To solve the cold flow problem in PTFE gaskets, you must combine two key strategies: selecting a mechanically enhanced PTFE material designed to resist creep and implementing a highly disciplined installation procedure. While pure PTFE is known for this weakness, advanced filled and structured PTFE variants, coupled with precise bolt loading, provide a reliable, long-term seal.
The core issue with PTFE is its tendency to deform under sustained pressure, a phenomenon known as cold flow or creep. The definitive solution is not to fight this property in pure PTFE, but to sidestep it by selecting an advanced, filler-reinforced gasket material and ensuring it is installed with engineering precision.

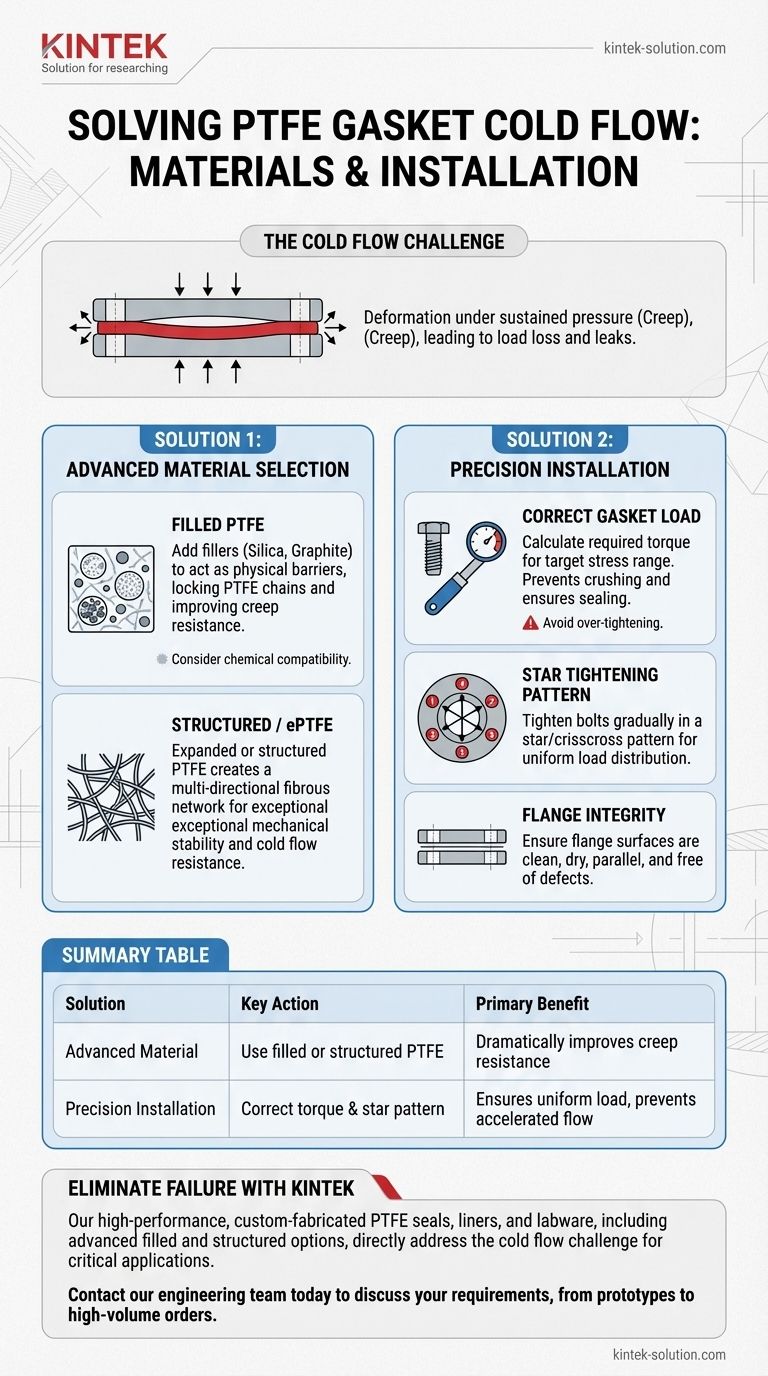
What is Cold Flow and Why Does it Matter?
Before addressing the solutions, it's critical to understand the mechanism of failure. This understanding forms the basis for every effective countermeasure.
The Nature of PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a polymer with incredibly long, smooth molecular chains. Its famous non-stick property and chemical inertness come from the fact that these chains don't easily bond with other substances—or with each other.
Cold Flow (Creep) Explained
Under the compressive force of a bolted flange, these smooth molecular chains begin to slip past one another. Cold flow is this slow, continuous deformation of the gasket material under a constant load. The gasket literally "flows" outward, away from the point of compression.
The Consequences of Failure
As the gasket thins out due to cold flow, the compressive stress on it decreases. This directly leads to a loss of bolt torque and a reduction in the sealing force. The ultimate result is a compromised seal and a potential leak.
Solution 1: Advanced Material Selection
The most effective way to combat cold flow is to choose a gasket material specifically engineered to resist it. Virgin, or pure, PTFE is rarely the right choice for critical applications.
The Limitation of Virgin PTFE
Unfilled, virgin PTFE has the highest susceptibility to cold flow. While it offers the best chemical resistance, its mechanical properties are poor, making it suitable for only low-pressure, low-temperature applications.
The Role of Fillers
Adding filler materials like silica, glass microspheres, or graphite to the PTFE matrix is the most common solution. These microscopic particles act as physical barriers, interrupting the slip planes and mechanically locking the PTFE polymer chains in place. This dramatically improves the gasket's creep resistance.
Structured and Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
A more advanced solution involves changing the physical structure of the material itself. In structured or expanded PTFE (ePTFE), the manufacturing process creates a multi-directional network of strong fibers. This fibrous web provides exceptional mechanical stability and makes the material highly resistant to cold flow, even at elevated temperatures.
Solution 2: Precision Installation and Design
Your choice of material can be completely undermined by poor installation practices. Proper procedure ensures that the gasket is loaded correctly, maximizing its sealing potential without accelerating creep.
Calculating the Correct Gasket Load
The gasket manufacturer provides specifications for the ideal compressive stress range. Engineers must correctly calculate the required bolt torque to achieve this target stress. This ensures the gasket is compressed enough to seal, but not so much that its internal structure is crushed.
The Criticality of the Torque Procedure
Applying the load evenly is paramount. Bolts must be tightened gradually in a star or crisscross pattern. This practice distributes the compressive force uniformly across the entire gasket face, preventing localized high-stress points that can initiate and accelerate cold flow.
Flange Condition and Alignment
The references correctly highlight the importance of the flange itself. Mating surfaces must be clean, dry, and free of defects. Furthermore, the flanges must be parallel. An uneven surface creates high and low-pressure zones on the gasket, guaranteeing failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right solution requires acknowledging the compromises involved.
Fillers vs. Chemical Resistance
While fillers dramatically improve mechanical performance, they can slightly reduce the universal chemical inertness of virgin PTFE. You must ensure the chosen filler (e.g., glass, silica) is compatible with the chemical media being sealed.
The Myth of Over-Tightening
A common but dangerous mistake is to over-tighten bolts to "make sure" a seal is tight. For PTFE gaskets, this is counterproductive. Excessive compression crushes the gasket's internal structure, destroying its ability to resist creep and drastically increasing the rate of cold flow, leading to a faster failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be based on the specific demands of your sealing environment.
- If your primary focus is sealing a critical or high-temperature service: Prioritize an advanced material like silica-filled or structured ePTFE, as material choice is the most dominant factor in performance.
- If your primary focus is maximizing reliability with a specified gasket: Concentrate entirely on a meticulous installation protocol, including precise torque calculations, verified flange conditions, and a disciplined star-pattern tightening sequence.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting a recurring leak: Investigate both material and process. A material upgrade combined with technician re-training on proper installation is often the only permanent solution.
Ultimately, achieving a reliable seal with PTFE gaskets is a function of combining modern material science with disciplined engineering practice.
Summary Table:
| Solution | Key Action | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Material Selection | Use filled or structured PTFE (e.g., silica, ePTFE) | Dramatically improves creep resistance and mechanical stability |
| Precision Installation | Apply correct bolt torque in a star/crisscross pattern | Ensures uniform load distribution and prevents accelerated cold flow |
Eliminate PTFE gasket failure with precision-engineered components from KINTEK.
Our expertise in manufacturing high-performance PTFE seals, liners, and labware directly addresses the cold flow challenge. We specialize in custom fabrication for the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors, using advanced filled and structured PTFE materials designed for superior creep resistance and long-term reliability.
Let us provide the solution for your critical sealing application. Contact our engineering team today to discuss your requirements, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















