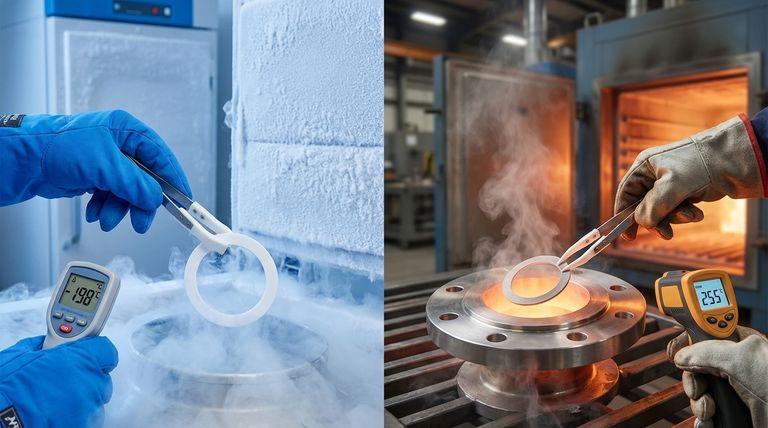
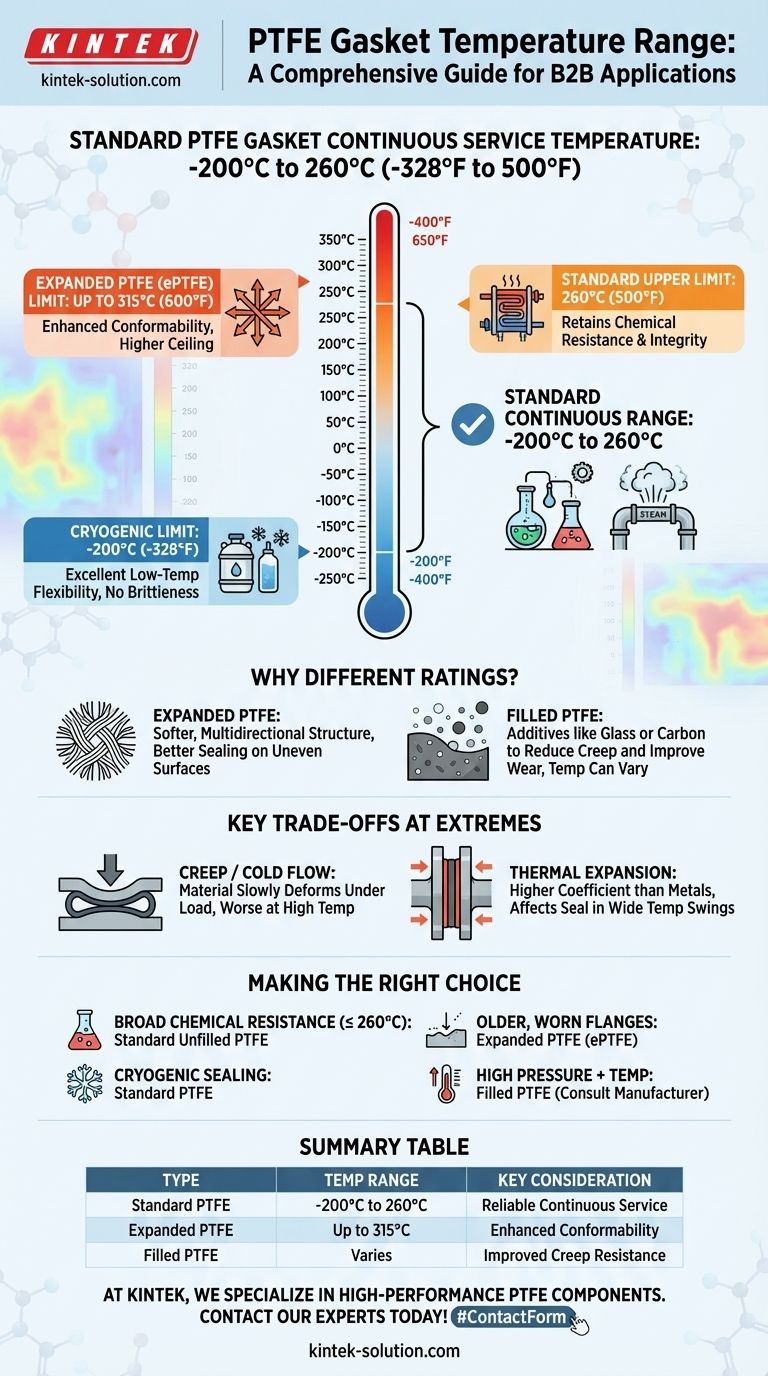
In short, a standard PTFE gasket can withstand a continuous service temperature range from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F). This remarkable thermal stability makes it one of the few materials suitable for both cryogenic applications and high-heat industrial processes. While this is the established benchmark, the specific type of PTFE and the application's conditions can influence its ultimate performance.
The key is to understand that 260°C (500°F) is the reliable upper limit for standard, unfilled PTFE. Higher temperature ratings often refer to specialized forms, like expanded or filled PTFE, which have enhanced properties but also different trade-offs.

The Definitive Temperature Range for Standard PTFE
To properly specify a gasket, you must understand its performance at both ends of the spectrum. PTFE excels where many other polymers fail.
The Upper Limit: Thermal Stability
The maximum continuous service temperature for most PTFE gaskets is 260°C (500°F).
At this temperature, the material retains its excellent chemical resistance and structural integrity, ensuring a reliable seal in applications like steam systems, heat exchangers, and chemical processing lines.
The Lower Limit: Cryogenic Performance
PTFE performs exceptionally well at extremely low temperatures, remaining functional down to approximately -200°C (-328°F).
Unlike many materials that become brittle and fracture in cryogenic conditions, PTFE retains a useful degree of flexibility and toughness, making it a primary choice for sealing liquid nitrogen or LNG systems.
Why You See Different Temperature Ratings
If you've seen ratings above 260°C, it's not a mistake; it's a reflection of material engineering. The term "PTFE gasket" can describe different formulations.
Standard vs. Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
Some sources cite a higher limit of 315°C (600°F). This rating typically applies to expanded PTFE (ePTFE).
This material is manufactured differently to create a soft, conformable, multidirectional fibrous structure. This structure not only seals rough or uneven surfaces more effectively but also slightly increases its temperature resistance.
The Role of Fillers
The performance of PTFE can be altered by adding fillers like glass, carbon, or graphite.
While primarily used to reduce creep and improve wear resistance, certain fillers can also enhance thermal stability. Gaskets made from filled PTFE may have different temperature specifications, which must be verified with the manufacturer.
Key Trade-offs at Temperature Extremes
A material's temperature rating is not the only factor. You must also consider how temperature affects its mechanical properties under pressure.
Creep and Cold Flow
The most significant limitation of PTFE is its tendency to creep, also known as cold flow. This is the process where the material slowly deforms over time under a constant load.
This effect is magnified at higher temperatures. As PTFE approaches its upper limit, it softens, and its resistance to creep decreases, which can lead to a loss of bolt torque and sealing pressure.
Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion compared to metals.
In applications with wide temperature swings, the gasket will expand and contract more than the surrounding metal flanges. This must be accounted for in the engineering design to maintain a consistent seal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct gasket requires matching the material's properties to the system's demands.
- If your primary focus is broad chemical resistance up to 260°C: Standard, unfilled PTFE is the most reliable and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic sealing: PTFE is an industry-standard material due to its excellent performance and lack of brittleness at extreme cold.
- If you need to seal older, worn, or uneven flanges: Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) provides superior conformability and a slightly higher temperature ceiling of 315°C.
- If your application involves high pressure combined with high temperature: Investigate filled PTFE gaskets, which are specifically designed to resist creep under severe conditions.
Ultimately, verifying the manufacturer's specific data sheet for the exact gasket you choose is the only way to guarantee a safe and reliable seal.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Application Context | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| -200°C to 260°C | Standard, unfilled PTFE | Reliable continuous service range |
| Up to 315°C | Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) | Enhanced conformability and sealing |
| Varies | Filled PTFE (glass, carbon) | Improved creep resistance under pressure |
Need a PTFE gasket that can handle your extreme temperatures?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including seals and gaskets, for the most demanding applications in semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require standard PTFE for broad chemical resistance up to 260°C, ePTFE for superior sealing on uneven surfaces, or custom-filled formulations to combat creep under high pressure and temperature, we provide precision production from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let us help you ensure a safe, reliable seal. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific temperature and pressure requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















