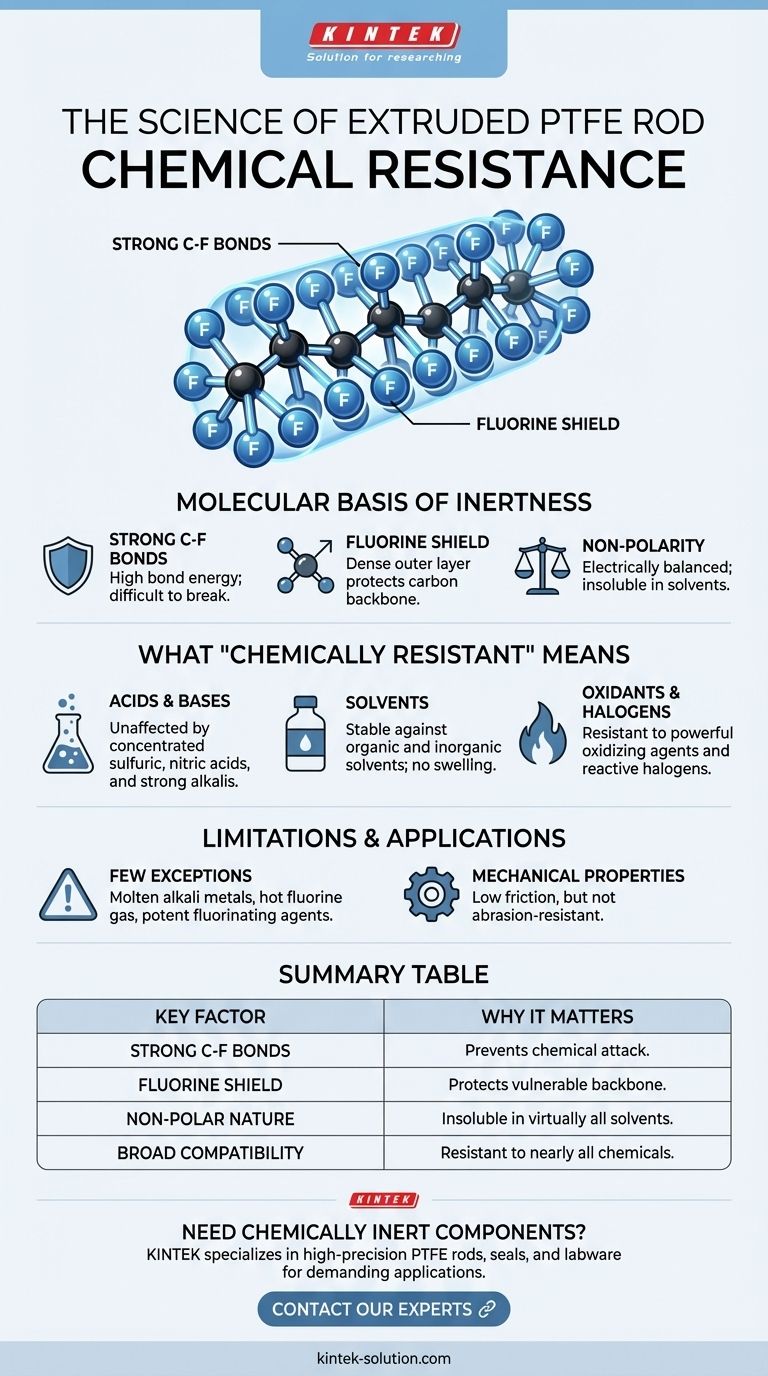
The exceptional chemical resistance of an extruded PTFE rod comes directly from its unique molecular structure. The bonds between its carbon and fluorine atoms are among the strongest in organic chemistry, creating a stable and non-reactive material that is virtually immune to attack from almost all acids, bases, and solvents.
The core reason for PTFE's chemical inertness is not just what it's made of, but how it's built. Its carbon backbone is completely shielded by a tight sheath of fluorine atoms, held together by incredibly strong bonds, presenting a nearly impenetrable barrier to other chemicals.
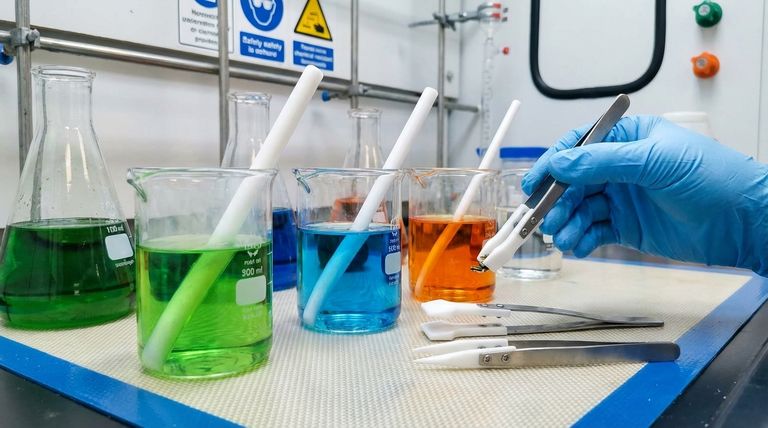

The Molecular Basis of PTFE's Inertness
To understand why PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) is so resilient, we must look at its atomic composition and structure. This isn't just a surface-level property; it's engineered at the molecular level.
The Power of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
The bond between a carbon atom and a fluorine atom is one of the strongest known single bonds. This high bond energy means a tremendous amount of energy is required to break it.
Most chemical reactions rely on breaking and forming bonds. Since the C-F bonds in PTFE are so difficult to break, other chemicals simply lack the power to react with it.
A Protective Fluorine Shield
The fluorine atoms are significantly larger than the carbon atoms they are bonded to. They arrange themselves in a tight, helical sheath around the central carbon backbone.
This dense outer layer of fluorine atoms effectively shields the more vulnerable carbon chain from any potential chemical contact or attack.
Non-Polarity and Insolubility
The symmetrical arrangement of the fluorine atoms around the carbon chain results in a molecule that is electrically balanced and non-polar.
This non-polarity makes it insoluble in virtually all solvents. It will not swell, dissolve, or degrade when immersed in substances that would destroy lesser polymers.
What "Chemically Resistant" Means in Practice
The molecular stability of PTFE translates into predictable, reliable performance when handling aggressive substances in demanding industrial and laboratory settings.
Immunity to Acids and Bases
PTFE is unaffected by the most corrosive acids and bases known. This includes substances like concentrated sulfuric acid, nitric acid, and strong alkalis that would rapidly degrade metals and other plastics.
Resilience Against Solvents
The material remains stable when exposed to a vast spectrum of organic and inorganic solvents. This makes it a primary choice for seals, gaskets, and containers in chemical processing.
Stability with Oxidants and Halogens
Powerful oxidizing agents and reactive halogens, such as chlorine gas, have no effect on PTFE. This broad resistance profile makes it one of the most versatile materials available for aggressive environments.
Understanding the Limitations
While PTFE's chemical resistance is nearly absolute, no material is perfect. Acknowledging its few exceptions is critical for proper application.
The Few Chemicals That Can Attack PTFE
Only a handful of highly reactive and uncommon substances can affect PTFE under specific conditions.
These include molten alkali metals (like sodium), hot gaseous fluorine, and potent fluorinating agents such as chlorine trifluoride and oxygen difluoride. For nearly all common industrial applications, these exceptions are irrelevant.
Resistance vs. Mechanical Properties
It is crucial to distinguish chemical resistance from mechanical properties. PTFE is a relatively soft material with a low coefficient of friction.
Its chemical inertness does not mean it has high resistance to mechanical abrasion or wear. Applications requiring both chemical and high abrasion resistance may require filled grades of PTFE or different material solutions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE is a decision for applications where chemical compatibility cannot be compromised. Consider your primary objective to confirm it's the right fit.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals: PTFE is the benchmark material for ensuring component longevity and preventing material degradation from acids, bases, or solvents.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processes: PTFE's inertness prevents it from leaching or contaminating the media it contacts, making it essential for laboratory, semiconductor, and pharmaceutical work.
- If your primary focus is safety in unknown chemical environments: PTFE provides the widest margin of safety due to its near-universal chemical resistance, making it a reliable choice for unpredictable conditions.
Ultimately, selecting PTFE is a strategic decision for achieving uncompromising chemical stability in the most demanding environments.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Why It Matters for Chemical Resistance |
|---|---|
| Strong C-F Bonds | Extremely high bond energy prevents chemical attack and degradation. |
| Fluorine Shield | Dense outer layer of fluorine atoms protects the vulnerable carbon backbone. |
| Non-Polar Nature | Makes PTFE insoluble in virtually all solvents, preventing swelling or dissolution. |
| Broad Compatibility | Resistant to nearly all acids, bases, oxidants, and halogens. |
Need chemically inert components you can trust?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision extruded PTFE rods, seals, liners, and custom labware. Our components are engineered for maximum chemical resistance, ensuring longevity and purity in the most demanding semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications.
Let us provide the reliable PTFE solution your project requires. Contact our experts today to discuss custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers



















