inner core, often made of compressed fiber or another stable material.
This design leverages PTFE's chemical inertness while the insert provides mechanical strength, rigidity, and significant resistance to creep. They are ideal for high-pressure applications or where a thicker, more stable seal is required.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Every gasket selection involves balancing competing factors. Being aware of these trade-offs prevents common failures.
Flange Condition vs. Gasket Thickness
Poorly maintained, warped, or rough flange surfaces often demand a thicker, more conformable gasket to achieve a seal. In this case, an expanded PTFE gasket is often the best choice.
For new, clean, and perfectly aligned flanges, a thin virgin PTFE gasket provides a reliable seal with the lowest risk of cold flow.
Pressure and Temperature Considerations
High operating pressures and temperatures will accelerate creep and cold flow in any PTFE material.
In these demanding environments, a thinner gasket profile is generally safer. Alternatively, a PTFE envelope gasket provides the necessary mechanical stability to resist deformation and maintain a long-term seal.
The Risk of Over-Compression
A common mistake is to overtighten bolts in an attempt to seal a leak. With PTFE, this is counterproductive.
Excessive bolt load crushes the material, accelerates cold flow, and permanently damages the gasket's ability to maintain sealing stress. Always tighten to the manufacturer's specified torque.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's primary requirement should guide your selection.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical purity (pharmaceutical/food): Use a thin, virgin PTFE gasket, but ensure your flange surfaces are in excellent condition.
- If your primary focus is sealing older or imperfect flanges: Choose an expanded PTFE (ePTFE) gasket, as its superior conformability will fill irregularities effectively.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure or high-temperature service: A PTFE envelope gasket provides the best resistance to creep and ensures a stable, long-lasting seal under demanding conditions.
Ultimately, a reliable seal comes from a deliberate choice based on your complete system conditions, not just a catalog number.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Gasket Type | Common Thickness Options | Key Characteristics & Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Virgin PTFE | 1 mm, 2 mm, 3 mm | Best chemical/temp resistance; low compressibility; best for smooth, flat flanges. |
| Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) | 2 mm, 3 mm, 4 mm, 5 mm | Superior compressibility/conformability; ideal for irregular or damaged flanges. |
| PTFE Envelope Gaskets | 3 mm, 4 mm, 5 mm, 6 mm+ | Combines PTFE shell with rigid core; excellent creep resistance for high-pressure/temp. |
Struggling to select the perfect PTFE gasket for your specific flange conditions, pressure, and temperature requirements?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom gaskets for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We provide expert guidance and precision production—from prototypes to high-volume orders—to ensure you get a reliable, long-lasting seal.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and let our experts help you solve your sealing challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















