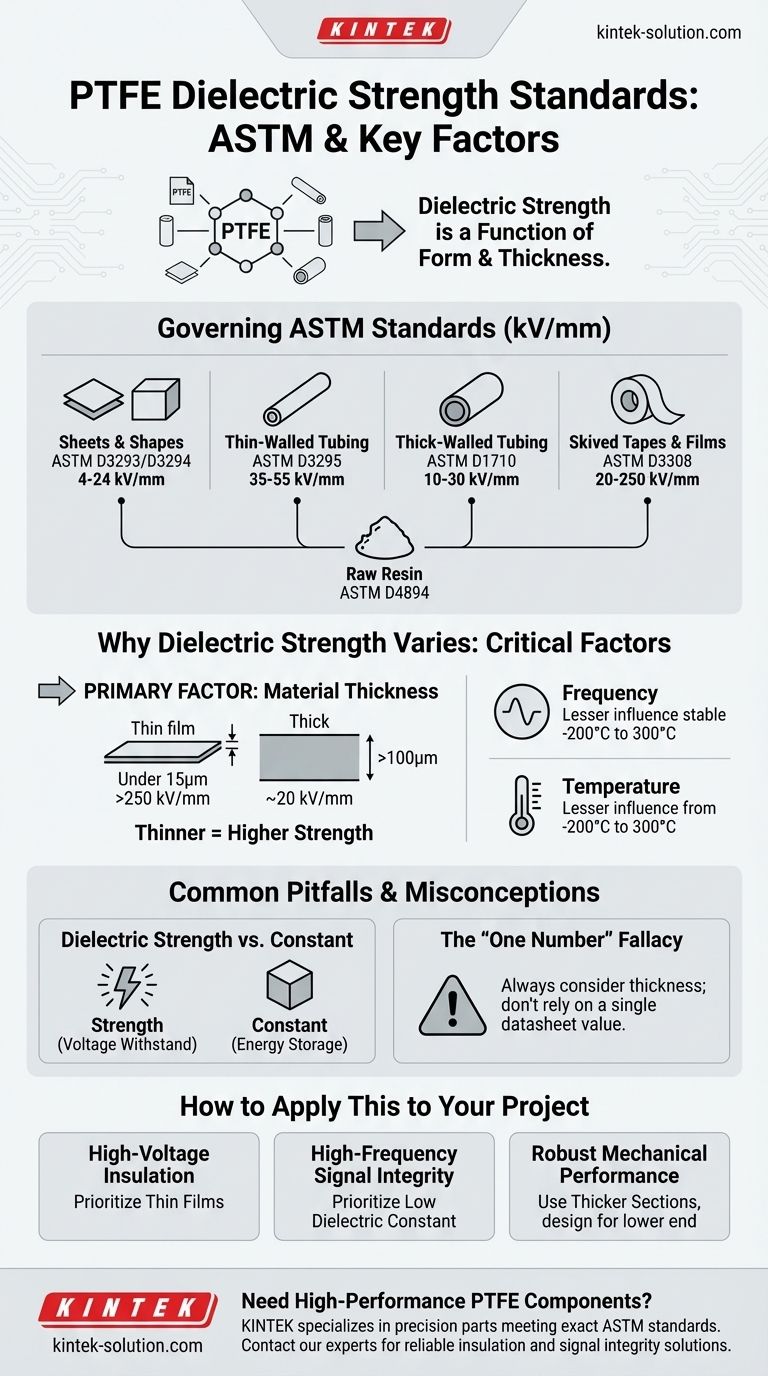
The dielectric strength of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) products is defined by a series of ASTM International standards, each corresponding to a specific physical form. These standards provide testing frameworks and expected performance ranges. Key standards include ASTM D3293 for sheets, D3308 for tapes, and D3295 for thin-walled tubing, each with a different specified dielectric strength range based on the product's typical dimensions and manufacturing process.
While specific ASTM standards define testing methods for various PTFE forms, the critical takeaway is that dielectric strength is not a single value. It is fundamentally dependent on the material's thickness—thinner films exhibit significantly higher breakdown voltage per millimeter than thicker sections.

The Governing ASTM Standards
The expected dielectric strength of a PTFE product is directly tied to its form factor. The relevant ASTM standard provides the context for these values.
For Sheets and Basic Shapes
ASTM D3293 covers PTFE sheets, which typically exhibit a dielectric strength of 4-24 kV/mm. Similarly, ASTM D3294 applies to other basic molded or machined shapes, with a range of 12-24 kV/mm.
For Tubing
The wall thickness of tubing is the critical differentiator. ASTM D3295 for thin-walled tubing specifies a high dielectric strength of 35-55 kV/mm, while ASTM D1710 for thicker-walled tubes specifies a lower range of 10-30 kV/mm.
For Tapes and Films
Skived tapes, covered by ASTM D3308, show the widest possible range: 20-250 kV/mm. This massive variation directly illustrates the principle that thickness is the dominant factor in performance.
For Raw Material
For unprocessed granular PTFE resins, ASTM D4894 is the applicable standard, defining the properties of the material before it is formed into a final product.
Why Dielectric Strength Varies: Critical Factors
Simply looking up a standard is not enough for reliable design. You must understand the physical principles that cause the dielectric strength values to vary so significantly.
The Primary Factor: Material Thickness
The relationship between thickness and dielectric strength is inverse. Thinner materials concentrate the electrical field more effectively and have fewer potential microscopic defects, leading to a higher breakdown voltage per unit of thickness.
Thin PTFE films (under 15 microns) can exceed 250 kV/mm. In contrast, thicker sections (over 100 microns) may have a dielectric strength as low as 20 kV/mm.
This principle is the single most important factor in explaining the wide performance ranges published in ASTM standards.
The Influence of Frequency
PTFE's dielectric strength tends to decrease as the frequency of the applied electric field increases. While its properties are remarkably stable across a wide frequency spectrum, this is a known factor in very high-frequency power applications.
The Role of Temperature
A key advantage of PTFE is its thermal stability. Its excellent dielectric properties show no substantial degradation at temperatures up to 300°C, and it maintains performance in cryogenic conditions as low as -200°C.
Common Pitfalls and Misconceptions
Understanding the nuances of electrical properties is critical to avoid design failures. Many engineers make incorrect assumptions based on simplified data sheets.
Dielectric Strength vs. Dielectric Constant
These two properties are often confused. Dielectric strength is the voltage a material can withstand before electrical breakdown or failure (an insulator's "strength"). Dielectric constant (relative permittivity) measures a material's ability to store electrical energy.
PTFE excels in both areas. It has a very high dielectric strength and a very low dielectric constant (around 2.1), which is ideal for high-frequency applications where minimizing signal loss is paramount.
The "One Number" Fallacy
A single dielectric strength value on a technical data sheet is almost meaningless without knowing the thickness of the sample tested. Always assume that a high value was achieved with a very thin film. For robust design, you must use the value that corresponds to the actual thickness of the material in your application.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your design goal will determine which electrical property of PTFE is most important and which value to use in your calculations.
- If your primary focus is high-voltage insulation in compact spaces: Prioritize the thinnest possible film or tape that meets your mechanical needs to maximize the dielectric strength.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency signal integrity: The exceptionally low and stable dielectric constant of PTFE is your most critical property, ensuring minimal signal loss and distortion.
- If your primary focus is robust mechanical and electrical performance: You will likely use thicker sheets or tubes and must design your system according to the lower end of the dielectric strength range (e.g., 10-30 kV/mm) to ensure a sufficient safety margin.
Ultimately, understanding that dielectric strength is a function of thickness—not a fixed property—is the key to reliable high-performance electrical design with PTFE.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Product Form | Key ASTM Standard | Typical Dielectric Strength Range (kV/mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Sheets & Basic Shapes | ASTM D3293 / D3294 | 4 - 24 kV/mm |
| Thin-Walled Tubing | ASTM D3295 | 35 - 55 kV/mm |
| Thick-Walled Tubing | ASTM D1710 | 10 - 30 kV/mm |
| Skived Tapes & Films | ASTM D3308 | 20 - 250 kV/mm |
| Raw Granular Resin | ASTM D4894 | Defines base material properties |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components with Guaranteed Dielectric Properties?
Understanding the precise dielectric strength required for your application is critical. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors. We ensure your parts meet the exact ASTM standards and performance thresholds your design demands, from prototype to high-volume production.
Let us help you achieve reliable insulation and signal integrity. Contact our experts today to discuss your project's specific requirements and receive a custom solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
People Also Ask
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers



















