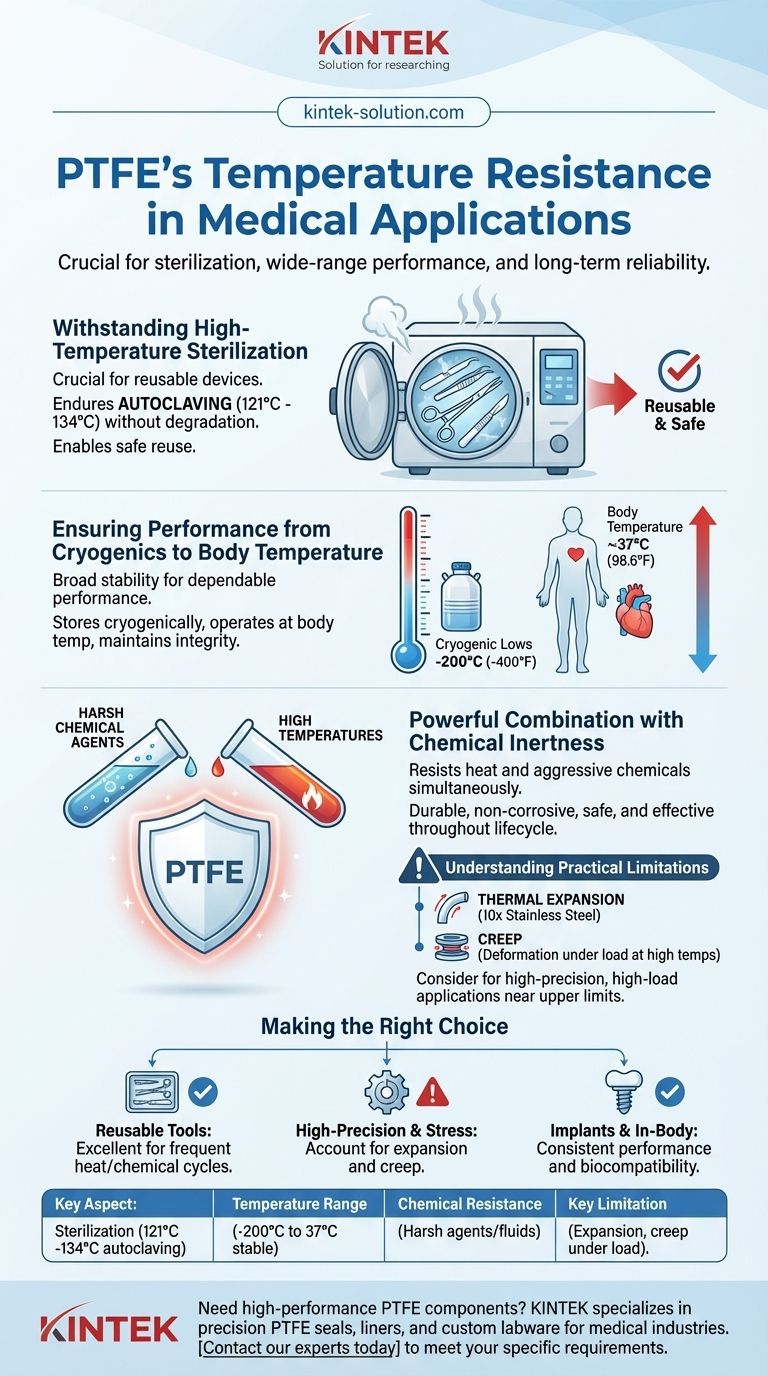
In the medical field, PTFE's temperature resistance is crucial because it allows devices to withstand high-temperature sterilization processes, such as autoclaving, without degrading. This ensures that instruments and components can be safely reused. Its stable performance across a vast temperature spectrum, from cryogenic lows to above boiling point, guarantees reliability in a wide range of medical environments.
The core value of PTFE in medicine isn't just about resisting heat; it's about maintaining its physical integrity and chemical inertness across the entire spectrum of temperatures a medical device will encounter, from manufacturing and sterilization to long-term use inside the human body.

Why Temperature Stability is Critical in Medicine
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is valued for its unique combination of properties. While its chemical inertness is well-known, its thermal stability is what enables its use in demanding medical applications where safety and reliability are non-negotiable.
Withstanding High-Temperature Sterilization
The most common application of PTFE's heat resistance is in sterilization. Medical equipment must be sterile, and a common method is autoclaving, which uses steam at high pressure and temperatures (typically 121°C to 134°C).
PTFE easily endures these conditions without melting, warping, or losing its critical properties. This allows for the creation of reusable surgical tools and components that can be reliably sterilized many times.
Ensuring Performance from Cryogenics to Body Temperature
PTFE maintains its properties across an exceptionally wide range, often cited from -200°C to +260°C (-400°F to 500°F).
While most medical devices don't experience such extremes, this broad stability ensures dependable performance. A component can be stored cryogenically, used at room temperature, and implanted in the body (~37°C) without any change in its structural integrity or function.
A Powerful Combination with Chemical Inertness
Temperature resistance rarely acts alone. Medical sterilization often involves not just heat but also harsh chemical agents.
PTFE's ability to resist both high temperatures and aggressive chemicals simultaneously makes it a uniquely durable material. It will not corrode or degrade, ensuring that the device remains safe and effective throughout its lifecycle.
Understanding the Practical Limitations
While highly capable, PTFE is not without its operational limits. Understanding these trade-offs is essential for proper material selection in engineering and medical device design.
The True Ceiling of Pure PTFE
The upper service temperature of PTFE is often cited as 260°C (500°F). However, for pure, unmodified PTFE, its practical resistance may be closer to 200°C (392°F), especially when under mechanical load.
Above this temperature, its physical properties can begin to change significantly, which could compromise the function of a precision component.
The Challenge of Thermal Expansion and Creep
PTFE has a high coefficient of thermal expansion, expanding about 10 times more than stainless steel when heated. At elevated temperatures, it is also susceptible to creep, which is permanent deformation under a sustained load.
In applications like valve seats or seals, this expansion and potential for creep could cause the component to fail or clog, making it a critical design consideration for high-temperature, high-pressure environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires balancing its strengths against the specific demands of the medical device. PTFE's thermal properties make it an excellent choice for many, but not all, situations.
- If your primary focus is reusable tools requiring frequent autoclaving: PTFE is a premier candidate due to its unmatched ability to withstand repeated heat and chemical sterilization cycles.
- If your primary focus is high-precision components under mechanical stress: You must carefully account for PTFE's thermal expansion and creep, especially if the device will operate near its upper temperature limits.
- If your primary focus is implants or in-body devices: PTFE's stability from cryogenic storage to body temperature ensures consistent, reliable performance and biocompatibility over the long term.
Ultimately, a deep understanding of PTFE's thermal behavior is fundamental to designing medical devices that are both safe and effective.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | PTFE's Role in Medical Applications |
|---|---|
| Sterilization | Withstands autoclaving (121°C to 134°C) without degrading, enabling reusable tools. |
| Temperature Range | Stable performance from cryogenic storage (-200°C) to body temperature (37°C). |
| Chemical Resistance | Resists harsh sterilization chemicals and bodily fluids, ensuring long-term safety. |
| Key Limitation | High thermal expansion and potential for creep under sustained load at high temperatures. |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your medical device?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the medical, semiconductor, and laboratory industries. Our expertise ensures your devices benefit from PTFE's critical temperature resistance and chemical inertness, from prototype to high-volume production.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can meet your specific material and fabrication requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















