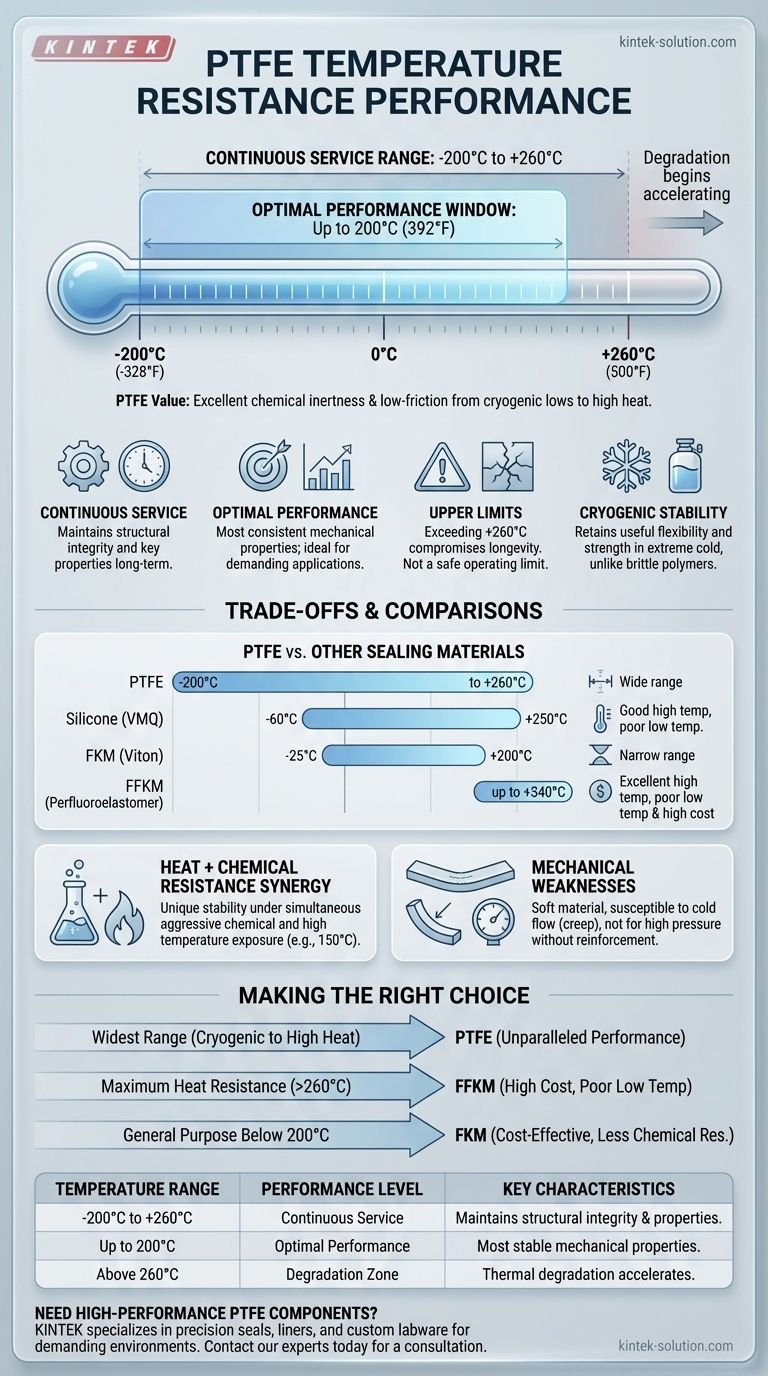
From a technical standpoint, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) has an extremely wide and effective operational temperature range. It is consistently recommended for continuous service in environments from approximately -200°C (-328°F) up to +260°C (500°F). While it can withstand these extremes, its optimal performance characteristics are most stable at temperatures up to 200°C (392°F).
The true value of PTFE is not just its high temperature resistance, but its unique ability to maintain excellent chemical inertness and low-friction properties across this exceptionally broad thermal range, from cryogenic lows to significant heat.

Deconstructing PTFE's Thermal Performance
To properly specify PTFE for an application, you must understand the difference between its continuous service range, its optimal window, and its absolute limits where material degradation begins.
The Continuous Service Range
The most critical specification for PTFE is its continuous service temperature range of -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to 500°F).
Within this range, PTFE reliably maintains its structural integrity and key properties without significant degradation over long operational periods.
The Optimal Performance Window
For applications demanding the highest stability and predictability, the optimal performance window for PTFE is generally considered to be up to 200°C (392°F).
In this sub-range, its mechanical properties are at their most consistent, making it the ideal target for demanding sealing or bearing applications.
Understanding the Upper Limits
Some data may mention temperatures as high as 290°C (554°F) or even note that the material should not be used above 350°C.
These figures represent temperatures where thermal degradation begins to accelerate, not safe operating limits. Exceeding the +260°C continuous limit will compromise the material's longevity and performance.
Exceptional Cryogenic Stability
A key differentiator for PTFE is its performance at extremely low temperatures.
Unlike many polymers that become brittle and fail in cryogenic conditions, PTFE retains a useful degree of flexibility and strength, making it suitable for applications involving liquid nitrogen or other cold environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Comparisons
No material choice exists in a vacuum. Selecting PTFE requires understanding its performance relative to other common polymers and acknowledging its inherent limitations.
PTFE vs. Other Sealing Materials
When compared to other elastomers, PTFE's thermal range is superior in its breadth.
- Silicone (VMQ): Matches PTFE's high-temperature performance (+250°C) but has a much poorer low-temperature limit (approx. -60°C) and far less chemical resistance.
- FKM (Viton): Has a much narrower range, typically from -25°C to +200°C.
- FFKM (Perfluoroelastomer): Can exceed PTFE's upper limit, reaching up to 340°C, but it performs poorly at low temperatures and comes at a significantly higher cost.
The Synergy of Heat and Chemical Resistance
PTFE's primary advantage is its ability to withstand aggressive chemicals while at elevated temperatures.
Many materials that have good chemical resistance at room temperature will fail when that same chemical exposure occurs at 150°C. PTFE's fluoropolymer structure is exceptionally stable under both conditions simultaneously.
Mechanical Weaknesses to Consider
The primary trade-off for PTFE's thermal and chemical performance is its relative mechanical weakness.
It is a soft material susceptible to cold flow (creep) and is not suitable for high-pressure applications without reinforcement or being incorporated into a filled-grade compound.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final material selection must be based on the complete set of operational demands, not just temperature.
- If your primary focus is the widest possible operating range: PTFE is an outstanding choice for its unparalleled performance from cryogenic lows to high heat.
- If your primary focus is maximum heat resistance above all else: A specialized material like FFKM may be necessary, but you must accept the trade-offs of higher cost and poor low-temperature capability.
- If your primary focus is a general-purpose seal below 200°C: A more cost-effective material like FKM (Viton) may be sufficient for your application if extreme chemical resistance is not required.
Ultimately, choosing the right material requires you to evaluate the entire operational environment to ensure reliability and performance.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Performance Level | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| -200°C to +260°C | Continuous Service | Maintains structural integrity and key properties. |
| Up to 200°C | Optimal Performance | Most stable mechanical properties for demanding applications. |
| Above 260°C | Degradation Zone | Thermal degradation accelerates; not recommended for continuous use. |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Demanding Environments?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—that deliver reliable performance across extreme temperature ranges, from cryogenic conditions up to 260°C. Our expertise is crucial for industries like semiconductor, medical, and laboratory, where material failure is not an option.
We provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your components meet exact specifications for thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical requirements.
Let's discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance your application's reliability and performance. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the similarities between PTFE and RPTFE? Unlocking the Core Fluoropolymer Identity
- What is PTFE and what class of plastics does it belong to? A Guide to High-Performance Fluoropolymers
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what type of material is it? A Guide to High-Performance PTFE Properties
- How does PTFE react to common solvents? Discover Its Near-Total Chemical Immunity
- What is Teflon and what is its chemical name? Unpacking the Science of PTFE



















