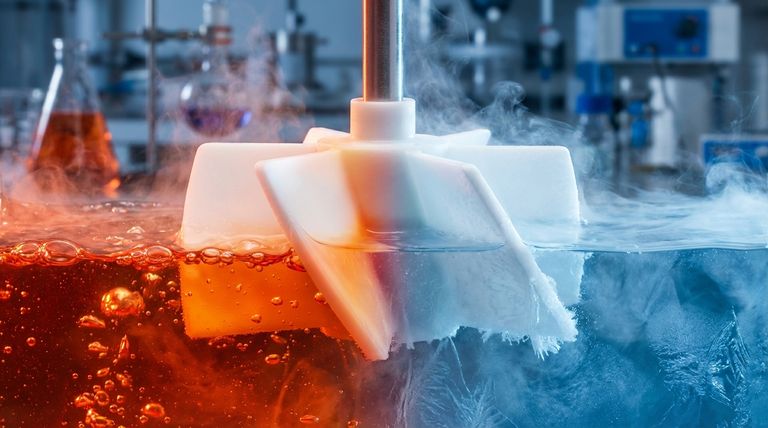
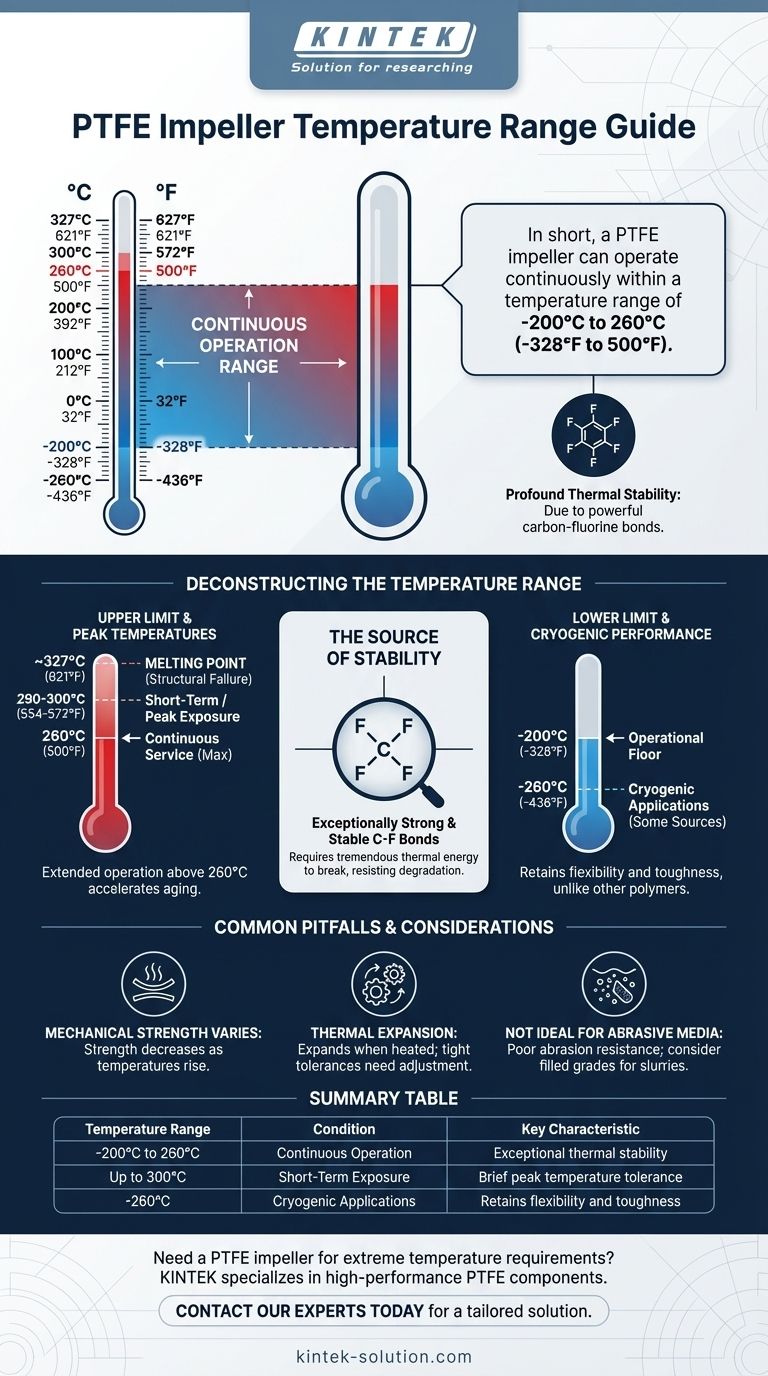
In short, a PTFE impeller can operate continuously within a temperature range of -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F). This exceptionally wide range makes it one of the most versatile materials for applications involving extreme cold and high heat, far surpassing the capabilities of most common plastics and elastomers. It can even handle brief excursions to temperatures as high as 300°C (572°F).
The core reason for selecting a PTFE impeller is its profound thermal stability. This isn't just a feature; it's the material's defining characteristic, stemming from its powerful carbon-fluorine bonds, which allows it to function where other materials would become brittle, melt, or degrade.

Deconstructing the Temperature Range
Understanding the numbers requires looking at both the upper and lower limits, as well as the point of material failure.
The Upper Limit: Continuous vs. Peak Temperature
The widely cited upper limit of 260°C (500°F) refers to the maximum temperature for continuous service. The material can operate indefinitely at this temperature without significant degradation of its properties.
For short-term, intermittent exposure, PTFE can often withstand temperatures up to 290-300°C (554-572°F). However, operating near or above the continuous limit for extended periods will accelerate material aging.
The absolute ceiling is PTFE's melting point, which is approximately 327°C (621°F). At this temperature, the material loses its structural integrity entirely.
The Lower Limit: Cryogenic Performance
PTFE performs exceptionally well at extremely low temperatures. Its operational floor is typically rated at -200°C (-328°F), with some sources noting effective use in applications as low as -260°C (-436°F).
Crucially, unlike many other polymers that become extremely brittle and fracture at cryogenic temperatures, PTFE retains a useful degree of flexibility and toughness.
The Source of PTFE's Stability
This remarkable thermal performance is not accidental. It is a direct result of PTFE's molecular structure.
The bonds between carbon and fluorine atoms are exceptionally strong and stable. This molecular backbone requires a tremendous amount of thermal energy to excite and break, which is why the material resists degradation at both high and low temperatures.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While the temperature range is impressive, it is not the only factor to consider. An effective design accounts for the material's other properties and potential limitations.
Mechanical Strength Varies with Temperature
PTFE is a relatively soft material with lower tensile strength and creep resistance compared to other high-performance polymers like PEEK.
As temperatures rise towards the upper limit, PTFE will become softer and its strength will decrease. This must be factored into the design of impellers intended for high-stress or high-pressure applications at elevated temperatures.
Thermal Expansion and Contraction
Like all materials, PTFE expands when heated and contracts when cooled. Its coefficient of thermal expansion is relatively high compared to metals.
In systems with tight tolerances—such as an impeller spinning within a pump housing—this expansion must be accounted for by engineers to prevent binding or damage across the operational temperature range.
Not Ideal for Abrasive Media
Standard PTFE has poor abrasion resistance. If the fluid being moved contains abrasive particles or is a slurry, the impeller can wear down quickly.
For such applications, a "filled" or "reinforced" grade of PTFE (e.g., glass-filled or carbon-filled) is often used to enhance mechanical strength and wear resistance, though this can sometimes alter its thermal or chemical properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to determine if a PTFE impeller is the correct solution for your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature stability: PTFE is a premier choice for applications ranging from cryogenic processing to high-temperature chemical mixing where other materials fail.
- If your primary focus is combined chemical and thermal resistance: PTFE's inertness to nearly all chemicals, maintained across its vast temperature range, makes it invaluable for handling aggressive media in harsh environments.
- If your primary focus is high mechanical load or abrasion resistance: You must evaluate if standard PTFE is sufficient or if a reinforced grade is necessary; in very high-stress scenarios, an alternative polymer like PEEK may be required.
Ultimately, selecting PTFE for its thermal range means leveraging one of the most stable polymers available, provided you account for its inherent mechanical characteristics in your design.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Condition | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F) | Continuous Operation | Exceptional thermal stability |
| Up to 300°C (572°F) | Short-Term Exposure | Brief peak temperature tolerance |
| -260°C (-436°F) | Cryogenic Applications | Retains flexibility and toughness |
Need a PTFE impeller that can handle your extreme temperature requirements?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance, precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, labware, and custom impellers—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We deliver the thermal stability and chemical resistance your application demands, with custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and get a solution tailored to your environment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Magnetic Stirring Bar
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
People Also Ask
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















